LISA是ARM公司开发的一款开源工具。在内核开发过程中,苦于无法针对修改内容进行一些量化或者可视化结果的测量,而无感。LISA对于模型调优,回归测试都有较强的支持。
什么是LISA?
LISA是Linux Interactive System Analysis的缩写,从字面意思可以看出是一个分析工具,具有交互性特点,这有赖于ipython脚本。
LISA是一个Linux环境下用于回归测试和对于各种workload进行交互测试的工具集。目前LISA主要专注于scheduler、power management和thermal框架的分析。但不仅于此,LISA提供一个框架且可以轻松扩展到其他用途。
LISA提供一些列API用于测试条例编写和回归测试条例开发。一系列针对内核核心功能的回归测试条例已经提供。另外,LISA使用卓越的IPython Notebook框架和一些示例用于进行实验。
LISA用来干什么?
- 有助于学习已有的功能
- 有助于开发新的代码
- 有助于发现问题,并且找到原因
- 有助于分享可复制的测试:
- 足够的弹性保证在不同待测设备上重复同样的实验
- 简化预定义workload的生成和执行
- 定义一系列方法来评估内核行为
- 更简单的获取数据文件来生成统计信息和报表
LISA框架结构

待续:devlib/workload/trappy/bart/target什么功能?扩展?
TRAPpy
TRAPpy,即Trace Analysis and Plotting in Python,是一个用于分析数据的可视化工具。它分析类ftrace日志文件,然后基于分析数据创建图表和数据分析。
TRAPpy需要一些其他工具的支持才能正常工作,比如trace-cmd、kernelshark。trace-cmd用于将trace.dat转换成trace.txt文件。
TRAPpy安装
Install additional tools required for some tests and functionalities
sudo apt install trace-cmd kernelshark
安装pip等工具:
sudo apt install python-pip python-dev
安装依赖库文件:
sudo apt install libfreetype6-dev libpng12-dev python-nose
sudo pip install numpy matplotlib pandas ipython[all]
安装TRAPpy:
sudo pip install --upgrade trappy
TRAPpy使用
启动一个ipython notebook服务:
ipython notebook
会弹出一个浏览器,可以在里面创建,修改,执行脚本。
API文档:https://pythonhosted.org/TRAPpy/
BART
BART,即Behavioural Analysis and Regression Toolkit,基于TRAPpy,分析kernel输出的ftrace来诊断当前的行为是否符合预期。
安装BART
Install additional tools required for some tests and functionalities
$ sudo apt install trace-cmd kernelshark
Install the Python package manager
$ sudo apt install python-pip python-dev
Install required python packages
$ sudo apt install libfreetype6-dev libpng12-dev python-nose
$ sudo pip install numpy matplotlib pandas ipython[all]
$ sudo pip install --upgrade trappy
ipython[all] will install IPython Notebook, a web based interactive python programming interface. It is required if you plan to use interactive plotting in BART.
