本篇主要介绍Android中的消息机制,即Looper、Handler是如何协同工作的;
Looper:主要用来管理当前线程的消息队列,每个线程只能有一个Looper
Handler:用来将消息(Message)插入到当前线程的消息队列,并负责分发Looper中的消息,将消息发送到当前线程执行
具体关系图如下所示:
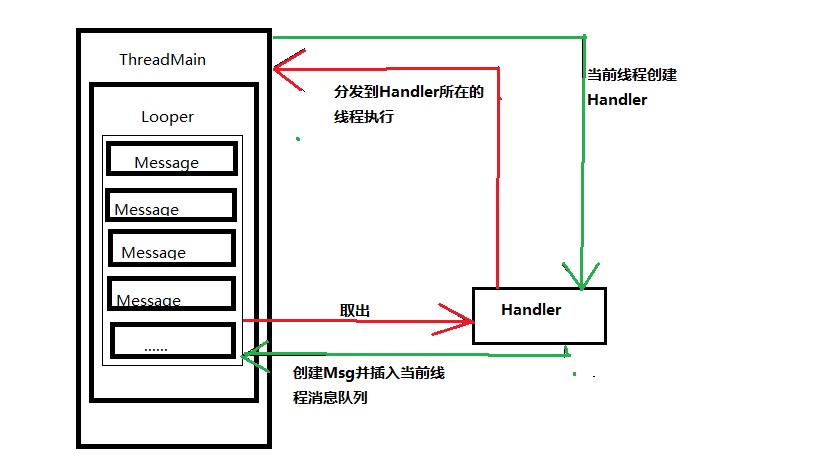
接下来我们来分析一下Looper和Handler的源码,了解一下其中的奥妙。
首先我们从一个程序运行的入口来分析,源码如下:
public static void main(String[] args){ ...... Looper.prepareMainLooper();//初始化Looper ...... if(smainThreadHandler==null){ smainThreadHandler=thread.getHandler();//初始化Handler } ...... Looper.loop();//消息循环执行 }
可以看出,程序在运行的时候首先会创建主线程的Looper对象,并通过Looper开启消息循环,不停的取出消息并执行;
接下来我们来研究Looper的源码;
第一部分:Looper源码
初始化
1 private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) { 2 mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed); 3 mThread = Thread.currentThread(); 4 } 5 6 初始化Looper对象(该过程包含初始化消息队列和当前线程对象) 7 private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { 8 if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { 9 throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); 10 } 11 sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); 12 }
可以看出Looper在初始化的时候,首先会创建消息队列,并通过sThreadLocal保存在当前的线程本地变量中;
再来看一下程序入口Looper.prepareMainLooper();//初始化Looper究竟执行了什么
1 //初始化主线程的Looper对象 2 public static void prepareMainLooper() { 3 prepare(false); 4 synchronized (Looper.class) { 5 if (sMainLooper != null) { 6 throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared."); 7 } 8 sMainLooper = myLooper(); 9 } 10 }
这里有两行关键的代码:prepare(false);和sMainLooper = myLooper();
首先我们来看prepare(false);即上面讲到的 初始化Looper,可以看看上面的源码;
我们来看sMainLooper = myLooper();
1 public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() { 2 return sThreadLocal.get(); 3 }
非常简单,我们上面提到在初始化Looper的时候会把Looper保存到当前线程的本地变量中,而这行代码的意思
就是从线程本地变量中将looper取出来
有了Looper,程序怎样才能运行?答案就在Looper.loop();//消息循环执行
1 public static void loop() { 2 final Looper me = myLooper();//得到当前线程的Looper对象 3 if (me == null) { 4 throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); 5 } 6 final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;//得到消息队列 7 8 ...... 9 10 //执行消息循环 11 for (;;) { 12 Message msg = queue.next(); // might block 13 if (msg == null) { 14 // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. 15 return; 16 } 17 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); 18 msg.recycleUnchecked(); 19 } 20 }
显而易见,loop方法就是获取到当前线程的Looper对象,并从中循环取出消息,并执行,程序就这样跑起来了,具体是如何分发消息的
我们将会在下面讲解;
至此我们至少应该明白,当主线程在执行的时候
1、初始化Looper,并将Looper保存的线程变量中
2、Looper在初始化的时候会创建消息队列,并管理消息队列
2、取出Looper,并从消息队列中取出消息,循环执行
第二部分:Handler源码
我们知道Handler有两种使用方式,一种是使用handler.post(Runnable r);另一种是复写handleMessage(Message msg)方法
复写handleMessage(Message msg)方法非常简单,Handler在消息分发的时候,直接回调该方法即可,我们主要来研究第一种
1 public final boolean post(Runnable r) 2 { 3 return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0); 4 }
看到这个我们首先得明白getPostMessage(r)干了什么
1 private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) { 2 Message m = Message.obtain(); 3 m.callback = r; 4 return m; 5 }
可以看出是将r封装成了一个消息,r作为该消息的回调;
我们接着看:
1 public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) 2 { 3 if (delayMillis < 0) { 4 delayMillis = 0; 5 } 6 return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis); 7 }
