1、概述
布局管理器的用途:
a、可以更好的管理组件;
b、通过使用布局管理器,Android应用程序可以做到平台无关性
布局管理器都是ViewGroup的子类,所有可充当容器的父类都是ViewGroup,而ViewGroup也是View的子类

下面分别介绍常用的布局管理器
2、线性布局管理器
LinearLayout,最常用的布局之一。它提供控件水平或垂直排列的模型
常用属性及其对应方法:

gravity 可取属性说明:

当需要为gravity设多个值时,可用|分隔开
布局XML:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:orientation="horizontal" 4 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 5 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 6 android:id="@+id/lla" 7 android:gravity="right" 8 > 9 10 <Button 11 android:text="添加" 12 android:id="@+id/Button01" 13 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 14 android:layout_height="wrap_content"> 15 </Button> 16 17 </LinearLayout>
JAVA代码:

1 // 计数器,记录按钮个数 2 int count = 0; 3 4 @Override 5 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // 重写 onCreate 方法 6 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 7 setContentView(R.layout.horizontal_layout); 8 // 获取屏幕中的按钮控件对象 9 Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.Button01); 10 11 // 为按钮添加 OnClickListener 接口实现 12 button.setOnClickListener( 13 14 15 new View.OnClickListener() { 16 17 public void onClick(View v) { 18 // 获取线性布局对象 19 LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.lla); 20 21 String msg = MainActivity.this.getResources().getString( 22 R.string.button); 23 // 创建一个 Button 对象 24 Button tempbutton = new Button(MainActivity.this); 25 26 27 28 tempbutton.setText(msg + (++count)); // 设置 Button 控件显示的内容 29 // 设置 Button 的宽度 30 tempbutton.setWidth(80); 31 // 向线性布局中添加 View 32 ll.addView(tempbutton); 33 34 35 36 } 37 38 }); 39 40 }
运行效果:每点击添加按钮一次会在下方垂直生成一个按钮
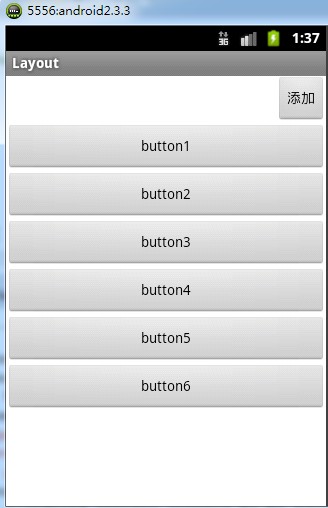
将布局文件中
android:orientation="vertical"
vertical改为horizontal
每点击一次会在右方水平方向生成一个按钮

当水平方向该行容不下一个宽度为80的按钮时,按钮就会被压缩,如下图

此时再点击添加按钮时,画面没有任何变化,不会另起一行添加按钮,超出屏幕的将不会被显示。
3、表格布局
TableLayout 类似HTML里的Table分为行和列来管理。
每一行为一个TableRow,也可以为View对象。当为View对象时就跨越该行所有列
TableRow中可以添加子控件,每个子控件为一列。并不会为每个单元格绘制边框
每个单元格为一个View,可以有空的单元格,也可以跨越多列
一个列的宽度由该列最宽的单元格决定的
TableLayout 可以设置三种属性
Shrinkable :它可以被压缩以适应其父容器的大小
Stretchable :它可以被拉伸以填满空闲区域
Collapsed :该列被隐藏

如果要对多列进行设置,用逗号隔开
这三个属性在JAVA代码也有对应的方法,值得一提的是它是继承Linearlayout的
布局XML:

1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01" 3 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 4 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 5 android:background="@drawable/water" 6 android:gravity="bottom" 7 android:orientation="vertical" > 8 9 <TableLayout 10 android:id="@+id/TableLayout01" 11 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 12 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 13 14 <TextView 15 android:id="@+id/TextView01" 16 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 17 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 18 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 19 android:layout_margin="4px" 20 android:background="@drawable/darkgray" 21 android:text="@string/tv1" > 22 </TextView> 23 </TableLayout> 24 25 <TableLayout 26 android:id="@+id/TableLayout02" 27 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 28 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 29 android:stretchColumns="0" > 30 31 <TableRow 32 android:id="@+id/TableRow01" 33 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 34 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 35 36 <TextView 37 android:id="@+id/TextView02" 38 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 39 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 40 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 41 android:layout_margin="4px" 42 android:background="@drawable/blue" 43 android:text="@string/tvStrech" > 44 </TextView> 45 46 <TextView 47 android:id="@+id/TextView03" 48 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 49 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 50 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 51 android:layout_margin="4px" 52 android:text="@string/tvShort" > 53 </TextView> 54 </TableRow> 55 </TableLayout> 56 57 <TableLayout 58 android:id="@+id/TableLayout03" 59 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 60 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 61 android:collapseColumns="1" 62 android:shrinkColumns="0" > 63 64 <TableRow 65 android:id="@+id/TableRow02" 66 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 67 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 68 69 <TextView 70 android:id="@+id/TextView04" 71 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 72 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 73 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 74 android:layout_margin="4px" 75 android:background="@drawable/darkgray" 76 android:text="@string/tvShrink" > 77 </TextView> 78 79 <TextView 80 android:id="@+id/TextView05" 81 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 82 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 83 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 84 android:layout_margin="4px" 85 android:background="@drawable/lightred" 86 android:text="@string/tvShort" > 87 </TextView> 88 89 <TextView 90 android:id="@+id/TextView06" 91 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 92 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 93 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 94 android:layout_margin="4px" 95 android:background="@drawable/blue" 96 android:text="@string/tvLong" > 97 </TextView> 98 </TableRow> 99 </TableLayout> 100 101 </LinearLayout>
运行效果:

4、相对布局
RelativeLayout子控件 的位置由兄弟控件或父容器来决定的
如果A控件由B控件来决定位置,则布局文件B控件要在A控件声明之前
常用属性
第一类:属性值为true或false
android:layout_centerHrizontal 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中
android:layout_centerInparent 相对于父元素完全居中
android:layout_alignParentBottom 贴紧父元素的下边缘
android:layout_alignParentLeft 贴紧父元素的左边缘
android:layout_alignParentRight 贴紧父元素的右边缘
android:layout_alignParentTop 贴紧父元素的上边缘
android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing 如果对应的兄弟元素找不到的话就以父元素做参照物
第二类:属性值必须为id的引用名“@id/id-name”
android:layout_below 在某元素的下方
android:layout_above 在某元素的的上方
android:layout_toLeftOf 在某元素的左边
android:layout_toRightOf 在某元素的右边
android:layout_alignTop 本元素的上边缘和某元素的的上边缘对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 本元素的左边缘和某元素的的左边缘对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 本元素的下边缘和某元素的的下边缘对齐
android:layout_alignRight 本元素的右边缘和某元素的的右边缘对齐
第三类:属性值为具体的像素值,如30dip,40px
android:layout_marginBottom 离某元素底边缘的距离
android:layout_marginLeft 离某元素左边缘的距离
android:layout_marginRight 离某元素右边缘的距离
android:layout_marginTop 离某元素上边缘的距离
布局XML:

1 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 6 android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 7 android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 8 android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 9 tools:context=".MainActivity" > 10 11 <TextView 12 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 13 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 14 android:text="@string/hello_world" 15 android:id="@+id/tv1" 16 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 17 /> 18 19 <TextView 20 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 22 android:text="big" 23 android:textSize="30sp" 24 android:id="@+id/tv2" 25 android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv1" 26 android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv1" 27 /> 28 29 <TextView 30 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 31 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 32 android:text="middle" 33 android:textSize="20sp" 34 android:id="@+id/tv3" 35 android:layout_above="@id/tv1" 36 android:layout_alignLeft="@id/tv1" 37 /> 38 39 </RelativeLayout>
运行效果:

5、帧布局
FrameLayout在屏幕上开辟一块区域,在这块区域可以添加多个控件
但都会被对其到屏幕左上角,并且大小取决于最大的控件,如果控件一样大,只能看到最上面的控件
布局XML:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 4 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <TextView 8 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 9 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 10 android:background="@drawable/lightgray" 11 android:gravity="center" 12 android:text="big" /> 13 14 <TextView 15 android:layout_width="150dp" 16 android:layout_height="150dp" 17 android:background="@drawable/darkgray" 18 android:gravity="center" 19 android:text="middle" /> 20 21 <TextView 22 android:layout_width="50dp" 23 android:layout_height="50dp" 24 android:background="@drawable/blue" 25 android:gravity="center" 26 android:text="small" /> 27 28 </FrameLayout>
运行效果:

6、绝对布局
AbsoluteLayout是绝对位置布局。在此布局中的子元素的android:layout_x和android:layout_y属性将生效,用于描述该子元素的坐标位置。
屏幕左上角为坐标原点(0,0),第一个0代表横坐标,向右移动此值增大,第二个0代表纵坐标,向下移动,此值增大。
在此布局中的子元素可以相互重叠。在实际开发中,通常不采用此布局格式,因为它的界面代码过于刚性,以至于有可能不能很好的适配各种终端。
由于不采用,在此就不演示代码了。