Install BART
$ sudo pip install --upgrade bart-py
BART的用途
BART具有广泛的用途,主要用于帮助开发者进行一些难以测试功能的自动化测试。
内核开发者:确保代码的正确性
性能优化工程师:图形化/诊断不同内核版本之间的性能表现。
质量管理、版本工程师:验证不同模块/patch集成特性。
API文档:https://pythonhosted.org/bart-py
devlib
代码路径:https://github.com/ARM-software/devlib
devlib提供一个基于Linux操作系统设备,用于交互和获取测量结果的接口。
wlgen/workload
用于生成各种负荷,目前主要支持rt-app。
LISA使用
准备工作
下载LISA:git clone https://github.com/ARM-software/lisa.git
运行LISA:source init_env,如下:
更新LISA依赖模块
lisa-update
使用LISA进行测试
lisa-test tests/eas/acceptance.py
使用LISA分析
执行lisa-ipython后,会打开浏览器。在浏览器中可以通过创建IPython脚本进行LISA相关测试。
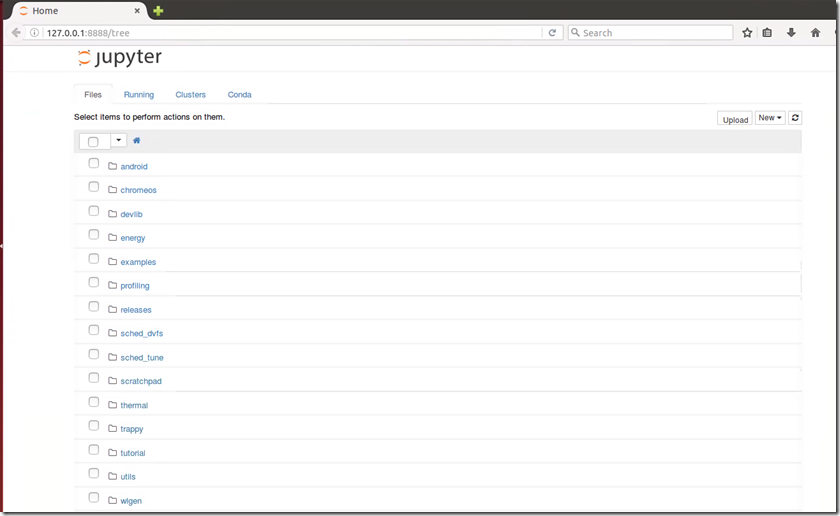
LISA代码分析
下面是LISA根目录的二级树,LISA具有明显的模块化区分,基于已有的框架可以轻松编写测试用例tests,编写自己想要的测试结果ipynb。
可以看出libs/utils提供LISA基础框架,
libs/devlib支持和待测设备之间交互连接,
测试用例在tests中,
libs/wlgen产生特定workload,
测试结果在results中,
使用ipynb下各种基本进行分析,
ipynb需要的python库在libs中。
|
├── assets
│ └── mp3-short.json
├── init_env source的环境脚本
├── ipynb 用来分析的ipython脚本
│ ├── chromeos
│ ├── energy
│ ├── examples
│ ├── profiling
│ ├── releases
│ ├── sched_dvfs
│ ├── sched_tune
│ ├── scratchpad
│ ├── thermal
│ └── tutorial
├── libs 各类基础功能和第三方应用
│ ├── bart
│ ├── devlib
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── trappy
│ ├── utils
│ └── wlgen
├── LICENSE.txt
├── LisaShell.txt
├── logging.conf
├── README.md
├── results 执行结果
│ └── LisaInANutshell_Backup
├── src shell配置文件
│ └── shell
├── target.config 待测设备配置文件
├── tests 测试用例编写脚本,host用到的x86和target用到的arm
│ ├── eas
│ ├── sfreq
│ └── stune
├── tools 测试用到的工作
│ ├── arm64
│ ├── armeabi
│ ├── LICENSE.perf
│ ├── LICENSE.rt-app
│ ├── LICENSE.sysbench
│ ├── LICENSE.taskset
│ ├── LICENSE.trace-cmd
│ ├── plots.py
│ ├── report.py
│ ├── scripts
│ └── x86_64
└── Vagrantfile
|
下面重点分析libs/utils、libs/wlgen、libs/devlib、libs/trappy、libs/bart,然后如何写自己的测试用例,并作分析。
libs/utils
class LisaTest是LISA测试用例的基类,调用class TestEnv配置测试环境,调用class Executor生成Executor。
|
@classmethod
def _runExperiments(cls):
"""
Default experiments execution engine
"""
cls.logger.info('Setup tests execution engine...')
test_env = TestEnv(test_conf=cls._getTestConf()) 基于test_conf文件生成TestEnv
experiments_conf = cls._getExperimentsConf(test_env)
cls.executor = Executor(test_env, experiments_conf) 基于experiments_conf生成Executor
# Alias executor objects to make less verbose tests code
cls.te = cls.executor.te
cls.target = cls.executor.target
# Execute pre-experiments code defined by the test
cls._experimentsInit() 测试前初始化
cls.logger.info('Experiments execution...')