关键代码在sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
继续:
1 //得到消息队列 2 public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { 3 MessageQueue queue = mQueue; 4 if (queue == null) { 5 RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( 6 this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); 7 Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); 8 return false; 9 } 10 return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis); 11 }
这段代码主要就是获取到消息队列,有了消息队列我们接着看enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
1 //handler和msg建立关联 2 private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { 3 msg.target = this; 4 if (mAsynchronous) { 5 msg.setAsynchronous(true); 6 } 7 return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis); 8 }
msg.target = this;这里将msg的target指向自己,msg的target只能是this
最后相信大家也看出来了,接下来就是真正将msg插入到消息队列了
1 //负责将msg插入到消息队列 2 boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) { 3 if (msg.target == null) { 4 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target."); 5 } 6 7 synchronized (this) { 8 //将msg插入到消息队列 9 10 msg.when = when; 11 Message p = mMessages; 12 boolean needWake; 13 //消息队列为链式存储 如果消息队列中的消息为0,将msg插入到第一个,并新建一个message对象,将 14 //msg对象的next指向新建的message 等待新msg插入 15 if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) { 16 // New head, wake up the event queue if blocked. 17 msg.next = p; 18 mMessages = msg; 19 needWake = mBlocked; 20 } else { 21 //将msg插入到队尾 22 for (;;) { 23 prev = p; 24 p = p.next; 25 if (p == null || when < p.when) { 26 break; 27 } 28 if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) { 29 needWake = false; 30 } 31 } 32 msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next 33 prev.next = msg; 34 } 35 36 37 } 38 return true; 39 }
绕了这么大一圈,最后是通过Handler中的消息队列,将消息成功插入队尾,至此handler在post的时候实际上
是将r封装成了一个msg并插入到消息队列;
另外这里再提一下Handler第二种方式即复写handleMessage(Message msg)方法使用
handler.sendMessage(msg);
其源代码其实就是执行以上的
1 public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) 2 { 3 if (delayMillis < 0) { 4 delayMillis = 0; 5 } 6 return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis); 7 }
重复以上一系列过程,将msg插入到消息队列;
最后我们来看一下比较关键的消息分发,消息分发是在以上Looper源码的loop方法中核心方法是:
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
我们知道msg的target只能是Handler本身,因此消息分发是在Handler中来完成的;
1 /** 2 * Handle system messages here. 3 */ 4 public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { 5 if (msg.callback != null) { 6 handleCallback(msg); 7 } else { 8 if (mCallback != null) { 9 if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { 10 return; 11 } 12 } 13 handleMessage(msg); 14 } 15 }
第一:if (msg.callback != null) 如果你传入了callback即Runnable,那么就执行 handleCallback(msg);
即调用r的run方法,通常是handler.post(r);类型的
第二:if (mCallback != null)这种方法允许让activity等来实现Handler.Callback接口,避免了自己编写handler重写handleMessage方法。
第三:handleMessage(msg); 即handler.sendMessage(msg);时调用的。直接回调Handler的handleMessage(msg);方法
至此,Android中的消息机制Looper和Handler相信你已经有了一定的了解;
最后我们再来总结一下
1、Looper 一个线程中只能有一个Looper,用来管理消息队列
2、Looper从消息队列里取出msg,交给Handler来进行分发,分发到Handler所在的线程执行,即创建Handler时的线程;
3、可以在当前线程中创建消息对象或直接复写Runnable的run方法,同过Handler将msg和r封装后的msg插入到消息队列