Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000K
Total Submissions: 9478 Accepted: 2376
Description
Imagine you are attending your math lesson at school. Once again, you are bored because your teacher tells things that you already mastered years ago (this time he's explaining that (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2). So you decide to waste your time with drawing modern art instead.
Fortunately you have a piece of squared paper and you choose a rectangle of size n*m on the paper. Let's call this rectangle together with the lines it contains a grid. Starting at the lower left corner of the grid, you move your pencil to the upper right corner, taking care that it stays on the lines and moves only to the right or up. The result is shown on the left:
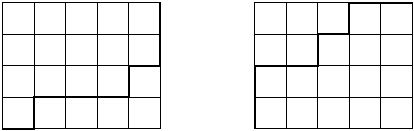 Really a masterpiece, isn't it? Repeating the procedure one more time, you arrive with the picture shown on the right. Now you wonder: how many different works of art can you produce?
Really a masterpiece, isn't it? Repeating the procedure one more time, you arrive with the picture shown on the right. Now you wonder: how many different works of art can you produce?
Input
The input contains several testcases. Each is specified by two unsigned 32-bit integers n and m, denoting the size of the rectangle. As you can observe, the number of lines of the corresponding grid is one more in each dimension. Input is terminated by n=m=0.
Output
For each test case output on a line the number of different art works that can be generated using the procedure described above. That is, how many paths are there on a grid where each step of the path consists of moving one unit to the right or one unit up? You may safely assume that this number fits into a 32-bit unsigned integer.
Sample Input
5 4
1 1
0 0
Sample Output
126
2
Source
Ulm Local 2002
//
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double CNM(unsigned int N, unsigned int M)
{
M = (M > N - M) ? N - M : M;
double ret = 1;
while(M > 0)ret *= double(N--) / double (M--);
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
unsigned int A, B;
while(scanf("%d %d", &A, &B) && !(A == 0 && B == 0))
printf("%.0lf\n",CNM(A + B, B));
return 0;
}