cls.executor.run() 测试执行实体
# Execute post-experiments code defined by the test
cls._experimentsFinalize() 测试后收尾工作
|
class TestEnv用于配置LISA执行环境,基于target_conf配置待测设备,基于test_conf配置需要针对测试进行设置,还进行工作目录、测试工具等设置。
|
def __init__(self, target_conf=None, test_conf=None, wipe=True,
force_new=False):
…
super(TestEnv, self).__init__()
…
# Keep track of android support
self.LISA_HOME = os.environ.get('LISA_HOME', '/vagrant')
self.ANDROID_HOME = os.environ.get('ANDROID_HOME', None)
self.CATAPULT_HOME = os.environ.get('CATAPULT_HOME',
os.path.join(self.LISA_HOME, 'tools', 'catapult'))
# Setup logging
self._log = logging.getLogger('TestEnv')
# Compute base installation path
self._log.info('Using base path: %s', basepath)
# Setup target configuration
if isinstance(target_conf, dict):
self._log.info('Loading custom (inline) target configuration')
self.conf = target_conf
elif isinstance(target_conf, str):
self._log.info('Loading custom (file) target configuration')
self.conf = self.loadTargetConfig(target_conf)
elif target_conf is None:
self._log.info('Loading default (file) target configuration')
self.conf = self.loadTargetConfig()
self._log.debug('Target configuration %s', self.conf)
# Setup test configuration
if test_conf:
if isinstance(test_conf, dict):
self._log.info('Loading custom (inline) test configuration')
self.test_conf = test_conf
elif isinstance(test_conf, str):
self._log.info('Loading custom (file) test configuration')
self.test_conf = self.loadTargetConfig(test_conf)
else:
raise ValueError('test_conf must be either a dictionary or a filepath')
self._log.debug('Test configuration %s', self.conf)
# Setup target working directory
if 'workdir' in self.conf:
self.workdir = self.conf['workdir']
# Initialize binary tools to deploy
if 'tools' in self.conf:
self.__tools = self.conf['tools']
# Merge tests specific tools
if self.test_conf and 'tools' in self.test_conf and
self.test_conf['tools']:
if 'tools' not in self.conf:
self.conf['tools'] = []
self.__tools = list(set(
self.conf['tools'] + self.test_conf['tools']
))
# Initialize ftrace events
# test configuration override target one
if self.test_conf and 'ftrace' in self.test_conf:
self.conf['ftrace'] = self.test_conf['ftrace']
if 'ftrace' in self.conf and self.conf['ftrace']:
self.__tools.append('trace-cmd')
# Initialize features
if '__features__' not in self.conf:
self.conf['__features__'] = []
self._init()
# Initialize FTrace events collection
self._init_ftrace(True)
# Initialize RT-App calibration values
self.calibration()
# Initialize local results folder
# test configuration override target one
…
res_lnk = os.path.join(basepath, LATEST_LINK)
if os.path.islink(res_lnk):
os.remove(res_lnk)
os.symlink(self.res_dir, res_lnk)
# Initialize energy probe instrument
self._init_energy(True)
|
class Executor是实际生成workload的部分,worload的具体情况在experiments_conf中配置。
|
def __init__(self, test_env, experiments_conf):
"""
Tests Executor
A tests executor is a module which support the execution of a
configured set of experiments. Each experiment is composed by:
- a target configuration
- a worload to execute
The executor module can be configured to run a set of workloads (wloads)
in each different target configuration of a specified set (confs). These
wloads and confs can be specified by the "experiments_conf" input
dictionary. Each (workload, conf, iteration) tuple is called an
"experiment".
All the results generated by each experiment will be collected a result
folder which is named according to this template:
results/<test_id>/<wltype>:<conf>:<wload>/<run_id>
where:
- <test_id> : the "tid" defined by the experiments_conf, or a timestamp
based folder in case "tid" is not specified
- <wltype> : the class of workload executed, e.g. rtapp or sched_perf
- <conf> : the identifier of one of the specified configurations
- <wload> : the identified of one of the specified workload
- <run_id> : the progressive execution number from 1 up to the
specified iterations
After the workloads have been run, the Executor object's `experiments`
attribute is a list of Experiment objects. The `out_dir` attribute of
these objects can be used to find the results of the experiment.
