Mybatis缓存介绍
MyBatis提供一级缓存和二级缓存机制。
一级缓存是Sqlsession级别的缓存,Sqlsession类的实例对象中有一个hashmap用于缓存数据。不同的Sqlsession实例缓存的hashmap数据区域互不影响。Mybatis默认启用一级缓存,在同一个sqlsession中多次执行相同的sql语句,第一次执行后会将数据缓存起来,后面的查询将会从缓存中读取。当一个sqlsession结束后(close),该sqlsession中缓存的数据也将不存在。
二级缓存是Mapper级别的缓存,多个sqlsession实例操作同一个Mapper配置可共享二级缓存。Mybatis默认没有启用二级缓存,需要手动配置开启二级缓存。
一张图看看一集缓存和二级缓存的区别:

一级缓存
一级缓存区域按sqlsession划分,当执行查询时会先从缓存区域查找,如果存在则直接返回数据,否则从数据库查询,并将结果集写入缓存区。 Mybatis一级缓存是在sqlsession内部维护一个hashmap用于存储,缓存key为hashcode+sqlid+sql,value则为查询的结果集。一级缓存在执行sqlsession.commit()后将会被清空。
一级缓存示例:
编写cacheMapper.xml配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.sl.mapper.CacheMapper"> <cache/> <select id="selectProductById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.sl.po.Product" > select * from products where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
Mapper接口:

public interface CacheMapper { Product selectProductById(int id); @Options(flushCache=FlushCachePolicy.TRUE) int updateProductById(Product product); }
测试方法:
public class TestCacheMapperClient {
SqlSessionFactory factory = null; @Before public void init() throws IOException { String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); factory = builder.build(inputStream); } // 一级缓存 @Test public void testSelectProductById() { SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); CacheMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Product product = mapper.selectProductById(1); System.out.println(product.getName()); //执行commit 将清空一级缓存 //session.commit(); //再次执行查询 从一级缓存读取 Product product2 = mapper.selectProductById(1); System.out.println(product.getName()); // 关闭会话 session.close(); } }
执行第一次执行selectProductById,查询数据库,第二次执行,从缓存中读取

如果在两次查询中间执行commit,即上面的注释掉的session.commit(),则运行结果如下,显然清空了一级缓存,再次执行数据库查询
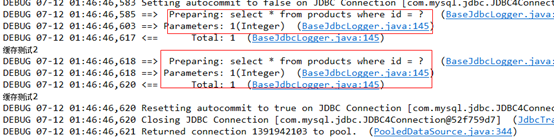
二级缓存
二级缓存按照mapper划分,一个mapper有一个自己的二级缓存(按照namespace区分不同缓存区域,如果多个mapper的namespace相同,则公用一个缓存区域),当多个sqlsession类实例加载相同的Mapper文件,执行mapper配置文件中的sql查询时,这些sqlsession可共享一个二级缓存。Mybatis默认没有启用二级缓存,需要自行配置。
二级缓存示例:
1. 启用二级缓存:
在mybatis置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中加入一下配置
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
在Mapper.xml配置文件中添加cache标签
<cache /> <!-- 表示此mapper开启二级缓存。-->
还可以配置其他参数,如:
<cache flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true" eviction="FIFO" type=”xxxxx” />
flushInterval:刷新时间间隔,单位毫秒,不设置则没有刷新时间间隔,在执行配置了flushCache标签的sql时刷新(清空)
size:缓存原数个数,默认1024
readOnly:是否只读,默认false:mybatis将克隆一份数据返回,true:直接返回缓存数据的引用(不安全,程序如果修改,直接改了缓存项)
eviction:缓存的回收策略(LRU 、FIFO、 SOFT 、WEAK ),默认LRU
type:指定自定义缓存的全类名(实现Cache接口即可)
2. 结果集映射对象实现序列化接口
使用Mybatis二级缓存需要将sql结果集映射的pojo对象实现java.io.Serializable接口,否则将出现序列化错误。
public class Product implements Serializable{ …}
3.编写cacheMapper.xml配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.sl.mapper.CacheMapper"> <cache/>
<select id="selectProductById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.sl.po.Product" ><!-- useCache="false" 禁用二级缓存或者在Mapper接口上通过注解禁用--> select * from products where id = #{id} </select> <!-- update – 映射更新语句 --> <update id="updateProductById" parameterType="com.sl.po.Product" flushCache="true"> <!-- flushCache="true" 禁用二级缓存或者在Mapper接口上通过注解禁用--> update products set Name = #{Name},IsNew=#{IsNew} where id=#{id} </update> </mapper>
4.Mapper.java接口
public interface CacheMapper { Product selectProductById(int id); //@Options(flushCache=FlushCachePolicy.TRUE) //清空 二级缓存 int updateProductById(Product product); }
5.测试方法:
public class TestCacheMapperClient {
SqlSessionFactory factory = null; @Before public void init() throws IOException { String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); factory = builder.build(inputStream); }
//二级缓存 @Test public void testSelectProductById2() throws IOException { SqlSession session1 = factory.openSession(); CacheMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Product product = mapper1.selectProductById(1); System.out.println(product.getName()); /************同一session 共享一级缓存***************/ //CacheMapper mapper2 = session1.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); //Product product2 = mapper2.selectProductById(1); //System.out.println(product2.getName()); //执行commit 将清空一级缓存,无法情况二级缓存 session1.commit(); session1.close(); //清空二级缓存 //Mapper接口注解@Options(flushCache=FlushCachePolicy.TRUE) 或者Mapper.xml配置属性 flushCache="true" SqlSession session4 = factory.openSession(); CacheMapper mapper4 = session4.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Product up = new Product(); up.setId(1); up.setIsNew(true); up.setName("缓存测试2"); int count = mapper4.updateProductById(up); session4.commit(); session4.close(); /**********不同session实例 共享二级缓存************/ SqlSession session3 = factory.openSession(); CacheMapper mapper3 = session3.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Product product3 = mapper3.selectProductById(1); System.out.println(product3.getName()); // 关闭会话 session3.close(); } }
测试结果,上面updateProductById方法在配置sql中清空了二级缓存,所以后面mapper3.selectProductById(1)仍然执行数据库查询。
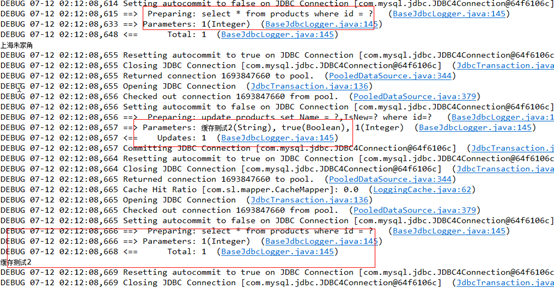
6. 禁用二级缓存
Mybatis还提供属性用于对指定的查询禁用二级缓存,在Mapper.xml配置文件中可是使用useCache=false禁止当前select使用二级缓存,即:
<select id="selectProductById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.sl.po.Product" useCache="false" ><!-- useCache="false" 禁用二级缓存或者在Mapper接口上通过注解禁用--> select * from products where id = #{id} </select>
在Mapper.Java接口中可是通过注解来禁用二级缓存,即:
@Options(useCache=false) Product selectProductById(int id);
7.缓存刷新
当mybatis执行数据更新sql语句后,DB数据与缓存数据可能已经不一致,如果不执行刷新缓存则可能出现脏读的情况,Mybatis同样提供xml配置和注解两种方式来实现缓存刷新
Xml配置形式:
<update id="updateProductById" parameterType="com.sl.po.Product" flushCache="true"> <!-- flushCache="true" 禁用二级缓存或者在Mapper接口上通过注解禁用--> update products set Name = #{Name},IsNew=#{IsNew} where id=#{id} </update>
注解形式:
@Options(flushCache=FlushCachePolicy.TRUE) //清空 二级缓存 int updateProductById(Product product);
使用Redis做Mybatis二级缓存
Mybatis默认启用二级缓存是服务器本地缓存,在程序部署到多台服务器时可能出现数据不一致的情况,这种情况下最好能有个集中式缓存来解决此问题。MyBatis的二级缓存允许自定义实现,Mybatis提供二级缓存接口,我们可以通过实现org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache接口来整合第三方缓存,比如redis、memcache等。
Demo实现步骤:
1. 添加jar包依赖
<!-- redis client --> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>${jedis.version}</version> </dependency>
2. 实现 Mybatis二级缓存org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache接口

