题意
空间中三个点,要用三个半径相等的球覆盖它们。要求三个球覆盖的区域连续。求半径的最小值。
题解
赛场上少考虑了一种情况坑了fqw啊..
首先,要三个球覆盖的区域连续,三个球的最大圆截面一定都在三个点固定的平面上。所以问题规约为:给出平面上三个点,要用三个半径相等的覆盖区域连续的圆覆盖它们。
计算出三点两两之间距离,通过余弦定理可以画在平面上。
所以最后的圆应如下摆放:
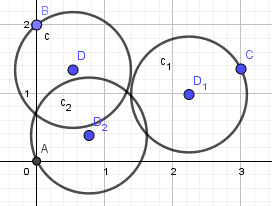 或
或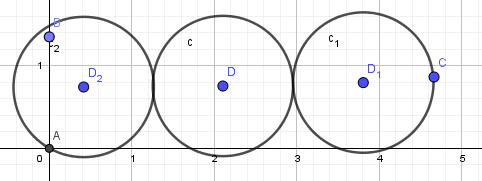
对于第一种情况:
由于要求三个圆连通,所以必有一个圆和其他两个圆都有交,我们称这个圆为主圆。由于主圆和另外两个圆都有交,而另外两个点分别在另外两个圆上,所以主圆圆心到另外两个点的距离小于等于3R。所以只需要用另外两个点为圆心画半径为3R的圆,用主圆点为圆心画半径为R的圆,判断三个圆是否有公共交即可。需要枚举主圆点。
对于第二种情况:
距离最短的两点共圆,而第三点到该圆心距离小于等于5R。所以以距离最短的两个点为圆心画两个半径为R的圆,以另外一个点为圆心画半径为5R的圆,判断三个圆是否有交即可。
至于如何判断三圆是否有交,只需要枚举是否存在其中两圆交点在第三圆内,或是否存在一个圆内含于另两圆交点处。
而答案的半径R有显然的单调性,所以对半径二分答案即可。
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 const double PI = acos(-1.0); 6 const double eps = 1e-8; 7 int dcmp(const double &x){ 8 if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0; 9 return x < 0 ? -1 : 1; 10 } 11 12 struct P3{ 13 double x, y, z; 14 P3(){} 15 P3(double a, double b, double c): x(a), y(b), z(c){} 16 P3 operator - (const P3 &p) const { return P3(x - p.x, y - p.y, z - p.z); } 17 double operator * (const P3 &p) const { return x * p.x + y * p.y + z * p.z; } 18 P3 operator ^ (const P3 &p) const { return P3(y * p.z - z * p.y, z * p.x - x * p.z, x * p.y - y * p.x); } 19 void read(){ 20 scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &x, &y, &z); 21 //cin >> x >> y >> z; 22 } 23 }; 24 25 struct P{ 26 double x, y; 27 P(){} 28 P(double a, double b): x(a), y(b){} 29 P operator - (const P &p) const { return P(x - p.x, y - p.y); } 30 double operator * (const P &p) const { return x * p.x + y * p.y; } 31 P operator * (const double &k) { return P(x * k, y * k); } 32 double operator ^ (const P &p) const { return x * p.y - y * p.x; } 33 bool operator == (const P &p) const{ return !dcmp(x - p.x) && !dcmp(y - p.y); } 34 }; 35 36 struct C{ 37 P c; 38 double r; 39 C(){} 40 C(P a, double b): c(a), r(b){} 41 void print(){ 42 printf("%.12f, %.12f : %.12f ", c.x, c.y, r); 43 } 44 P get_point(double rad){ 45 return P(c.x + cos(rad) * r, c.y + sin(rad) * r); 46 } 47 }; 48 49 int T; 50 P3 p[3]; 51 P pp[3]; 52 C cir[3]; 53 double dis[3]; 54 vector<P> sol; 55 56 double length(P3 a, P3 b){ 57 return sqrt((b - a) * (b - a)); 58 } 59 60 double length(P a, P b){ 61 return sqrt((b - a) * (b - a)); 62 } 63 64 double cos_law(double a, double b, double c){ 65 return (a * a + b * b - c * c) / (2 * a * b); 66 } 67 68 P normalize(P p){ 69 double len = sqrt(p * p); 70 return P(p.x / len, p.y / len); 71 } 72 73 P rot(P p, double ang){ 74 return P(p.x * cos(ang) - p.y * sin(ang), p.y * cos(ang) + p.x * sin(ang)); 75 } 76 77 double angle(const P &p){ return atan2(p.y, p.x); } 78 79 int circirintr(C C1, C C2, vector<P> &sol){ 80 double d = length(C1.c, C2.c); 81 if (!dcmp(d)){ 82 if (dcmp(C1.r - C2.r) == 0) return -1; //overlap, infinite intersection points 83 return 0; // no intersection 84 } 85 if (dcmp(C1.r + C2.r - d) < 0) return 0; // xiang li 86 if (dcmp(fabs(C1.r - C2.r) - d) > 0) return 0; // nei han 87 double a = angle(C2.c - C1.c); 88 double da = acos((C1.r * C1.r + d * d - C2.r * C2.r) / (2 * C1.r * d)); //cos law to get angle 89 P p1 = C1.get_point(a - da), p2 = C1.get_point(a + da); //get the corresponding point 90 sol.push_back(p1); 91 if (p1 == p2) return 1; 92 sol.push_back(p2); 93 return 2; 94 } 95 96 bool incir(C cir1, C cir2){ 97 double d = length(cir1.c, cir2.c); 98 return dcmp(d - fabs(cir1.r - cir2.r)) <= 0; 99 } 100 101 double solve(){ 102 double l = 0, r = dis[2]; 103 double res; 104 while (dcmp(fabs(r - l) - eps)){ 105 double mid = 0.5 * (l + r); 106 bool ok = false; 107 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 108 cir[0] = C(pp[i], mid); 109 cir[1] = C(pp[(i + 1) % 3], 3 * mid); 110 cir[2] = C(pp[(i + 2) % 3], 3 * mid); 111 bool flag = false; 112 for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++){ 113 sol.clear(); 114 circirintr(cir[k], cir[(k + 1) % 3], sol); 115 for (int x = 0; x < (int)sol.size(); x++) { 116 double len = length(sol[x], cir[(k + 2) % 3].c); 117 if (dcmp(length(sol[x], cir[(k + 2) % 3].c) - cir[(k + 2) % 3].r) <= 0) flag =true; 118 } 119 if (incir(cir[k], cir[(k + 1) % 3]) && incir(cir[k], cir[(k + 2) % 3])) flag = true; 120 if (flag){ 121 ok = true; 122 break; 123 } 124 } 125 } 126 if (ok){ 127 res = mid; 128 r = mid; 129 }else{ 130 l = mid; 131 } 132 } 133 return res; 134 } 135 136 double solve2(){ 137 double l = 0, r = dis[2]; 138 double res; 139 int tt = 0; 140 while (tt < 1000){ 141 tt++; 142 double mid = 0.5 * (l + r); 143 bool ok = false; 144 cir[0] = C(pp[0], mid); 145 cir[1] = C(pp[1], mid); 146 cir[2] = C(pp[2], 5 * mid); 147 sol.clear(); 148 circirintr(cir[0], cir [1], sol); 149 if (sol.size() > 0){ 150 bool flag = false; 151 for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++){ 152 sol.clear(); 153 circirintr(cir[k], cir[(k + 1) % 3], sol); 154 for (int x = 0; x < (int)sol.size(); x++) { 155 double len = length(sol[x], cir[(k + 2) % 3].c); 156 //printf("\ %.12f, %.12f // ", len, cir[(k + 2) % 3].r); 157 if (dcmp(length(sol[x], cir[(k + 2) % 3].c) - cir[(k + 2) % 3].r) <= 0) flag =true; 158 } 159 if (incir(cir[k], cir[(k + 1) % 3]) && incir(cir[k], cir[(k + 2) % 3])) flag = true; 160 if (flag){ 161 ok = true; 162 break; 163 } 164 } 165 } 166 if (ok){ 167 res = mid; 168 r = mid; 169 }else{ 170 l = mid; 171 } 172 } 173 return res; 174 } 175 176 #define JUDGE 177 178 int main(){ 179 #ifndef JUDGE 180 freopen("1.in", "r", stdin); 181 #endif // JUDGE 182 #ifdef JUDGE 183 freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin); 184 freopen("1.out", "w", stdout); 185 #endif // JUDGE 186 scanf("%d", &T); 187 for (int ca = 1; ca <= T; ca++){ 188 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 189 p[i].read(); 190 } 191 dis[0] = length(p[0], p[1]); dis[1] = length(p[1], p[2]); dis[2] = length(p[0], p[2]); 192 sort(dis, dis + 3); 193 if (!dcmp(dis[0] + dis[1] - dis[2])) { 194 printf("Case #%d: %.10f ", ca, dis[2] / 6); 195 continue; 196 } 197 double cosa = cos_law(dis[0], dis[1], dis[2]); 198 double sina = sqrt(1 - cosa * cosa); 199 pp[0] = P(0, 0); pp[1] = P(0, dis[0]); pp[2] = P(dis[1] * sina, dis[1] * cosa); 200 double res = solve(); 201 res = min(res, solve2()); 202 printf("Case #%d: %.10f ", ca, res); 203 } 204 return 0; 205 }