1. 概述
Ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。Ansible是一个批量的自动化部署工具。
ansible:
模块:
1) yaml 用来编写yaml脚本的语言
2) paramiko 模拟ssh协议连接linux客户端
3) jinja2 模板语言
工作原理:
ansible通过hosts文件和免秘钥(配置文件用户名密码端口号)来实现批量管理主机。
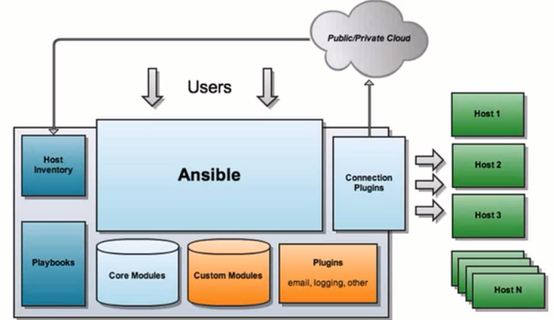
Ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。主要包括:
1> Ansible:Ansible的核心程序;
2> connection plugins:连接插件,负责和被监控端实现通信,即Ansible和host的通信;
3> Host inventory:指定操作的主机,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机;
4> Core Modules:核心模块,Ansible执行任何管理任务都不是由Ansible自己完成,而是由核心模块完成;Ansible管理主机之前,先调用core Modules中的模块,然后指明管理Host Lnventory中的主机,就可以完成管理主机。
5> Custom Modules:自定义模块,完成Ansible核心模块无法完成的功能,此模块支持任何语言编写。
Ansible将很多命令集成为模块调用。
6> Playbook:YAML格式文件,多个任务定义在一个文件中,使用时可以统一调用,“剧本”用来定义那些主机需要调用那些模块来完成的功能。剧本执行多个任务时,非必需可以让节点一次性运行多个任务。
简而言之ansible有如下的特点:
- Stupied Simple ,上手简单,学习曲线平滑
- SSH by default ,安全,无需安装客户端(agent)
- 配置简单、功能强大、扩展性强
- 支持API及自定义模块,可通过Python轻松扩展
- 通过Playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理
- 提供一个功能强大、操作性强的Web管理界面和REST API接口——AWX平台(web界面很少用)
- 幂等性:一种操作重复多次结果相同
2. Ansible的安装
三台主机,192.168.16.4为服务机,.5、.6为服务机
Ansible安装需要用到扩展源(epel源),扩展源配置完成即可用yum进行下载
在.3上下载安装
[root@localhost ~]# yum install ansible -y
稍等……..
Complete!
Ansible的配置文件
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
/etc/ansible/hosts
3. Ansible客户端配置
有两种方法
1> 进入服务端配置文件进行配置
#在文件末尾写入配置 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [zxj] #组名 192.168.16.5 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_pass=zxjwrl 192.168.16.6 ansible_ssh_user=root ansibel_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_pass=zxjwrl #远程节点主机 用户 端口 密码 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg host_key_checking = False #进入配置文件,关掉检查
2> 免秘钥登录
sshd服务
配置完成后,查看Ansible是否与管理节点通
[root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m ping #主机组名可以替换为单独的节点ip或者直接改为all,all表示所有主机,ip表示组名下单独的一个节点 192.168.16.6 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" } 192.168.16.5 | SUCCESS => { "changed": false, "ping": "pong" }
4. Ansible支持的模块
查看Ansible的模块
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -l
常用的模块
ping 模块: 尝试连接主机,如果测试成功会返回‘pong’
command模块: 在远程节点执行命令
yum模块: 使用yum软件包管理工具管理软件包
shell模块: 和command模块类似,执行命令,支持变量等符号
cron模块 : 管理定时任务,计划任务
service模块: 管理程序服务
file模块: 设置文件属性
copy模块: 复制本地文件到远程主机
script模块: 传送本地的一个脚本并在远程主机上执行
setup模块: 获取远程主机的参数信息
user模块: 管理用户账户
group模块: 添加或者删除用户组
查看具体模块的用法,以yum模块为例
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -s yum - name: Manages packages with the `yum' package manager yum: allow_downgrade: # Specify if the named ……. state: # Whether to install (`present' or `installed', `latest'), or remove (`absent' or `removed') a package. `present' and `installed' will simply ensure that a desired package is installed. `latest' will update the specified package if it's not of the latest available version. `absent' and `removed' will remove the specified package. Default is `None', however in effect the default action is `present' unless the `autoremove' option is¬ enabled for this module, then `absent' is inferred.