"""
# Initialize globals
self._default_cgroup = None
self._cgroup = None
# Setup logging
self._log = logging.getLogger('Executor')
# Setup test configuration 解析experiments_conf,这些参数都会传递给wlgen执行。
…
self._print_section('Experiments configuration') 打印此实验配置
…
|
Executor.run根据Executor.__init__解析的配置,以workload为单位开始执行。
|
def run(self):
self._print_section('Experiments execution')
self.experiments = []
# Run all the configured experiments
exp_idx = 0
for tc in self._experiments_conf['confs']:
# TARGET: configuration
if not self._target_configure(tc): 配置待测设备
continue
for wl_idx in self._experiments_conf['wloads']:
# TEST: configuration
wload, test_dir = self._wload_init(tc, wl_idx) workload初始化
for itr_idx in range(1, self._iterations + 1):
exp = Experiment(
wload_name=wl_idx,
wload=wload,
conf=tc,
iteration=itr_idx,
out_dir=os.path.join(test_dir, str(itr_idx)))
self.experiments.append(exp)
# WORKLOAD: execution
self._wload_run(exp_idx, exp) worload执行
exp_idx += 1
self._target_cleanup(tc)
self._print_section('Experiments execution completed')
self._log.info('Results available in:')
self._log.info(' %s', self.te.res_dir)
|
Executor._wload_run执行单个workload:
|
def _wload_run(self, exp_idx, experiment):
tc = experiment.conf
wload = experiment.wload
tc_idx = tc['tag']
self._print_title('Experiment {}/{}, [{}:{}] {}/{}'
.format(exp_idx, self._exp_count,
tc_idx, experiment.wload_name,
experiment.iteration, self._iterations))
# Setup local results folder
self._log.debug('out_dir set to [%s]', experiment.out_dir)
os.system('mkdir -p ' + experiment.out_dir)
# Freeze all userspace tasks that we don't need for running tests
need_thaw = False
if self._target_conf_flag(tc, 'freeze_userspace'):
need_thaw = self._freeze_userspace()
# FTRACE: start (if a configuration has been provided)
if self.te.ftrace and self._target_conf_flag(tc, 'ftrace'):
self._log.warning('FTrace events collection enabled') 准备抓取ftrace
self.te.ftrace.start()
# ENERGY: start sampling 抓取Power Meter数据
if self.te.emeter:
self.te.emeter.reset()
# WORKLOAD: Run the configured workload
wload.run(out_dir=experiment.out_dir, cgroup=self._cgroup) 执行workload
下面是收集Power Meter和ftrace数据。
# ENERGY: collect measurements
if self.te.emeter:
self.te.emeter.report(experiment.out_dir)
# FTRACE: stop and collect measurements
if self.te.ftrace and self._target_conf_flag(tc, 'ftrace'):
self.te.ftrace.stop()
trace_file = experiment.out_dir + '/trace.dat'
self.te.ftrace.get_trace(trace_file)
self._log.info('Collected FTrace binary trace:')
self._log.info(' %s',
trace_file.replace(self.te.res_dir, '<res_dir>'))
stats_file = experiment.out_dir + '/trace_stat.json'
self.te.ftrace.get_stats(stats_file)
self._log.info('Collected FTrace function profiling:')
self._log.info(' %s',
stats_file.replace(self.te.res_dir, '<res_dir>'))
# Unfreeze the tasks we froze
if need_thaw:
self._thaw_userspace()
self._print_footer()
|
为了尽量降低测试的干扰,引入了freeze_userspace这个flag,这是基于CGroup的freezer子系统实现的。将必须要保留的进程之外的进程,全部冻结。
