redis设计关系数据库
[toc]
第一次用redis 如何设计数据库的笔记,但是后面觉得还是太麻烦了改用了json,感兴趣可以看一看吧。
前言
最近需要一张用户信息表,因为数据量并不大,想先放在内存中,等需求变更了,再移到磁盘上,或者往mysql塞,那么问题来了,怎么用redis的数据类型设计一个关系数据库呢。
redis只有key-value这种存储结构,如果想利用它做成想其他数据库一样具备 增删改查等功能只能再设计了,这里分享一下我的设计方法,比较简单,我不知道算不算好,只是网上找了很久没找到一种通用的方法,如果有什么好的方法,还是想请教一下各位,十分感谢。
设计用户信息表结构
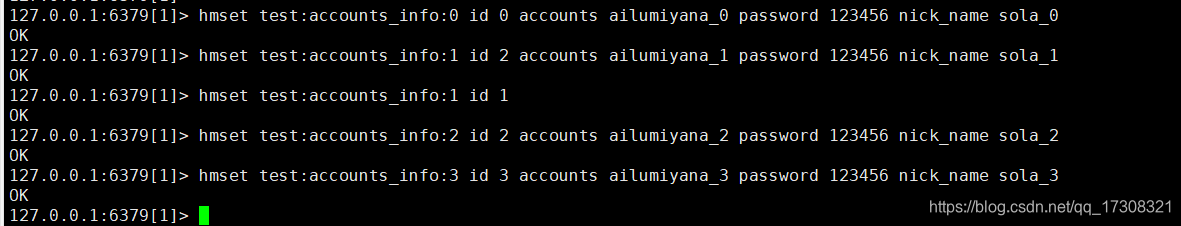
hash存储记录
key值 : 域名:表名:主键
value值 :直接使用redis的Hash类型
如:
test:accounts_info:0 id 0 accounts ailumiyana_0 password 123456 nick_name sola_0
test:accounts_info:1 id 1 accounts ailumiyana_1 password 123456 nick_name sola_1
test:accounts_info:2 id 2 accounts ailumiyana_2 password 123456 nick_name sola_2
test:accounts_info:3 id 3 accounts ailumiyana_3 password 123456 nick_name sola_3
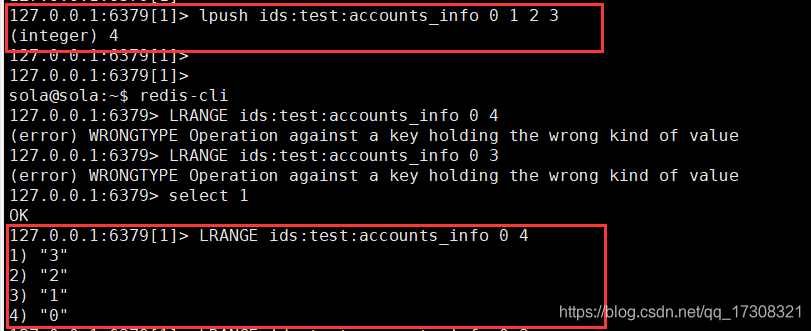
set存储id
另添加一个set集存放表主键, 也即id.
key值 : ids:域名:表名
value值: id
将已生成的用户id同时添加进set集合中.
我这里用了list演示,不设计类型的特殊方法的话,演示效果是一样的。
图示

索引/查询:
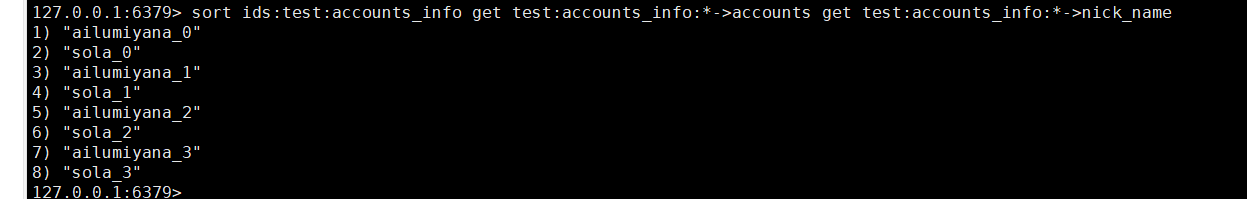
1、select*
查询所有记录 : 类似sql的select * from table_name
有了set表后我们就可以使用redis中sort的get方法,获取所有记录.
