Hadoop排序,从大的范围来说有两种排序,一种是按照key排序,一种是按照value排序。如果按照value排序,只需在map函数中将key和value对调,然后在reduce函数中在对调回去。从小范围来说排序又分成部分排序,全局排序,辅助排序(二次排序)等。本文介绍如何在Hadoop中实现全局排序。
全局排序,就是说在一个MapReduce程序产生的输出文件中,所有的结果都是按照某个策略进行排序的,例如降序还是升序。MapReduce只能保证一个分区内的数据是key有序的,一个分区对应一个reduce,因此只有一个reduce就保证了数据全局有序,但是这样又不能用到Hadoop集群的优势。
对于多个reduce如何保证数据的全局排序呢?通常的做法是按照key值分区,通过MapReduce的默认分区函数HashPartition将不同范围的key发送到不同的reduce处理,例如一个文件中有key值从1到10000的数据,我们使用两个分区,将1到5000的key发送到partition1,然后由reduce1处理,5001到10000的key发动到partition2然后由reduce2处理,reduce1中的key是按照1到5000的升序排序,reduce2中的key是按照5001到10000的升序排序,这样就保证了整个MapReduce程序的全局排序。但是这样做有两个缺点:
1、当数据量大时会出现OOM。
2、会出现数据倾斜。
Hadoop提供TotalOrderPartitioner类用于实现全局排序的功能,并且解决了OOM和数据倾斜的问题。
TotalOrderPartitioner类提供了数据采样器,对key值进行部分采样,然后按照采样结果寻找key值的最佳分割点,将key值均匀的分配到不同的分区中。
TotalOrderPartitioner 类提供了三个采样器,分别是:
- SplitSampler 分片采样器,从数据分片中采样数据,该采样器不适合已经排好序的数据
- RandomSampler随机采样器,按照设置好的采样率从一个数据集中采样
- IntervalSampler间隔采样机,以固定的间隔从分片中采样数据,对于已经排好序的数据效果非常好。
三个采样器都实现了K[] getSample(InputFormat<K,V> inf, Job job)方法,该方法返回的是K[]数组,数组中存放的是根据采样结果返回的key值,即分隔点,MapRdeuce就是根据K[]数组的长度N生成N-1个分区partition数量,然后按照分割点的范围将对应的数据发送到对应的分区中。
下面介绍使用TotalOrderPartitioner类实现全局排序的功能。代码如下:
Map类:
1 public class TotalSortMap extends Mapper<Text, Text, Text, IntWritable> { 2 @Override 3 protected void map(Text key, Text value, 4 Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 5 context.write(key, new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(key.toString()))); 6 } 7 }
Reduce类:
1 public class TotalSortReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, IntWritable, NullWritable> { 2 @Override 3 protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, 4 Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 5 for (IntWritable value : values) 6 context.write(value, NullWritable.get()); 7 } 8 }
入口类:
1 public class TotalSort extends Configured implements Tool{ 2 3 //实现一个Kye比较器,用于比较两个key的大小,将key由字符串转化为Integer,然后进行比较。 4 public static class KeyComparator extends WritableComparator { 5 protected KeyComparator() { 6 super(Text.class, true); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public int compare(WritableComparable writableComparable1, WritableComparable writableComparable2) { 11 int num1 = Integer.parseInt(writableComparable1.toString()); 12 int num2 = Integer.parseInt(writableComparable2.toString()); 13 14 return num1 - num2; 15 } 16 } 17 @Override 18 public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { 19 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 20 conf.set("mapreduce.totalorderpartitioner.naturalorder", "false"); 21 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "Total Sort app"); 22 job.setJarByClass(TotalSort.class); 23 24 //设置读取文件的路径,都是从HDFS中读取。