|
critical_tasks = {
'linux': ['init', 'systemd', 'sh', 'ssh'],
'android': [
'sh', 'adbd', 'init',
'usb', 'transport',
# We don't actually need this task but on Google Pixel it apparently
# cannot be frozen, so the cgroup state gets stuck in FREEZING if we
# try to freeze it.
'thermal-engine'
]
}
|
在Executor._wload_conf根据wordload配置,调用wlgen生成workload。
|
def _wload_conf(self, wl_idx, wlspec):
# CPUS: setup execution on CPUs if required by configuration
cpus = self._wload_cpus(wl_idx, wlspec)
# CGroup: setup CGroups if requried by configuration
self._cgroup = self._default_cgroup
if 'cgroup' in wlspec:
if 'cgroups' not in self.target.modules:
raise RuntimeError('Target not supporting CGroups or CGroups '
'not configured for the current test configuration')
self._cgroup = wlspec['cgroup']
if wlspec['type'] == 'rt-app':
return self._wload_rtapp(wl_idx, wlspec, cpus) rtapp类型的workload
if wlspec['type'] == 'perf_bench':
return self._wload_perf_bench(wl_idx, wlspec, cpus) perf_bench类型的workload
raise ValueError('unsupported "type" value for [{}] '
'workload specification'
.format(wl_idx))
|
platforms下存放的是不同类型主板的配置文件。
analysis目录下存放的是针对不同关注点(比如,cpus、eas、frequency、idle)等解析trace.txt的脚本,经过这些脚本处理。ipython Notebook可以生成可视化图表。
class CpusAnalysis
如何扩展?
需要编写自己设备的配置文件target.conf:
|
{
/* Platform */
/* - linux : accessed via SSH connection */
/* - android : accessed via ADB connection */
/* - host : run on the local host */
"platform" : "android", 不同类型的Target,对应不同类型的Connection
/* Board */
/* Currently supported boards are: */
/* juno : target is a JUNO board */
/* tc2 : target is a TC2 board */
/* Leave commented if your board is not listed above */
"board" : "hikey", 主板类型对应libs/utils/platforms/hikey.json文件。
/* Target Android device ID */
"device" : "0123456789abcdef", adb设备的ID
/* Login username (has to be sudo enabled) */
"username" : "root",
…
/* Devlib modules to enable/disbale for all the experiments */
"modules" : [],
"exclude_modules" : [],
…
/* List of test environment features to enable */
/* no-kernel : do not deploy kernel/dtb images */
/* no-reboot : do not force reboot the target at each */
/* configuration change */
/* debug : enable debugging messages */
"__features__" : "no-kernel no-reboot"
}
|
在utils/analysis下,基于class AnalysisModule扩展自己的分析脚本,生成图表。
libs/wlgen
class Workload作为各种workload的基类,class RTA是class Workload子类。
class Workload的__init__最主要的是进行参数的初始化,使用target.config配置。
run是class Workload的核心,该方法是负荷的执行主体。如果需要抓取ftrace,也会在这里收集。
|
def run(self,
ftrace=None,
cgroup=None,
cpus=None,
background=False,
out_dir='./',
as_root=False,
start_pause_s=None,
end_pause_s=None):
self.cgroup = cgroup
# Compose the actual execution command starting from the base command
# defined by the base class
_command = self.command
if not _command:
self._log.error('Error: empty executor command')
# Prepend eventually required taskset command
if cpus or self.cpus: 如果需要设置CPU亲和性,使用taskset进行设置。
cpus_mask = self.getCpusMask(cpus if cpus else self.cpus)
self.taskset_cmd = '{}/taskset 0x{:X}'
.format(self.target.executables_directory,
cpus_mask)
_command = '{} {}'
.format(self.taskset_cmd, _command)
if self.cgroup and hasattr(self.target, 'cgroups'):
