我们在上面对ASP.NET Core默认提供的具有跨平台能力的KestrelServer进行了详细介绍(《聊聊ASP.NET Core默认提供的这个跨平台的服务器——KestrelServer》),为了让读者朋友们对管道中的Server具有更加深刻的认识,接下来我们采用实例演示的形式创建一个自定义的Server。这个自定义的Server直接利用HttpListener来完成针对请求的监听、接收和响应,我们将其命名为HttpListenerServer。在正式介绍HttpListenerServer的设计和实现之前,我们先来显示一下如何将它应用到 一个具体的Web应用中。
一、HttpListenerServer的使用
我们依然采用最简单的Hello World应用来演示针对HttpListenerServer的应用,所以我们在Startup类的Configure方法中编写如下的程序直接响应一个“Hello World”字符串。
1: public class Startup
2: {3: public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
4: {5: app.Run(context => context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!"));
6: } 7: }在作为程序入口的Main方法中,我们直接创建一个WebHostBuilder对象并调用扩展方法UseHttpListener完成针对自定义HttpListenerServer的注册。我们接下来调用UseStartup方法注册上面定义的这个启动类型,然后调用Build方法创建一个WebHost对象,最后调用Run方法运行这个作为宿主的WebHost。
1: public class Program
2: {3: public static void Main()
4: {5: new WebHostBuilder()
6: .UseHttpListener() 7: .UseStartup<Startup>() 8: .Build() 9: .Run(); 10: } 11: } 12: 13: public static class WebHostBuilderExtensions
14: {15: public static IWebHostBuilder UseHttpListener(this IWebHostBuilder builder)
16: { 17: builder.ConfigureServices(services => services.AddSingleton<IServer, HttpListenerServer>());18: return builder;
19: } 20: }我们自定义的扩展方法UseHttpListener的逻辑很简单,它只是调用WebHostBuilder的ConfigureServices方法将我们自定义的HttpListenerServer类型以单例模式注册到指定的ServiceCollection上而已。我们直接运行这个程序并利用浏览器访问默认的监听地址(http://localhost:5000),服务端响应的“Hello World”字符串会按照如下图所示的形式显示在浏览器上。

二、总体设计
接下来我们来介绍一下HttpListenerServer的大体涉及。除了HttpListenerServer这个实现了IServer的自定义Server类型之外,我们只定义了一个名为HttpListenerServerFeature的特性类型,下图所示的UML基本上体现了HttpListenerServer的总体设计。
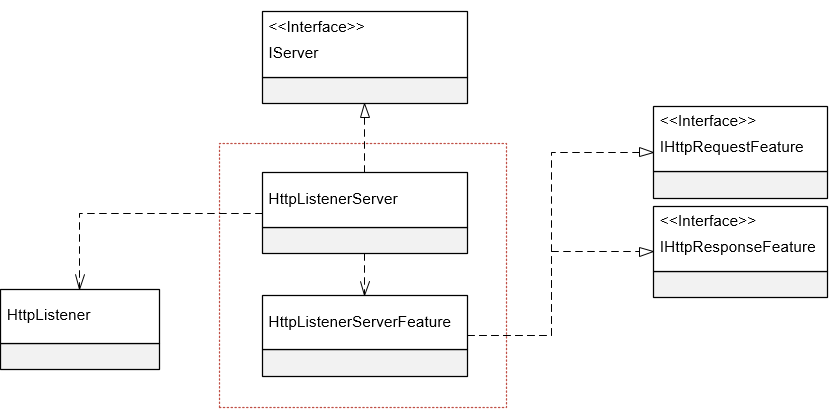
三、HttpListenerServerFeature
如果我们利用HttpListener来监听请求,它会为接收到的每次请求创建一个属于自己的上下文,具体来说这是一个类型为HttpListenerContext对象。我们可以利用这个HttpListenerContext对象获取所有与请求相关的信息,针对请求的任何响应也都是利用它完成的。上面这个HttpListenerServerFeature实际上就是对这个作为原始上下文的HttpListenerContext对象的封装,或者说它是管道使用的DefaultHttpContext与这个原始上下文之间沟通的中介。
如下所示的代码片段展示了HttpListenerServerFeature类型的完整定义。简单起见,我们并没有实现上面提到过的所有特性接口,而只是选择性地实现了IHttpRequestFeature和IHttpResponseFeature这两个最为核心的特性接口。它的构造函数除了具有一个类型为HttpListenerContext的参数之外,还具有一个字符串的参数pathBase用来指定请求URL的基地址(对应IHttpRequestFeature的PathBase属性),我们利用它来计算请求URL的相对地址(对应IHttpRequestFeature的Path属性)。IHttpRequestFeature和IHttpResponseFeature中定义的属性都可以直接利用HttpListenerContext对应的成员来实现,这方面并没有什么特别之处。
1: public class HttpListenerServerFeature : IHttpRequestFeature, IHttpResponseFeature
2: {3: private readonly HttpListenerContext httpListenerContext;
4: private string queryString;
5: private IHeaderDictionary requestHeaders;
6: private IHeaderDictionary responseHeaders;
7: private string protocol;
8: private readonly string pathBase;
9: 10: public HttpListenerServerFeature(HttpListenerContext httpListenerContext, string pathBase)
11: {12: this.httpListenerContext = httpListenerContext;
13: this.pathBase = pathBase;
14: } 15: 16: #region IHttpRequestFeature
