一、获取html和字体库
三步骤:获取字库,解析字库,替换字库符号
知道原理后非常简单,需要注意每次生成的字体库顺序是不一样的
import requests import re from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont from lxml import etree import json import base64 def get_html(): headers = { "user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36" } res = requests.get("https://sh.58.com/chuzu/", headers=headers) html = res.text print(html) # 正则匹配到字体库base64字符串 res = re.findall("data:application/font-ttf;charset=utf-8;base64,(.*?)') format", html) base64_str = res[0] res = base64.b64decode(base64_str) # 保存为ttf格式文件 file = open('58.ttf', 'wb') file.write(res) file.close() # 读取ttf文件保存为xml文件 font = TTFont('58.ttf') font.saveXML('58.xml') return html
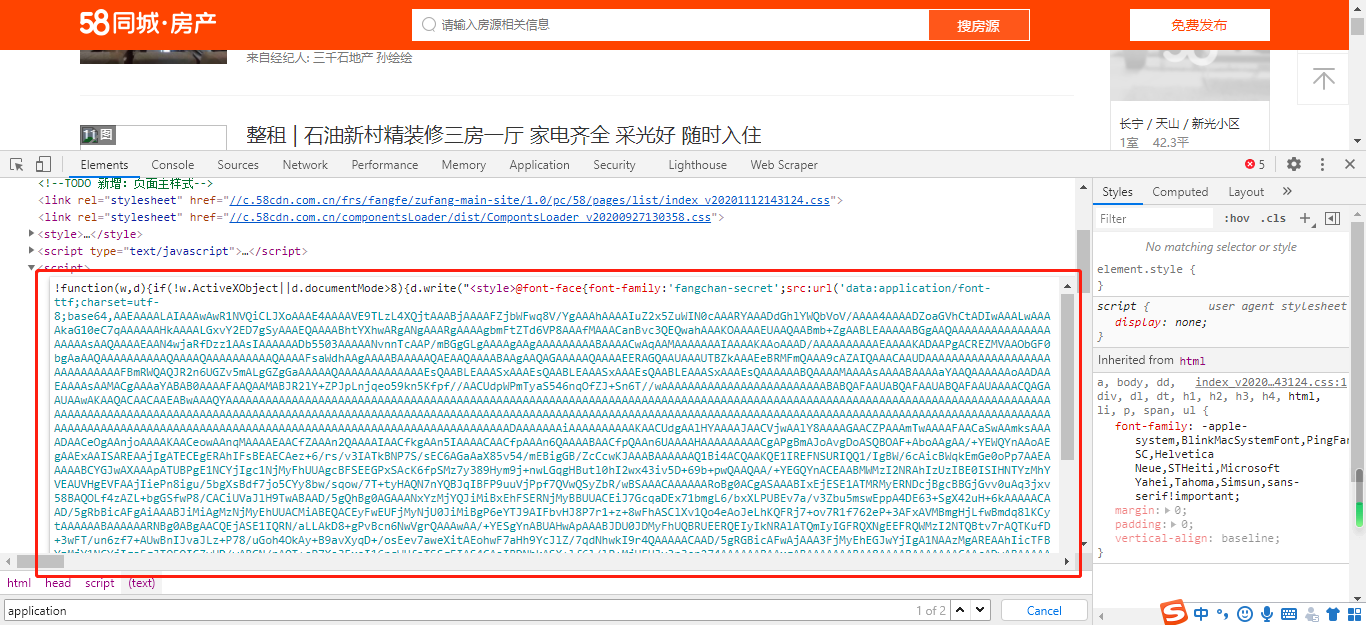
二、解析字体库
def readXML(): glyph_dict = {'glyph00001': '0', 'glyph00002': '1', 'glyph00003': '2', 'glyph00004': '3', 'glyph00005': '4', 'glyph00006': '5', 'glyph00007': '6', 'glyph00008': '7', 'glyph00009': '8', 