5. Ansible常用命令相关概念
协程:线程的处理单元;
线程:最小的调度单位;
进程:是最小的管理单元;
一个进程里面至少1个线程,一个线程或者多个线程可以在一个进程里面。
hoc命令行下的命令:
|
ansible-doc -l |
查看支持的模块 |
|
ansible-doc -s MODEL_NAME |
查看模块的用法 |
|
-f forks |
指定启动并发线程数以减少服务器压力,如ansible -f 5 表示启动五个线程 |
|
-m model_name |
要使用的模块 |
|
-a args1 |
特有的参数,即调用的模块里面的参数,使用-a调用 |
|
ansible all -m ping |
查看client端是否正常ping通 |
通过调用来执行命令举例详解
格式: ansible 组名 -m model_name -a 执行命令
#查看客户端信息 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m setup …….. #复制文件 #复制并改名 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m copy -a "src=/root/zxj.txt dest=/root/wrl.txt" 192.168.16.6 | CHANGED => { #源文件 目标文件 "changed": true, #注意幂等性 "checksum": "da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709", "dest": "/root/wrl.txt", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "md5sum": "d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "secontext": "system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0", "size": 0, "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1557345658.29-197424182241042/source", "state": "file", "uid": 0 } 192.168.16.5 | CHANGED => { "changed": true, "checksum": "da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709", "dest": "/root/wrl.txt", "gid": 0, "group": "root", "md5sum": "d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e", "mode": "0644", "owner": "root", "secontext": "system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0", "size": 0, "src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1557345658.28-200767865941415/source", "state": "file", "uid": 0 } #在客户机下查看 .5: [root@localhost ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg wrl.txt .6: [root@localhost ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg wrl.txt #command命令 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m command -a 'date' #-a后面的引号内可以加任何正确的命令 192.168.16.6 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> Thu May 9 03:52:53 CST 2019 192.168.16.5 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> Thu May 9 03:52:53 CST 2019 #command命令会进行警告。进入配置文件/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg改command_warnings = False #创建、删除用户 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m user -a "name=zxj state=present" #user模块 用户名 执行状态(此处为别名) [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m user -a "name=zxj state=absent" #安装、卸载软件 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m yum -a "name=httpd state=latest" [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m yum -a "name=httpd state=absent" #如果用install、remove等必须写成单词的过去式 #注意:yum模块和yum命令同名,因此执行时会警告,进入配置文件/etc/ansible/ansible.dfg改deprecation_warnings = False #启动apache服务 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m service -a "name=httpd state=started" #stopped、restarted、started等均为过去式,ansible不支持systemctl,用centos6及以前版本的service代替 #运行脚本 [root@localhost ~]# ansible zxj -m script -a "/tmp/test.sh" #为脚本绝对路径 等等
6. Playbook
一个任务为play,多个任务为playbooks
6.1 yaml(yml)
yaml是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式,yaml参考了其他多种语言,包括:xml,c语言,python,perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等,ClarkEvans在2001年在首次发表了这种语言。
yaml的可读性好
yaml和脚本语言的交互性好
yaml使用实现语言的数据类型
yaml有一个一致的信息模型
yaml易于实现
yaml可以基于流程来处理
yaml表达能力强,扩展性好
6.2 playbook下的5种模块
tasks:主程序;
variables:变量,以变量形式传参;
templates:模板;
handlers:触发器;
roles:角色。
6.3 playbook书写规范
脚本名以 .yaml或yml结尾;
一定不能使用tab键,yaml有严格的缩进要求;
每个冒号:后面必须有空格;
注意:
1)以冒号结尾不需要空格
2)表示文件路径的模版可以不需要空格
想要表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一个列表的一部。
