前言
前面介绍了如何通过node实现了简单的request和response,项目只有一个文件index.js,做demo没有问题,如果在开发真实项目时显得会很混乱,借下来介绍如何去组织项目。
过程
这里使用model-view-router(MVR)模式去管理各个模块,管理可通过模块consign实现,这样我们就可以有效地管理模型,路由,中间件,配置等。
npm i consign --save
组织路由
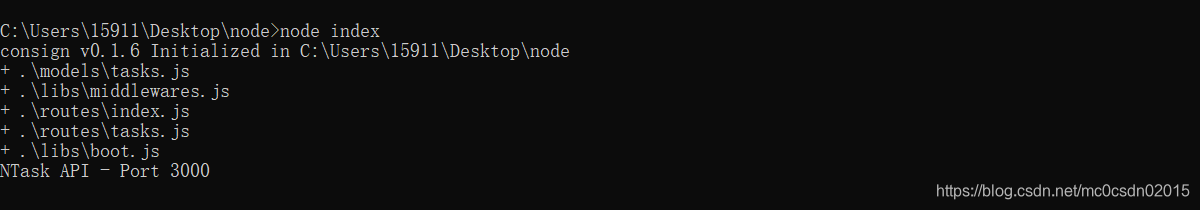
创建routes文件夹,新建文件routes/index.js,routes/tasks
// routes/index.js
module.exports = app => {
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.json({ status: "OK" });
});
};
// routes/tasks.js
module.exports = app => {
app.get("/tasks", (req, res) => {
res.json({
tasks: [{ title: "go shopping" }, { title: "go fishing" }]
});
});
};
在入口index文件中引入该模块
var express = require("express");
var consign = require("consign");
const PORT = 3000;
const app = express();
consign()
.include("routes")
.into(app);
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`监视端口${PORT}。。。`));
运行程序,可看到成功引入路由模块
组织模型
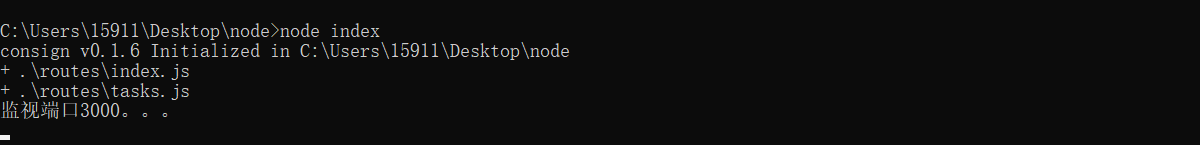
我们通过新建路由文件夹,将所有路由文件集中在一起。接下来我们将路由文件中的数据模块分离出来即为model,新建文件models/tasks.js,
module.exports = app => {
return {
findAll: (params, callback) => {
return callback([{ title: "go shopping" }, { title: "go fishing" }]);
}
};
};
相应的调整routes/tasks.js
module.exports = app => {
const Tasks = app.models.tasks;
app.get("/tasks", (req, res) => {
Tasks.findAll({}, tasks => {
res.json({ tasks: tasks });
});
});
};
引入models.tasks,回调函数返回models数据
调整入口文件index.js
import express from "express";
import consign from "consign";
const PORT = 3000;
const app = express();
app.set("json spaces", 4);
consign()
.include("models")
.then("routes")
.into(app);
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`监视端口${PORT}。。。`));
运行程序,可看到成功引入模型模块
组织其他
中间件
新建libs/middlewares.js,配置端口等
module.exports = app => {
app.set("port", 3000);
app.set("json spaces", 4);
};
监视端口
新建libs/boot.js,配置监视
module.exports = app => {
app.listen(app.get("port"), () => {
console.log(`监视端口${app.get("port"}。。。`);
});
};
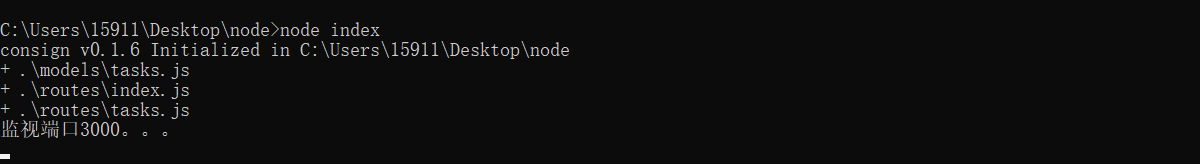
调整入口文件index.js,引入对应模块
import express from "express";
import consign from "consign";
const app = express();
consign()
.include("models")
.then("libs/middlewares.js")
.then("routes")
.then("libs/boot.js")
.into(app);
运行程序,可看到成功引入其他模块