Reference: http://www.programcreek.com/2013/09/top-8-diagrams-for-understanding-java/
A diagram is sometimes worth 1000 words. The following diagrams are from Java tutorials on Program Creek, they have received the most votes so far. Hopefully, they can help you review what you already know. If the problem is not clear by the diagram itself, you may want to go to each article to take a further took.
1. String Immutability
The following diagram shows what happens for the following code:
1 String s = "abcd"; 2 s = s.concat("ef");

2. The equals() and hashCode() Contract
HashCode is designed to improve performance. The contract between equals() and hasCode() is that:
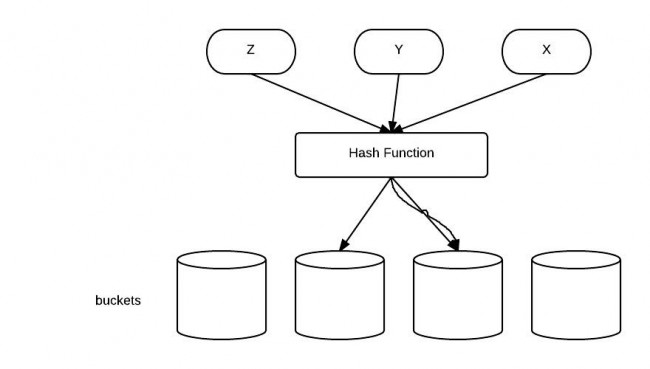
- If two objects are equal, then they must have the same hash code.
- If two objects have the same hashcode, they may or may not be equal.
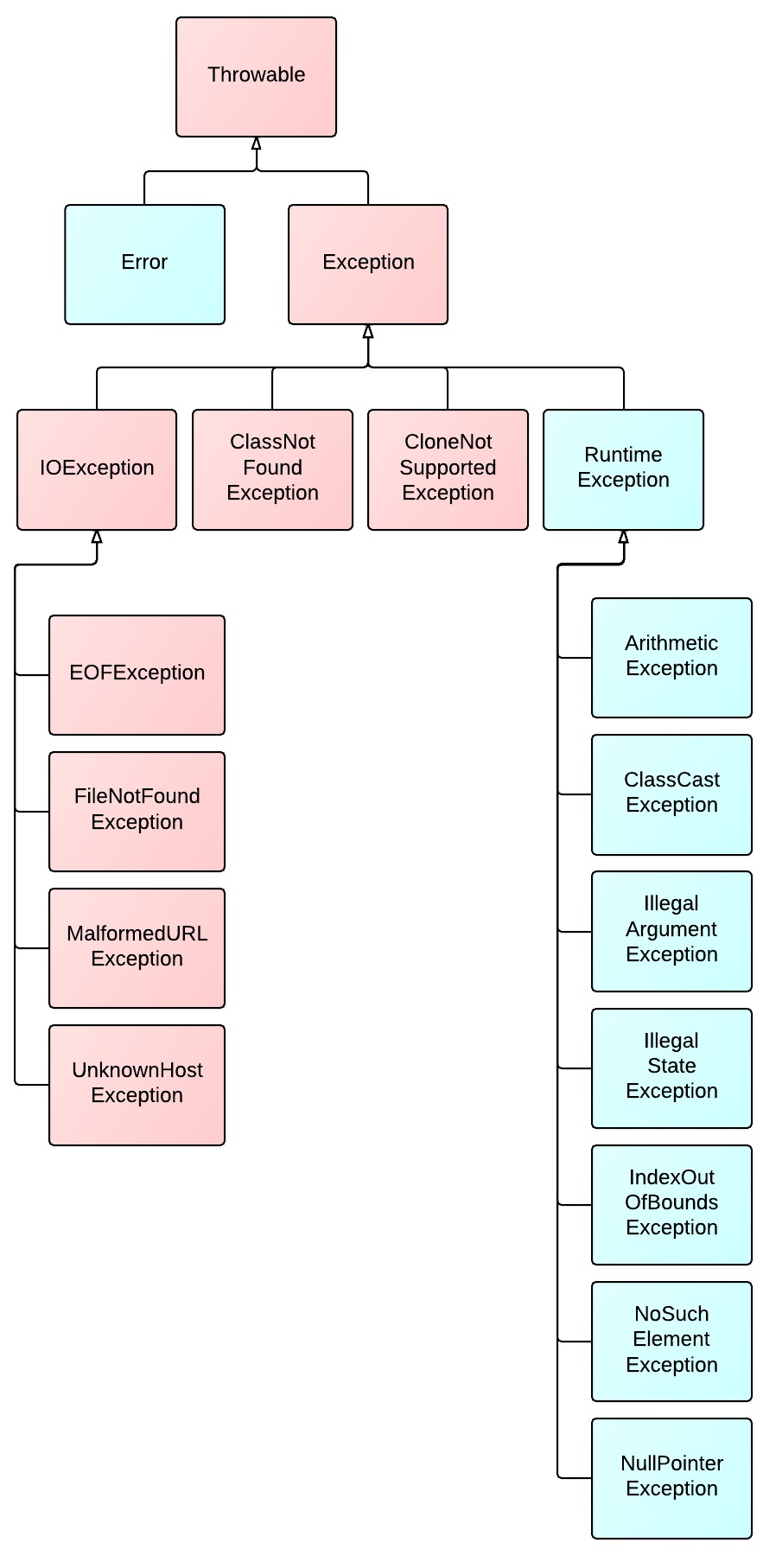
3. Java Exception Class Hierarchy
Red colored are checked exceptions which must either be caught or declared in the method’s throws clause.
4. Collections Class Hierarchy
Note the difference between Collections and Collection.


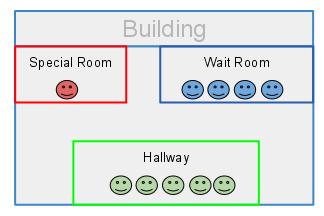
5. Java synchronization
Java synchronization mechanism can be illustrated by an analogy to a building.
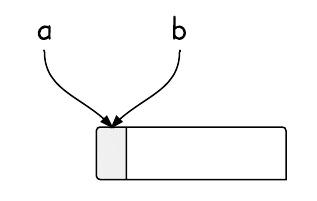
6. Aliasing
Aliasing means there are multiple aliases to a location that can be updated, and these aliases have different types.
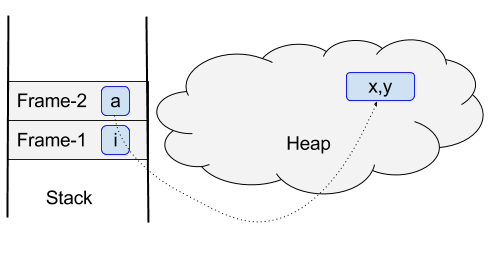
7. Stack and Heap
This diagram shows where methods and objects are in run-time memory.
8. JVM Run-Time Data Areas
This diagram shows overall JVM run-time data areas.