6.4 ansiblb-playbook常用命令
1)对剧本语法检测
ansible-playbook --syntax-check /root/ansible/httpd.yaml
2)-C模拟执行剧本
ansible-playbook -C /root/ansible/httpd.yaml
3)执行剧本
ansible-playbook /root/ansible/httpd.yaml
6.5 ansible实例详解
#创建实例文件 [root@localhost ~]# vim example.yaml # 以yaml或者yml - hosts: zxj # - 必须顶格写,后面必须加空格,hosts:表示定义主机组,冒号后面必须加空格,后面跟的内容可以是all、ip或主机名 remote_user: root # 指定远程用户,以root运行,remote必须和host对齐,冒号后面必须加空格 tasks: # 调用任务模块,tasks必须与remote对齐,在tasks下面开始写命令 - name: create userzxj # 横杆和task对齐,与name之间必须有空格,冒号后面必须加空格,后面定义任务名 user: name=userzxj # 调用user模块,user必须与name对齐,冒号后面必须加空格。一个任务已经完成,可以继续往下添加任务,格式一致 #如添加复制任务 - name: copy httpd.conf copy: src=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf dest=/root/test/httpd.conf
#或者定义变量,通过jinjia2里的模板语言{{ }}来引用变量执行 - hosts: zxj remote_user: root vars: #定义变量 - p: httpd.conf #p为变量名,与横杠间必须有空格,http为变量值 tasks: - name: create userzxj user: name=userzxj - name: copy httpd.conf copy: src=/etc/httpd/conf/{{ p }} dest=/root/test/{{ p }} #引用变量 #再定义触发器,触发器仅由相邻的上一个任务触发,上一个任务执行成功才触发执行 - hosts: zxj remote_user: root vars: - p: httpd.conf tasks: - name: create userzxj user: name=userzxj - name: copy httpd.conf copy: src=/etc/httpd/conf/{{ p }} dest=/root/test/{{ p }} notify: #申明定义触发器 - service httpd restarted #定义触发器名字 handlers: #定义触发器,必须在最后,必须与hosts对齐 - name: service httpd restarted #定义任务名,必须与触发器名字相同 service: name=httpd state=restarted #调用service模块,执行命令
:wq #执行yaml文件用命令ansible-playbook [root@localhost ~]# ansible-playbook example.yaml PLAY [zxj] ********************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ********************************************** #测试ansible是否与客户端连通,该任务自动执行 ok: [192.168.16.5] #幂等性,由于先前执行过,并没有改变,但该命令执行成功 ok: [192.168.16.6]
TASK [create userzxj] ********************************************* #执行第一个任务 ok: [192.168.16.6] ok: [192.168.16.5] TASK [copy httpd.conf] ********************************************** #执行第二个任务 changed: [192.168.16.5] #幂等性,由于先前并没有执行过,因此改变,任务执行成功 changed: [192.168.16.6] RUNNING HANDLER [service httpd restarted] ************************* #第二个命令执行成功自动触发 changed: [192.168.16.6] changed: [192.168.16.5] PLAY RECAP ***************************************************** 192.168.16.5 : ok=4 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 192.168.16.6 : ok=4 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 #服务端查看httpd启动 #.5: [root@localhost ~]# ss -tnl LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::* .6 [root@localhost ~]# ss -tnl LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::* #端口前的星号表示ipv4,冒号表示ipv6和ipve4 #可以创建多个触发器,依托于上一个任务
#还可以进行迭代创建 - hosts: zxj remote_user: root vars: - p: httpd.conf tasks: - name: create many users user: name={{ item }} #进行迭代创建 with_items: #使用迭代 - zxj1 #创建多个用户 - zxj2 - zxj3 #模块均可进行迭代执行 #对于模板模块template,在配置文件里写入对应模板,yaml文件在执行命令模块的时候调用模板模块就可以了,如: #要执行复制http文件任务,进入httpd配置文件,将监听端口改为jinjia2的模板文件,紧接着修改ansible的配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #Listen 12.34.56.78:80 Listen {{ port }} # 变量名可以任意取 [root@localhost ~]# vim example.yaml - name: copy httpd.conf template: src=/etc/httpd/conf/{{ p }} dest=/root/test/{{ p }} [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts ## db-[99:101]-node.example.com [zxj] 192.168.16.5 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_pass=zxjwrl port=5000 #写入端口,写入变量 192.168.16.6 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_pass=zxjwrl port=6000 #引用多个模板文件时可以在该配置文件后面空格后继续写
7. Roles
什么情况下用到roles:
假如现在有3个被管理主机,第一个要配置成httpd,第二个要配置成php服务器,第三个要配置成MySQL服务器。要如何来定义playbook?