# Get a reference to the CGroup to use
_command = self.target.cgroups.run_into_cmd(self.cgroup, _command)
# Start FTrace (if required)
if ftrace: 设置ftrace相关sysfs节点,启动ftrace抓取
ftrace.start()
# Wait `start_pause` seconds before running the workload
if start_pause_s:
self._log.info('Waiting %f seconds before starting workload execution',
start_pause_s)
sleep(start_pause_s)
# Start task in background if required
if background: 是否作为背景进程运行
self._log.debug('WlGen [background]: %s', _command)
self.target.background(_command, as_root=as_root)
self.output['executor'] = ''
# Start task in foreground
else:
self._log.info('Workload execution START:')
self._log.info(' %s', _command)
# Run command and wait for it to complete
results = self.target.execute(_command, as_root=as_root) 在class TestEnv的_init_target创建了class Target的子类class AndroidTarget。此处execute都是通过adb shell执行。
self.output['executor'] = results
# Wait `end_pause` seconds before stopping ftrace
if end_pause_s:
self._log.info('Waiting %f seconds before stopping trace collection',
end_pause_s)
sleep(end_pause_s)
# Stop FTrace (if required)
ftrace_dat = None
if ftrace: 停止ftrace抓取,并导出ftrace内容。
ftrace.stop()
ftrace_dat = out_dir + '/' + self.test_label + '.dat'
dirname = os.path.dirname(ftrace_dat)
if not os.path.exists(dirname):
self._log.debug('Create ftrace results folder [%s]',
dirname)
os.makedirs(dirname)
self._log.info('Pulling trace file into [%s]...', ftrace_dat)
ftrace.get_trace(ftrace_dat)
if not background:
self.__callback('postrun', destdir=out_dir)
self._log.debug('Workload execution COMPLETED')
return ftrace_dat
|
在了解了基类Workload之后,稍微了解一下class RTA。
RTA根据需要增加了calibrate,用于在执行rtapp workload之前,校准cpu的性能。
另外扩展了四种任务类型,class Ramp、class Step、class Pulse和class Periodic。
如何扩展?
workload的扩展都是基于class Workload进行。如果需要创建自己的workload,就需要参照rta.py,写一个自己的子类;class LocalLinuxTarget作为class LinuxTarget的子类,用于测试本地host设备。
libs/devlib
target.py中定义了基类class Target,以及两种类型的子类class LinuxTarget和class AndroidTarget,针对ssh连接设备和adb连接设备。
class Workload的三个子类,分别对应三种不同类型的连接class AdbConnection、class SshConnection和class LocalConnection。
class FtraceController进行ftrace抓取前buffer大小、filter等的设置,导出ftrace,进行trace.dat到trace.txt的转变,以及抓取结束后的清理工作。
instrument的__init__.py中定义了基类class Instrument,用于扩展不同类型的测量仪器,一般对应的是物理上存在的设备。
class DaqInstrument、class EnergyProbeInstrument和class HwmonInstrument分别对应DAQ、Energy Probe和hwmon三种设备。
class Module基类用于针对不同模块进行配置,有的是配置某一模块的内核sysfs节点,有的是使用命令执行操作。
比如class BigLittleModule,online/offline不同cluster的CPU,或者获取CPU的各种信息。
class CpufreqModule显示/设置CPU的governor、最高频率、当前频率等等信息。
bin存放devlib用到的可执行文件,比如busybox、trace-cmd等。
如何扩展?
所以综合下来,在devlib中可能根据class Workload需要扩展不同类型的连接。
如果有新的测试仪器,需要扩展class Instrument。
有时候为了方便对摸快操作,可以基于class Module进行扩展。
libs/trappy
从TRAPpy的缩写即可知道,一是解析trace,二是对解析结果进行可视化显示。
在trappy/trappy下有很多python脚本,里面注册了很多ftrace的解析器,register_ftrace_parser和register_dynamic_ftrace。
libs/bart
在进行了这些分析之后,可以看出test、experiment、workload之间的关系。
一个test可以对应一个或多个experiment;一个experiment可以对应一个或多个workload。
test对应tests目录中的脚本,experiment对应Executor,workload对应wlgen。
编写测试用例
编写分析脚本
参考资料
- LISA Wiki:https://github.com/ARM-software/lisa/wiki
- LISA Git:https://github.com/ARM-software/lisa