17: 18: Stream IHttpRequestFeature.Body 19: {20: get { return httpListenerContext.Request.InputStream; }
21: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
22: } 23: 24: IHeaderDictionary IHttpRequestFeature.Headers 25: {26: get { return requestHeaders
27: ?? (requestHeaders = GetHttpHeaders(httpListenerContext.Request.Headers)); }28: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
29: } 30: 31: string IHttpRequestFeature.Method
32: {33: get { return httpListenerContext.Request.HttpMethod; }
34: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
35: } 36: 37: string IHttpRequestFeature.Path
38: {39: get { return httpListenerContext.Request.RawUrl.Substring(pathBase.Length);}
40: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
41: } 42: 43: string IHttpRequestFeature.PathBase
44: {45: get { return pathBase; }
46: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
47: } 48: 49: string IHttpRequestFeature.Protocol
50: {51: get{ return protocol ?? (protocol = this.GetProtocol());}
52: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
53: } 54: 55: string IHttpRequestFeature.QueryString
56: {57: Get { return queryString ?? (queryString = this.ResolveQueryString());}
58: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
59: } 60: 61: string IHttpRequestFeature.Scheme
62: {63: get { return httpListenerContext.Request.IsWebSocketRequest ? "https" : "http"; }
64: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
65: }66: #endregion
67: 68: #region IHttpResponseFeature
69: Stream IHttpResponseFeature.Body 70: {71: get { return httpListenerContext.Response.OutputStream; }
72: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
73: } 74: 75: string IHttpResponseFeature.ReasonPhrase
76: {77: get { return httpListenerContext.Response.StatusDescription; }
78: set { httpListenerContext.Response.StatusDescription = value; }
79: } 80: 81: bool IHttpResponseFeature.HasStarted
82: {83: get { return httpListenerContext.Response.SendChunked; }
84: } 85: 86: IHeaderDictionary IHttpResponseFeature.Headers 87: {88: get { return responseHeaders
89: ?? (responseHeaders = GetHttpHeaders(httpListenerContext.Response.Headers)); }90: set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
91: }92: int IHttpResponseFeature.StatusCode
93: {94: get { return httpListenerContext.Response.StatusCode; }
95: set { httpListenerContext.Response.StatusCode = value; }
96: } 97: 98: void IHttpResponseFeature.OnCompleted(Func<object, Task> callback, object state)
99: {100: throw new NotImplementedException();
101: } 102: 103: void IHttpResponseFeature.OnStarting(Func<object, Task> callback, object state)
104: {105: throw new NotImplementedException();
106: }107: #endregion
108: 109: private string ResolveQueryString()
110: {111: string queryString = "";
112: var collection = httpListenerContext.Request.QueryString;113: for (int i = 0; i < collection.Count; i++)