读取文件路径从脚本文件中传进来 25 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path(args[0])); 26 //设置mapreduce程序的输出路径,MapReduce的结果都是输入到文件中 27 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1])); 28 job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class); 29 //设置比较器,用于比较数据的大小,然后按顺序排序,该例子主要用于比较两个key的大小 30 job.setSortComparatorClass(KeyComparator.class); 31 job.setNumReduceTasks(3);//设置reduce数量 32 33 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 34 job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); 35 job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); 36 job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); 37 38 //设置保存partitions文件的路径 39 TotalOrderPartitioner.setPartitionFile(job.getConfiguration(), new Path(args[2])); 40 //key值采样,0.01是采样率, 41 InputSampler.Sampler<Text, Text> sampler = new InputSampler.RandomSampler<>(0.01, 1000, 100); 42 //将采样数据写入到分区文件中 43 InputSampler.writePartitionFile(job, sampler); 44 45 job.setMapperClass(TotalSortMap.class); 46 job.setReducerClass(TotalSortReduce.class); 47 //设置分区类。 48 job.setPartitionerClass(TotalOrderPartitioner.class); 49 return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1; 50 } 51 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{ 52 53 int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new TotalSort(), args); 54 System.exit(exitCode); 55 } 56 }
生成测试数据的代码如下:
1 #!/bin/bash 2 do 3 for k in $(seq 1 10000) 4 echo $RANDOM; 5 done
将上面代码保存成create_data.sh,然后执行
sh create_data.sh > test_data.txt
会生成一个test_data.txt的文本文件,文本中的内容是一行一个随机数字
将test_data.txt上传到HDFS中:
hadoop fs -put test_data.txt /data/
将上面的实现全局排序的代码打成一个jar包,然后通过shell文件执行。
执行MapReduce代码的脚本如下:
1 /usr/local/src/hadoop-2.6.1/bin/hadoop jar TotalSort.jar 2 hdfs://hadoop-master:8020/data/test_data1.txt 3 hdfs://hadoop-master:8020/total_sort_output 4 hdfs://hadoop-master:8020/total_sort_partitions
看下运行结果,我们只需要看part-r-00000的尾10行和part-r-00001的头10行数据,只要它们收尾相接就证明是全局有序的:
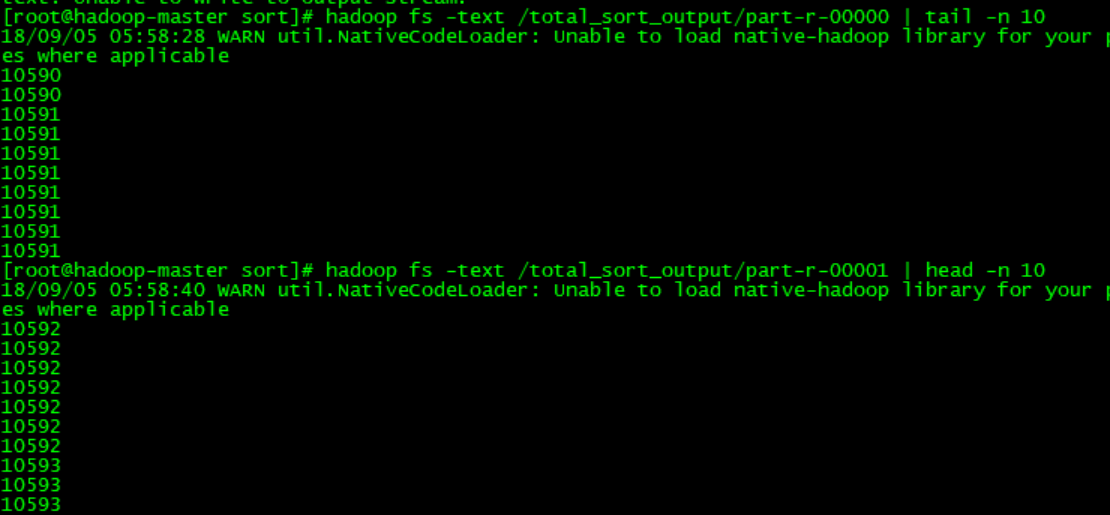
下面有几个坑要注意,大家不要踩:
- 数据的输入类型必须使用KeyValueTextInputFormat类而不是TextInputFormat类,因为hadoop采样器是对key值采样,而TextInputFormat的key是位置偏移量,value存放的是每行的输入数据,对该key采样没有任何意义。KeyValueTextInputFormat的key存放的是输入数据,对key采样才能更好的划分分区。用法:
job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class); -
使用代码conf.set("mapreduce.totalorderpartitioner.naturalorder", "false")设置分区的排序策略,否则是每个分区内有序,而不是全局有序。
-
采样器只能是Text,Text类型:InputSampler.Sampler<Text, Text>,否则会报Exception in thread "main" java.io.IOException: wrong key class: org.apache.hadoop.io.Text is not class org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable这个错误。
-
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class)和job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class)这两行代码必须在InputSampler.Sampler<Text, Text> sampler = new InputSampler.RandomSampler<>(0.01, 1000, 100);这行代码之前调用,否则会报Exception in thread "main" java.io.IOException: wrong key class: org.apache.hadoop.io.Text is not class org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable错误。
-
调用setSortComparatorClass方法设置排序类,对key进行排序。job.setSortComparatorClass(KeyComparator.class);类似例子中的KeyComparator类。否则是按照字典序进行排序。MapReduce默认输出的key是字符类型时,默认是按照字典序排序。