'glyph00010': '9'} parser = etree.XMLParser(load_dtd=True) # 首先根据dtd得到一个parser(注意dtd文件要放在和xml文件相同的目录) tree = etree.parse("./58.xml", parser) # 用上面得到的parser将xml解析为树结构 cmap = tree.xpath("//cmap//map") code_dict = {} for m in cmap: values = m.items() code_dict[values[0][1]] = glyph_dict.get(values[1][1]) code_dict = json.loads(json.dumps(code_dict).replace("0x", "&#x").replace('":', ';":')) return code_dict
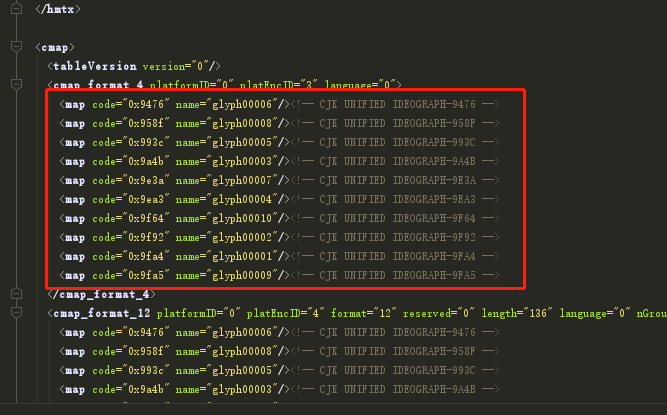
使用百度字库编辑器查看字体库:http://fontstore.baidu.com/static/editor/
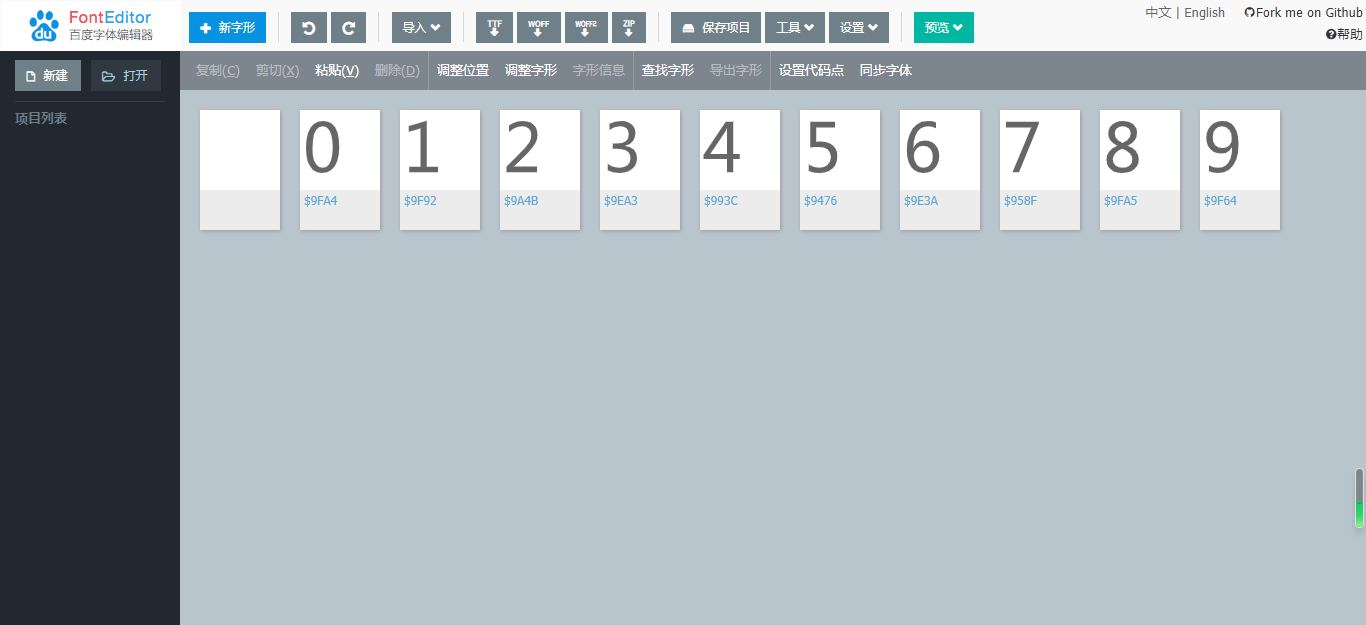
三、替换html中的字体符号
def replace_secret_code(raw_string, rep_string, rep_dict): """替换加密字体""" return raw_string.replace(rep_string, rep_dict[rep_string]) def final_run(): html=get_html() code_dict = readXML() new_html = None for k in code_dict.keys(): if not new_html: new_html = replace_secret_code(html, k, code_dict) else: new_html = replace_secret_code(new_html, k, code_dict) print(new_html)