原创转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/agilestyle/p/12246482.html
·reshape()
In many cases, you can convert an array from one shape to another without copying any data. To do this, pass a tuple indicating the new shape to the reshape array instance method.


A multidimensional array can also be reshaped:

One of the passed shape dimensions can be -1, in which case the value used for that dimension will be inferred from the data:

The opposite operation of reshape from one-dimensional to a higher dimension is typically known as flattening or raveling
·ravel()
The ravel method does not produce a copy of the underlying values if the values in the result were contiguous in the original array

·flatten()
The flatten method behaves like ravel except it always returns a copy of the data

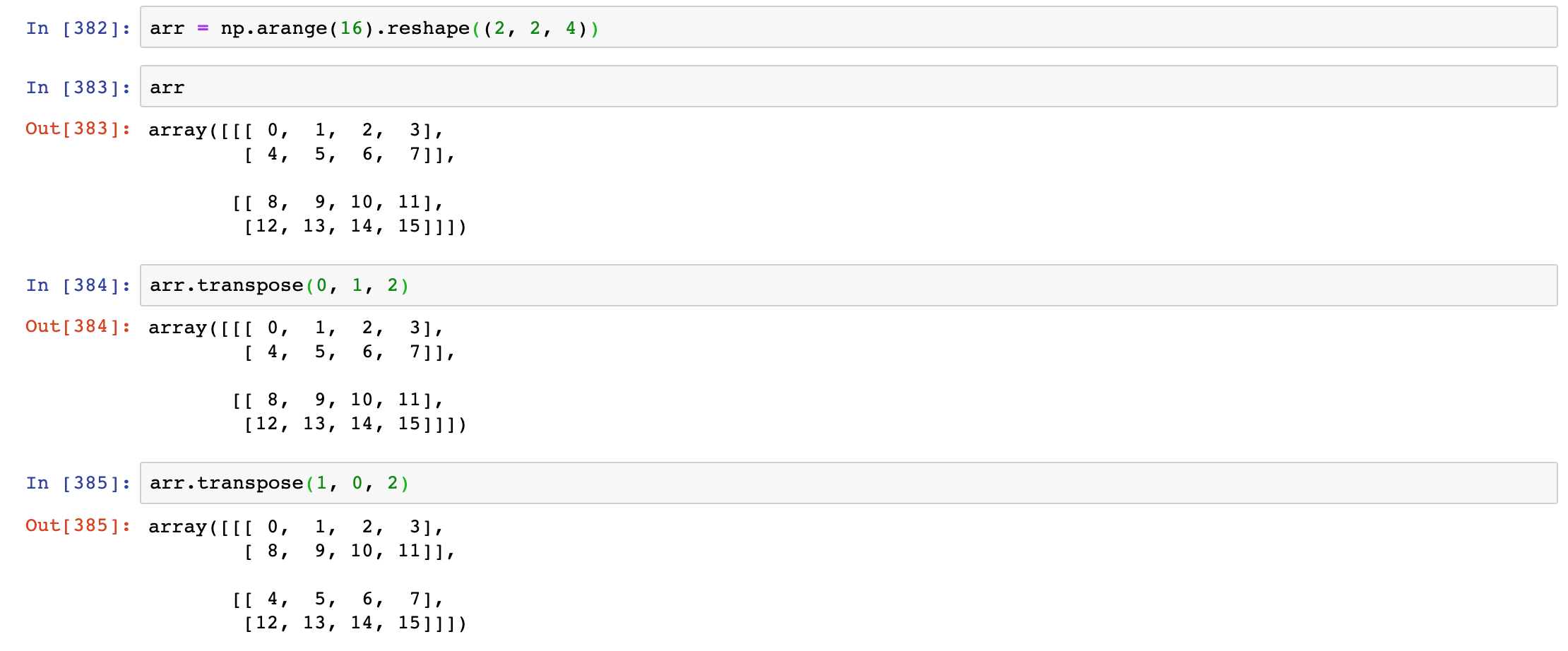
·transpose()
For higher dimensional arrays, transpose will accept a tuple of axis numbers to permute the axes:
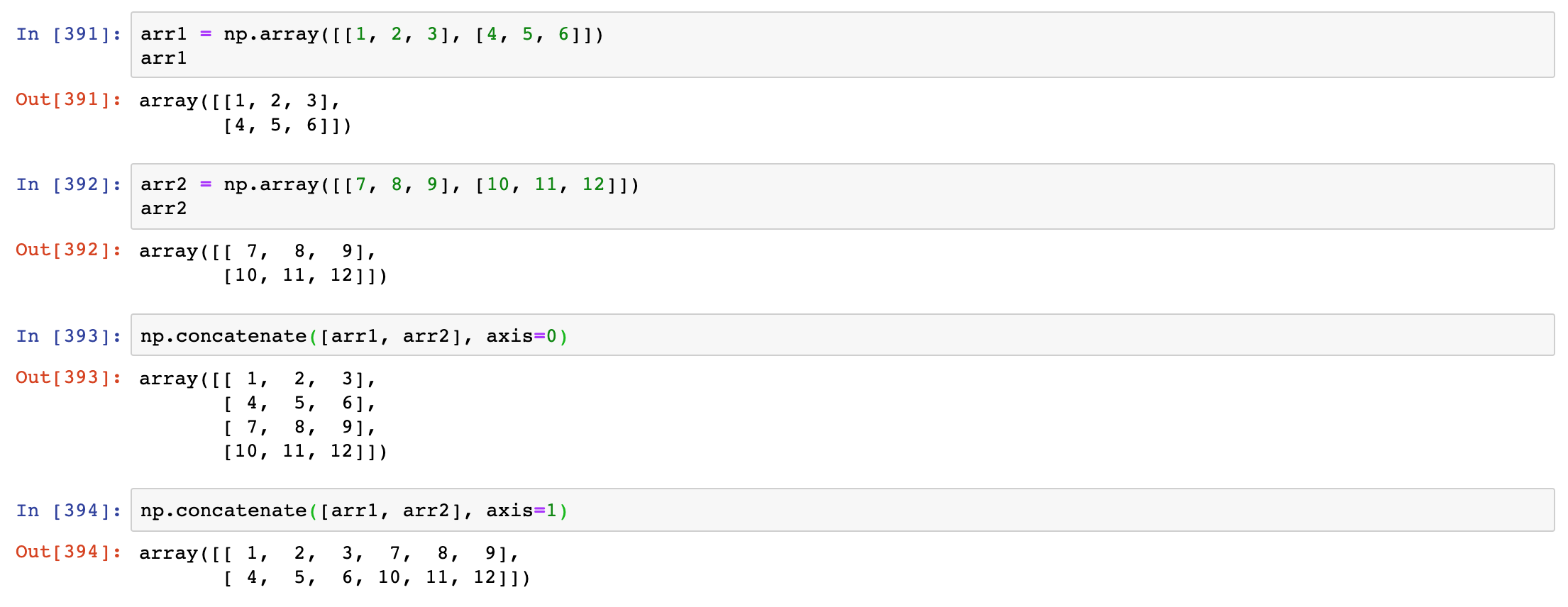
np.concatenate
numpy.concatenate takes a sequence (tuple, list, etc.) of arrays and joins them together in order along the input axis
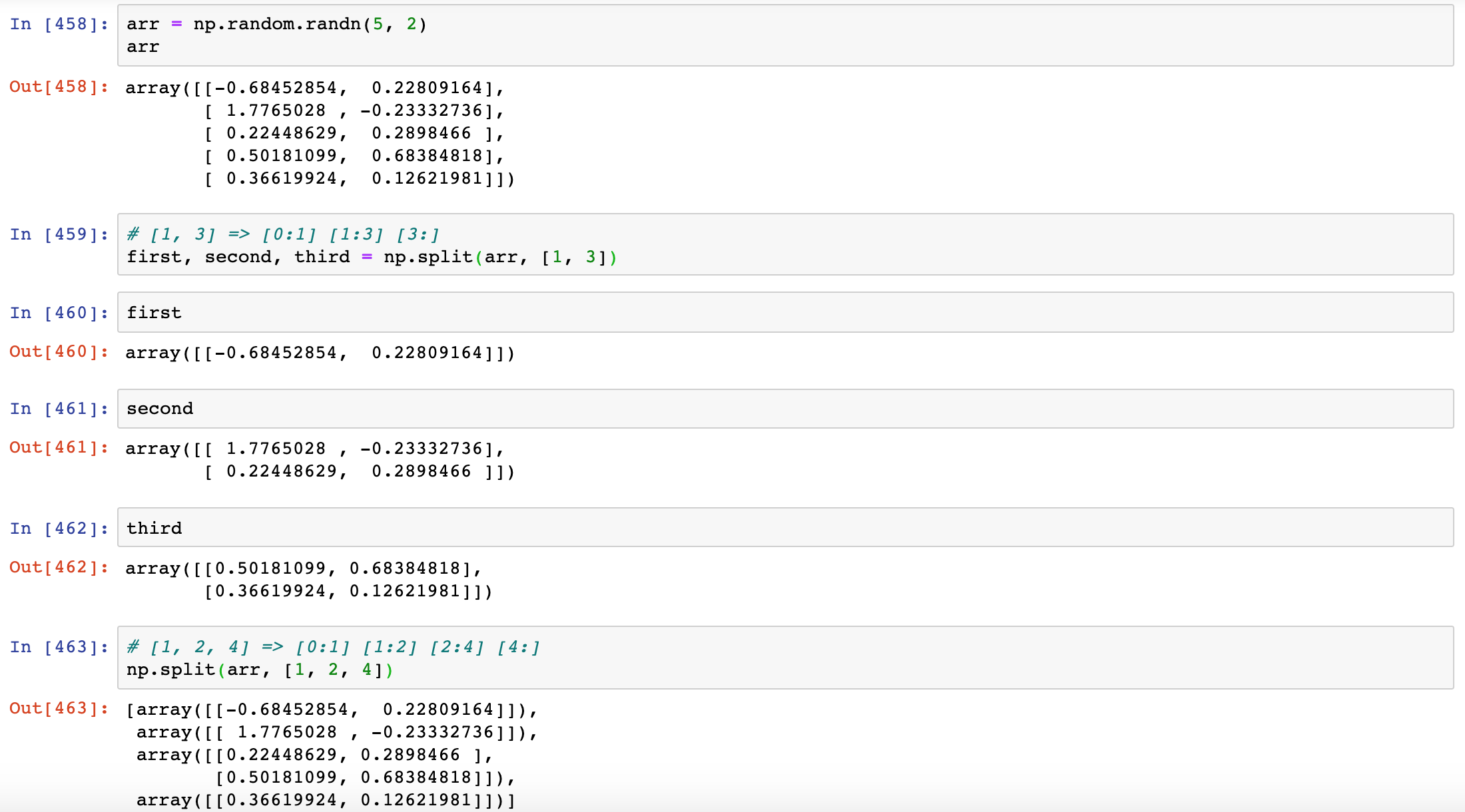
np.split
split slices apart an array into multiple arrays along an axis
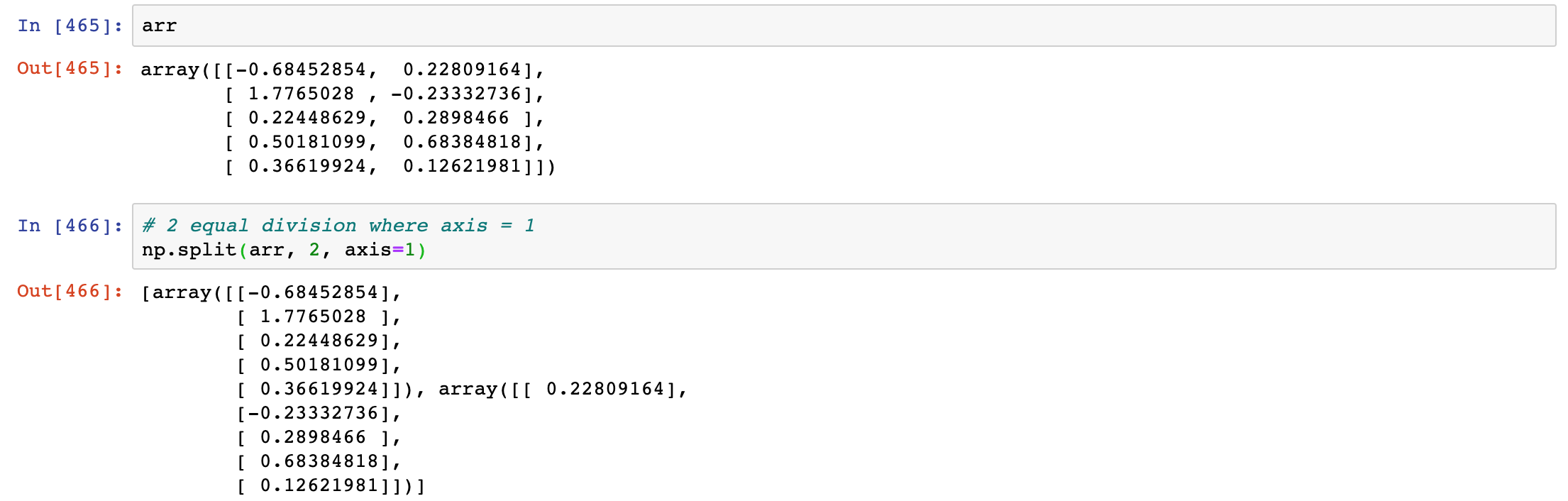
2 equal division where axis = 1
Reference
Python for Data Analysis Second Edition