114: {115: queryString += $"{collection.GetKey(i)}={collection.Get(i)}&";
116: }117: return queryString.TrimEnd('&');
118: } 119: 120: private IHeaderDictionary GetHttpHeaders(NameValueCollection headers)
121: {122: HeaderDictionary dictionary = new HeaderDictionary();
123: foreach (string name in headers.Keys)
124: {125: dictionary[name] = new StringValues(headers.GetValues(name));
126: }127: return dictionary;
128: } 129: 130: private string GetProtocol()
131: { 132: HttpListenerRequest request = httpListenerContext.Request; 133: Version version = request.ProtocolVersion;134: return string.Format("{0}/{1}.{2}", request.IsWebSocketRequest ? "HTTPS" : "HTTP", version.Major, version.Minor);
135: } 136: }
四、HttpListenerServer
接下来我们来看看HttpListenerServer的定义。如下面的代码片段所示,用来监听请求的HttpListener在构造函数中被创建,与此同时,我们会创建一个用于获取监听地址的ServerAddressesFeature对象并将其添加到属于自己的特性列表中。当HttpListenerServer随着Start方法的调用而被启动后,它将这个ServerAddressesFeature对象提取出来,然后利用它得到所有的地址并添加到HttpListener的Prefixes属性表示的监听地址列表中。接下来,HttpListener的Start方法被调用,并在一个无限循环中开启请求的监听与接收。
1: public class HttpListenerServer : IServer
2: {3: private readonly HttpListener listener;
4: 5: public IFeatureCollection Features { get; } = new FeatureCollection();
6: 7: public HttpListenerServer()
8: {9: listener = new HttpListener();
10: this.Features.Set<IServerAddressesFeature>(new ServerAddressesFeature());
11: } 12: 13: public void Dispose()
14: { 15: listener.Stop(); 16: } 17: 18: public void Start<TContext>(IHttpApplication<TContext> application)
19: {20: foreach (string address in this.Features.Get<IServerAddressesFeature>().Addresses)
21: {22: listener.Prefixes.Add(address.TrimEnd('/') + "/");
23: } 24: 25: listener.Start();26: while (true)
27: { 28: HttpListenerContext httpListenerContext = listener.GetContext(); 29: 30: string listenUrl = this.Features.Get<IServerAddressesFeature>().Addresses.First(address => httpListenerContext.Request.Url.IsBaseOf(new Uri(address)));
31: string pathBase = new Uri(listenUrl).LocalPath.TrimEnd('/') ;
32: HttpListenerServerFeature feature = new HttpListenerServerFeature(httpListenerContext, pathBase);
33: 34: FeatureCollection features = new FeatureCollection();
35: features.Set<IHttpRequestFeature>(feature); 36: features.Set<IHttpResponseFeature>(feature); 37: TContext context = application.CreateContext(features); 38: 39: application.ProcessRequestAsync(context).ContinueWith(task => 40: { 41: httpListenerContext.Response.Close(); 42: application.DisposeContext(context, task.Exception); 43: }); 44: } 45: } 46: }HttpListener的GetContext方法以同步的方式监听请求,并利用接收到的请求创建返回的HttpListenerContext对象。我们利用它解析出当前请求的基地址,并进一步创建出描述当前原始上下文的HttpListenerServerFeature。接下来我们将这个对象分别采用特性接口IHttpRequestFeature和IHttpResponseFeature添加到创建的FeatureCollection对象中。然后我们将这个FeatureCollection作为参数调用HttpApplication的CreateContext创建出上下文对象,并将其作为参数调用HttpApplication的ProcessContext方法让注册的中间件来逐个地对请求进行处理。