package com.sl.redis; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig; public class RedisCache implements Cache { private Jedis redisClient = createClient(); private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); private String id; public RedisCache(final String id) { if (id == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache instances require an ID"); } this.id = id; } public String getId() { return this.id; } public int getSize() { return Integer.valueOf(redisClient.dbSize().toString()); } public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { redisClient.set(SerializeHelper.serialize(key.toString()), SerializeHelper.serialize(value)); } public Object getObject(Object key) { Object value = SerializeHelper.unserialize(redisClient.get(SerializeHelper.serialize(key.toString()))); return value; } public Object removeObject(Object key) { return redisClient.expire(SerializeHelper.serialize(key.toString()), 0); } public void clear() { redisClient.flushDB(); } public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() { return readWriteLock; } protected static Jedis createClient() { try { JedisPool pool = new JedisPool(new JedisPoolConfig(),"localhost"); return pool.getResource(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } throw new RuntimeException("初始化连接池错误"); } } package com.sl.redis; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class SerializeHelper { public static byte[] serialize(Object object) { ObjectOutputStream oos = null; ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null; try { // 序列化 baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos); oos.writeObject(object); byte[] bytes = baos.toByteArray(); return bytes; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } public static Object unserialize(byte[] bytes) { if (bytes == null) return null; ByteArrayInputStream bais = null; try { // 反序列化 bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais); return ois.readObject(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
3. 修改Mapper.xml配置文件,通过type属型指定自定义二级缓存实现 type="com.sl.redis.RedisCache"
<mapper namespace="com.sl.mapper.CacheMapper"> <cache type="com.sl.redis.RedisCache"/> <select id="selectProductById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.sl.po.Product" ><!-- useCache="false" 禁用二级缓存或者在Mapper接口上通过注解禁用--> select * from products where id = #{id} </select> <!-- update – 映射更新语句 --> <update id="updateProductById" parameterType="com.sl.po.Product" flushCache="true"> <!-- flushCache="true" 禁用二级缓存或者在Mapper接口上通过注解禁用--> update products set Name = #{Name},IsNew=#{IsNew} where id=#{id} </update> </mapper>
测试方法同上。
以上通过重写Mybatis二级缓存接口Cache类中的方法,将mybatis中默认的二级缓存空间替换成Redis。mybatis的二级缓存默认存储1024个对象(通过size可配置),且自带的二级缓存是存储在服务器本地内存的,实际开发中往往放弃直接使用默认二级缓存。使用redis 可以将数据存储到专用缓存服务器上,同时redis的高性能也保证了缓存数据的高速读取。