第一个play用到第一个主机上,用来构建httpd,第二个play用到第二个主机上,用来构建php,第三个play用到第三个主机上,用来构建MySQL。这些个play定义在playbook中比较麻烦,将来也不利于模块化调用,不利于多次调用。比如说后来又加进来一个主机,这个第4个主机既是httpd服务器,又是php服务器,只能写第4个play,上面写上安装httpd和php。这样playbook中的代码就重复了。这时我们可以通过roles来实现,将各个模块命令集成在roles下的服务里面,直接调用服务即可。
Roles实例详解
使用目录代替命令,各个目录如下:
files:定义src(源)文件
handlers:定义触发器
tasks:定义任务
templates:定义模板文件
vars:定义变量
各个目录写入文件后放入server目录,执行时直接调用目录。
#1 创建级联目录 [root@localhost ~]#mkdir-p playbooks/roles/{webservers,dbservers}/{files,handlers,tasks,templates,vars} [root@localhost ~]# tree playbooks/ #查看定义的roles树 playbooks/ └── roles ├── dbservers #角色 │ ├── files │ ├── handlers │ ├── tasks │ ├── templates │ └── vars └── webservers #角色 ├── files ├── handlers ├── tasks ├── templates └── vars #2. 编辑命令 [root@localhost ~]# vim playbooks/roles/webservers/tasks/main.yml #文件名必须是main.yaml或者main.yml在创建的文件里直接写任务,不必再声明组名等信息 - name: create user userzxj #写入多个命令 user: name=userzxj - name: service httpd start service: name=httpd state=started :wq #3. 创建与roles同等级别的site(站点)文件 [root@localhost ~]# cd playbooks/ [root@localhost playbooks]# vim site.yml #文件名必须为site - hosts: zxj #定义组名和远程用户 remote_user: root roles: #调用roles - webservers #写入角色,执行角色下的任务 - dbservers :wq #4. 执行任务 [root@localhost playbooks]# ansible-playbook site.yml #执行site文件 PLAY [zxj] ********************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts]*********************************************** ok: [192.168.16.6] ok: [192.168.16.5] TASK [webservers : create user userzxj]********************************** changed: [192.168.16.6] changed: [192.168.16.5] TASK [webservers : service httpd start]************************************ changed: [192.168.16.6] changed: [192.168.16.5] PLAY RECAP ******************************************************* 192.168.16.5 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 192.168.16.6 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 #执行成功
files目录:定义roles后scr(源文件)不需要写绝对路径,只声明路径即可
#1. 准备实验文件 [root@localhost playbooks]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf roles/webservers/files/ #2. 写入任务目录 [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/tasks/main.yml - name: copy httpd copy: src=httpd.conf dest=/root/test/httpd.conf #scr不需要再写绝对路径 :wq #3. 执行site.yml [root@localhost playbooks]# ansible-playbook site.yml …… 192.168.16.5 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 192.168.16.6 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
handlers目录,触发任务
#1. 写入任务文件,不需要以handlers结尾 [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/tasks/main.yml - name: copy httpd copy: src=httpd.conf dest=/root/test/httpd.conf notify: #声明触发 - restart httpd #定义名称,不需要再以handlers结尾 #2. 写入handlers下的main.yml [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/handlers/main.yml - name: restart httpd service: name=httpd state=restarted #3. 执行site.yml [root@localhost playbooks]# ansible-playbook site.yml PLAY [zxj] *************** TASK [Gathering Facts] ********* ok: [192.168.16.5] ok: [192.168.16.6] TASK [webservers : copy httpd] ************** changed: [192.168.16.5] changed: [192.168.16.6] RUNNING HANDLER [webservers : restart httpd] ************* #触发 changed: [192.168.16.6] changed: [192.168.16.5] PLAY RECAP ************ 192.168.16.5 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 192.168.16.6 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
template目录,执行copy命令时调用定义的模板参数
#1. 写入任务文件 [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/tasks/main.yml - name: copy httpd template: src=httpd.conf dest=/root/test/httpd.conf #src不写绝对路径 notify: - restart httpd #2. 定义模板参数 [root@localhost playbooks]# cp roles/webservers/files/httpd.conf roles/webservers/templates/httpd.conf [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/templates/httpd.conf #Listen 12.34.56.78:80 Listen {{ port }} #更改监听端口为模板参数 #3. 更改配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [zxj] 192.168.16.5 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_pass=zxjwrl port=5000 #写入参数 192.168.16.6 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_pass=zxjwrl port=6000 #写入参数 #4. 执行site.yml文件 [root@localhost playbooks]# ansible-playbook site.yml PLAY [zxj]……. TASK [webservers : copy httpd] * changed: [192.168.16.5] changed: [192.168.16.6] RUNNING HANDLER [webservers : restart httpd] changed: [192.168.16.6] changed: [192.168.16.5] PLAY RECAP *************** changed: [192.168.16.6] changed: [192.168.16.5] PLAY RECAP *************** 192.168.16.5 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 192.168.16.6 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
var目录,定义参数
#1. 定义var的main.yml [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/vars/main.yml p: httpd.conf #定义变量p,变量值为httpd.conf
#2. 修改任务变量 [root@localhost playbooks]# vim roles/webservers/tasks/main.yml - name: copy httpd template: src={{ p }} dest=/root/test/{{ p }} notify: - restart httpd
#3. 执行site.yml
roles下的角色,如webserver、dbserver等可以并排写入与roles同级的site.yml文件,执行多个角色,每个角色都可以写入多个任务,实现不同量的批量部署。