Java的线程池都是通过ThreadPoolExecutor来构建。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || keepAliveTime < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; this.workQueue = workQueue; this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.handler = handler; }
在Executors工厂类中,Java默认提供了四种类型的线程池。
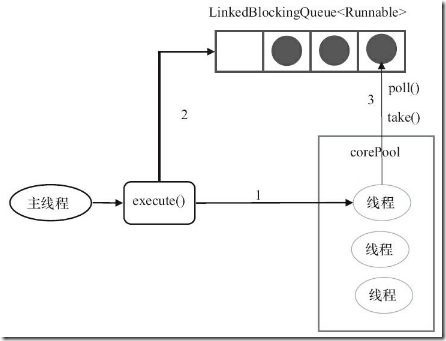
FixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }
这个线程池的特点:
- 这是一种线程数量固定的线程池,因为corePoolSize和maximunPoolSize都为用户设定的线程数量nThreads;
- keepAliveTime为0,意味着一旦有多余的空闲线程,就会被立即停止掉,不过因为最多只有nThreads个线程,且corePoolSize和maximunPoolSize值一致,所以这个值无法发挥作用;
- 阻塞队列采用了LinkedBlockingQueue,它是一个无界队列,由于阻塞队列是一个无界队列,因此永远不可能拒绝任务。
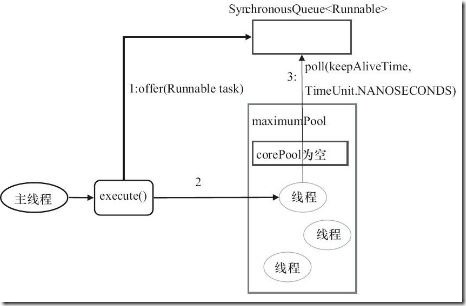
CachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }
- 这是一个线程数量可以“无限”扩大(不能超过整型最大值)的线程池;
- 比较适合处理执行时间比较小的任务;
- corePoolSize为0,maximumPoolSize为无限大,意味着线程数量可以无限大;
- keepAliveTime为60S,意味着线程空闲时间超过60S就会被杀死;
- 采用SynchronousQueue装等待的任务,这个阻塞队列没有存储空间,这意味着只要有请求到来,就必须要找到一条工作线程处理他,如果当前没有空闲的线程,那么就会再创建一条新的线程。
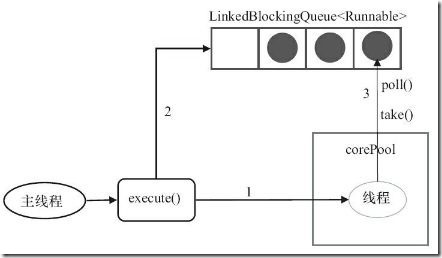
SingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }
这个线程池的特点:
- 只有一个线程,使用了无界队列LinkedBlockingQueue,某种意义上等同于newFixedThreadPool(1);
- 因为只有一个线程,所以能够保证所有任务是FIFO地执行。
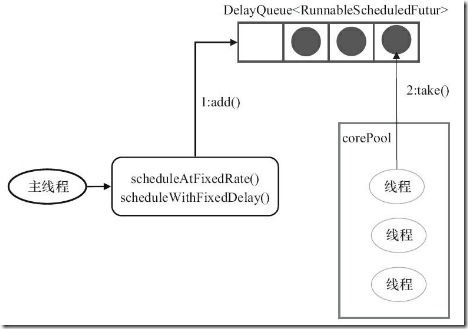
ScheduledThreadPool
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) { super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue()); }
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承自ThreadPoolExecutor。
这个线程池的特点:
它接收SchduledFutureTask类型的任务,有两种提交任务的方式:
- scheduledAtFixedRate
- scheduledWithFixedDelay
从提交方式可以看出,这个线程池主要处理定时任务或延时任务。
SchduledFutureTask接收的参数:
- time:任务开始的时间s
- equenceNumber:任务的序号
- period:任务执行的时间间隔
它采用DelayQueue存储等待的任务:
- DelayQueue内部封装了一个PriorityQueue,它会根据time的先后时间排序,若time相同则根据sequenceNumber排序;
- DelayQueue也是一个无界队列;
工作线程的执行过程:
- 工作线程会从DelayQueue取已经到期的任务去执行;
- 执行结束后重新设置任务的到期时间,再次放回DelayQueue
#########