sort ids:test:accounts_info get test:accounts_info:*->accounts get test:accounts_info:*->nick_name
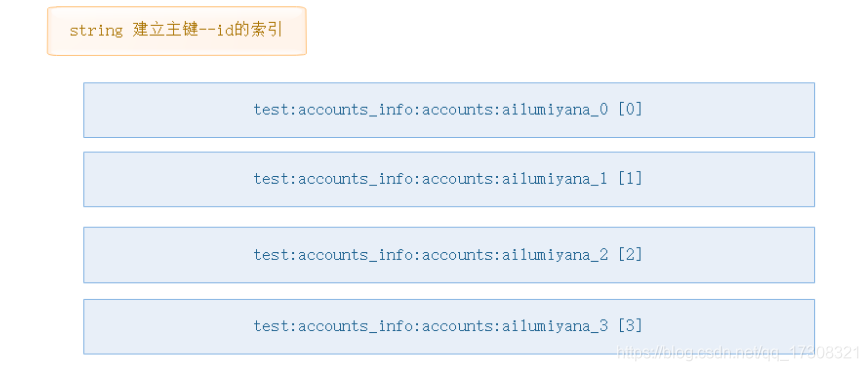
2、根据主键查询记录
直接使用string类型建立主键到id的索引,其实id就是主键,但是我们一般不会用id去找记录,更多的使用account账号去找.
key值 : 域名:表名:列键名:列键值
这样我们直接用get 取得accounts的id 后再去hash中查找记录就行了.
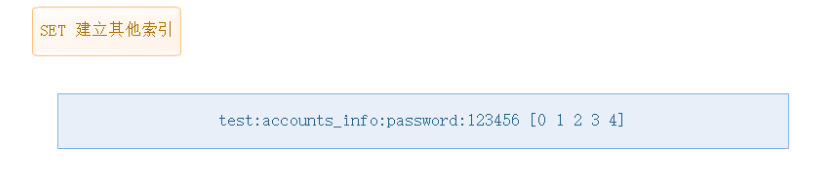
3、其他列索引
最后可以根据表的需要建立一些其他索引,
方法同 2 ,使用类型不一定是set 哪个方便用哪个。
例如 我要统计最近登录的10个用户的信息, 那么我直接用list 的 lrange limit 0 10 就能取到.
c++ 实现
以上设计的c++实现,其中的redis的客户端使用了cpp_redis库。
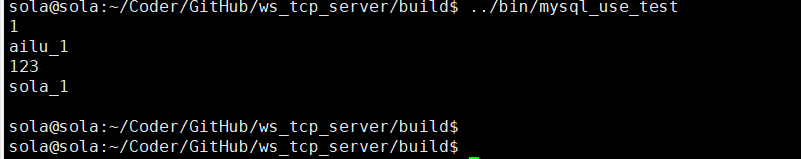
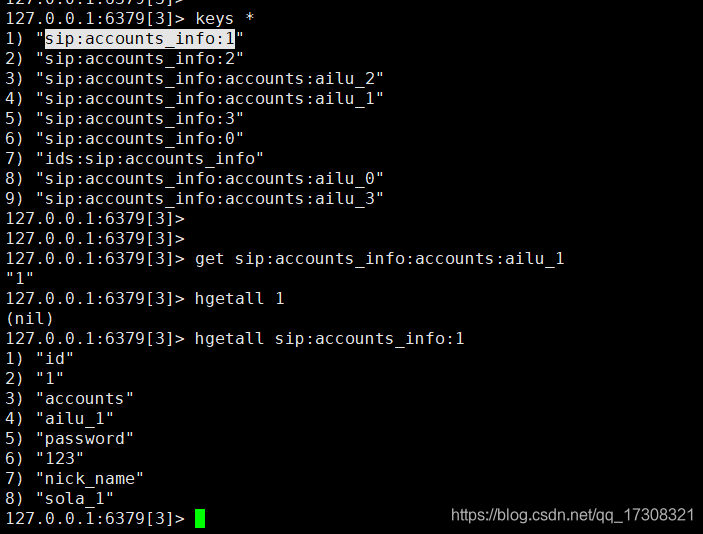
例程中 : 1、我创建了一张 account_info的表 默认使用accounts 作为主键
2、插入4个用户信息.
3、查询用户ailu_1的记录值.
class table// : public redis::er_table
{
public:
//! ctor
table(void);
//! dtor
~table(void) = default;
//! copy ctor
table(const table&) = delete;
//! assignment operator
table& operator=(const table&) = delete;
public:
//! vector type to save table records.
typedef std::vector<std::string> records_t;
//! vector type to save table records entitys.
typedef std::vector<std::string> entitys_t;
public:
//! create table,
//! default primary key is the records_t vec[0], if primary_key is empty!
void create(const std::string& table_name, const records_t& vec, const std::string& primary_key = "");
public:
//! incr primary key id.
std::string incr_id();
//! insert new entity to table, pelease orderly insert refer to records vector !
//! return false while entity exits.
bool insert(const entitys_t& vec);
//! get entitys by primary key value.
entitys_t get_entitys_by_primary_key_value(const std::string& primary_key_value);
private:
//! get id by primary key value
//! retrun "" while primary key inexitences.
std::string get_id_by_primary_key_value(const std::string& primary_key_value);
private:
//! redis client
cpp_redis::client m_redis_client;
//!
records_t m_records;
//! records count.
std::size_t m_records_count;
//! ids set key
std::string m_ids;
//! table name
std::string m_table_name;
//! incr key
uint64_t m_incr_key;
//! primary key
std::string m_primary_key;
std::size_t m_primary_key_index;
};
table::table()
:m_records_count(0),
m_incr_key(0)
{
m_redis_client.connect();
m_redis_client.select(3);
m_redis_client.sync_commit();
}
void table::create(const std::string& table_name, const records_t& vec, const std::string& primary_key){
assert(m_records_count == 0);
m_ids = "ids:" + table_name;
m_table_name = table_name;
m_records = vec;
m_records_count = vec.size();
if(primary_key.empty()){
m_primary_key = vec[0];
m_primary_key_index = 0;
} else {
m_primary_key = primary_key;
auto iter = std::find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), primary_key);
if(iter == vec.end()){
LOG_FATAL << "no such key.";
}
m_primary_key_index = iter - vec.begin();
}
}
std::string table::incr_id(){
return std::move(std::to_string(m_incr_key++));
}
std::string table::get_id_by_primary_key_value(const std::string& primary_key_value){
std::future<cpp_redis::reply> fu = m_redis_client.get(primary_key_value);
m_redis_client.sync_commit();
cpp_redis::reply reply = fu.get();
if(!reply.is_null()){
return std::move(reply.as_string());
}
LOG_DEBUG << "primary_key " << primary_key_value << " inexitences. return "".";
return "";
}
bool table::insert(const entitys_t& vec){
assert(m_records_count != 0);
assert(m_records_count == vec.size());
std::string get_id = incr_id();
// check whether the primary key already exists.
std::string check_id = get_id_by_primary_key_value(vec[m_primary_key_index]);
if(!check_id.empty()){
return false;
}
// redis string type primary key to id index.
//LOG_DEBUG << m_table_name + ":" + m_records[m_primary_key_index] + ":" + vec[m_primary_key_index];
m_redis_client.set(m_table_name + ":" + m_records[m_primary_key_index] + ":" + vec[m_primary_key_index], get_id);
// redis set type to save id.
std::vector<std::string> id_vec = {get_id};
m_redis_client.sadd(m_ids, id_vec);
// redis hash type to save records key-value.
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, std::string>> entitys_pair_vec;
for(std::size_t i = 0; i < m_records_count; i++){
entitys_pair_vec.emplace_back(make_pair(m_records[i], vec[i]));
}
m_redis_client.hmset(m_table_name + ":" + get_id, entitys_pair_vec);
m_redis_client.sync_commit();
return true;
}
table::entitys_t table::get_entitys_by_primary_key_value(const std::string& primary_key_value){
std::string id = get_id_by_primary_key_value(m_table_name + ":" + m_records[m_primary_key_index] + ":" + primary_key_value);
if(id == ""){
static entitys_t static_empty_entitys_vec;
return static_empty_entitys_vec;
LOG_ERROR << "no this entitys";
}
entitys_t vec;
std::future<cpp_redis::reply> reply = m_redis_client.hgetall(m_table_name + ":" + id);
m_redis_client.sync_commit();
std::vector<cpp_redis::reply> v = reply.get().as_array();
auto iter = v.begin();
for(iter++; iter < v.end(); iter += 2){
//LOG_DEBUG << (*iter).as_string();
vec.emplace_back((*iter).as_string());
}
return std::move(vec);
}
int main()
{
table accounts_info;
table::records_t records_vec = {"id", "accounts", "password", "nick_name"};
accounts_info.create("sip:accounts_info", records_vec, "accounts");
table::entitys_t entitys_vec0 = {"0", "ailu_0", "123", "sola_0"};
accounts_info.insert(entitys_vec0);
table::entitys_t entitys_vec1 = {"1", "ailu_1", "123", "sola_1"};
accounts_info.insert(entitys_vec1);
table::entitys_t entitys_vec2 = {"2", "ailu_2", "123", "sola_2"};
accounts_info.insert(entitys_vec2);
table::entitys_t entitys_vec3 = {"3", "ailu_3", "123", "sola_3"};
accounts_info.insert(entitys_vec3);
table::entitys_t ailu_1_accounts = accounts_info.get_entitys_by_primary_key_value("ailu_1");
auto it = ailu_1_accounts.begin();
while(it != ailu_1_accounts.end()){
std::cout << *it << std::endl;
it++;
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
小结
目前给出了redis增查简单设计方法,更新和删除也是通过redis的基本方法对应设计即可,这里不再详述。 此外,可以看出redis的数据库设计还是比较灵活的,如何设计出最适合我们场景需求且高效的正是它难点所在。