实现多线程共有两种方法:①继承一个Thread类;②实现Runnable、Callable接口(推荐)
一、继承Thread类实现多线程
Thread是一个线程操作的核心类,定义一个线程的主类最简单的方法就是继承Thread类,而后覆写类中的run()方法。实现如下(首先定义一个主体类,而后启动多线程即为调用Thread中的start()方法):
1 class MyThread extends java.lang.Thread{//线程主体类 2 private String title; 3 public MyThread(String title){ 4 this.title = title; 5 } 6 @Override 7 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 8 for (int x = 0; x<10; x++){ 9 System.out.println(this.title + ",x = " + x); 10 } 11 } 12 } 13 public class Thread { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 //创建线程 16 MyThread mt1 =new MyThread("A"); 17 MyThread mt2 =new MyThread("B"); 18 MyThread mt3 =new MyThread("C"); 19 //启动多线程 20 mt1.start(); 21 mt2.start(); 22 mt3.start(); 23 } 24 }
执行结果:多个线程交替执行
二、Runnable接口实现多线程
Thread类继承的缺点是单继承局限,而Runnable则没有这个缺点,其定义如下(使用的仍是Thread类的start()方法):
class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private String title;// 共10张票 public MyRunnable(String title) { this.title = title; } @Override public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 for (int x= 0; x<10; x++) { System.out.println(this.title + ",x = " + x); } } } public class TestRunnable { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程 MyThread mt1 =new MyThread("A"); MyThread mt2 =new MyThread("B"); MyThread mt3 =new MyThread("C"); //启动多线程 new java.lang.Thread(mt1).start(); new java.lang.Thread(mt2).start(); new java.lang.Thread(mt3).start(); } }
或者使用匿名内部类来定义:
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private String title;// 共10张票 3 4 public MyRunnable(String title) { 5 this.title = title; 6 } 7 @Override 8 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 9 for (int x= 0; x<10; x++) { 10 System.out.println(this.title + ",x = " + x); 11 } 12 13 } 14 } 15 public class TestRunnable { 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 new java.lang.Thread(new Runnable() { 18 @Override 19 public void run() { 20 System.out.println("Hello"); 21 } 22 }).start(); 23 } 24 }
Runnable接口可以比Thread有更好的实现数据共享的概念,即产生若干线程进行同一数据的处理操作。实现如下:
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private int ticket = 10;// 共10张票 3 @Override 4 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 5 for (int x= 0; x<20; x++) { 6 if (this.ticket > 0) 7 System.out.println("卖票,ticket:" + ",x = " + this.ticket--); 8 } 9 10 } 11 } 12 public class TestRunnable { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(); 15 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 16 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 17 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 18 } 19 }
执行结果:(三个线程之间的数据实现了共享)
卖票,ticket:,x = 10 卖票,ticket:,x = 8 卖票,ticket:,x = 9 卖票,ticket:,x = 6 卖票,ticket:,x = 7 卖票,ticket:,x = 4 卖票,ticket:,x = 5 卖票,ticket:,x = 1 卖票,ticket:,x = 2 卖票,ticket:,x = 3
三、Collable实现多线程
由于Runnable方法中的多线程没有返回值,难以满足某些需要一些返回值的程序,因此使用Collable来实现多线程。实现过程如下:(①定义Collable线程主体类②使用Thread中start方法启动多线程)
1 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 2 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 3 4 class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{//线程主体类 5 public String call() throws Exception{ 6 for (int x = 20; x > 0; x--) 7 System.out.println("卖票:" + x); 8 return "票卖完了……"; 9 } 10 } 11 public class TestCallable { 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 13 FutureTask<String> task = new FutureTask<String>(new MyCallable()); 14 new java.lang.Thread(task).start();//启动多线程 15 System.out.println(task.get()); 16 17 } 18 }
四、多线程的命名和取得
Thread类提供的线程名称的操作方法:
|
NO. |
方法 |
类型 |
描述 |
|
1 |
Public Thread(Runnable target,String name) |
构造 |
创建线程时设置好名字 |
|
2 |
Public final void setName(String name) |
普通 |
设置线程名字 |
|
3 |
Public final String getName() |
普通 |
取得线程名字 |
取得当前正在执行的线程的对象:public static Thread currentThread()
取得线程姓名执行如下:
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private int ticket = 10;// 共10张票 3 @Override 4 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 5 for (int x= 0; x<10; x++) 6 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",x = " + x);//取得线程名字 7 } 8 } 9 public class TestRunnable { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(); 12 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 13 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 14 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"有名字").start(); 15 } 16 }
执行结果:
Thread-0,x = 0 有名字,x = 0 有名字,x = 1 有名字,x = 2 Thread-0,x = 1 有名字,x = 3 Thread-1,x = 0 有名字,x = 4 Thread-0,x = 2 有名字,x = 5 Thread-1,x = 1 有名字,x = 6 Thread-0,x = 3 有名字,x = 7 Thread-1,x = 2 有名字,x = 8 Thread-0,x = 4 有名字,x = 9 Thread-1,x = 3 Thread-0,x = 5 Thread-1,x = 4 Thread-0,x = 6 Thread-1,x = 5 Thread-0,x = 7 Thread-1,x = 6 Thread-0,x = 8 Thread-1,x = 7 Thread-0,x = 9 Thread-1,x = 8 Thread-1,x = 9
注:设置名字不能重复,同时中间不能修改
主方法直接调用和启动线程调用run的区别:
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private int ticket = 10;// 共10张票 3 @Override 4 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 5 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName()); 6 } 7 } 8 public class TestRunnable { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(); 11 mt.run();//直接通过对象调用 12 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start();//通过线程调用run 13 } 14 }
执行结果:
main Thread-0
可以知道:主方法本身就是一个线程,所有的线程都是通过主线程创建并启动的
五、线程休眠
线程休眠是指让线程暂停执行一段时间后再次执行,方法:public static void sleep(long millis)throws InterruptedException,休眠时间使用毫秒作为单位。休眠操作实现如下:
1 class MySleep implements Runnable{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for (int x = 0; x < 20; x++){ 5 try { 6 java.lang.Thread.sleep(1000);//休眠一秒 7 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",x = " + x); 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 public class TestSleep { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 MySleep mt = new MySleep(); 17 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 18 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 19 new java.lang.Thread(mt).start(); 20 } 21 }
注:并不是三个一起执行的,而是代码依次进入run()方法,并发执行
六、线程的优先级
优先级越高越可能先执行,但不是一定先执行。
设置优先级方法:public final void setPriority(int newPriority)
取得优先级方法:public final int getPriority
设置优先级可以通过Thread类的几个常量来确定:
最高优先级:public static final int MAX_PRIORITY、10(常量的值)
中等优先级:public static final int NORM_PRIORITY、5
最低优先级:public static final int MIN_PRIORITY、1
设置优先级实现如下:
1 class MyPrority implements Runnable{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for (int x = 0; x < 2; x++){ 5 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",x = " + x); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class TestSetPrior { 10 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 11 //查看主方法的优先级 12 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); 13 MyPrority mt = new MyPrority(); 14 java.lang.Thread t1 = new java.lang.Thread(mt,"线程A"); 15 java.lang.Thread t2 = new java.lang.Thread(mt,"线程B"); 16 java.lang.Thread t3 = new java.lang.Thread(mt,"线程C"); 17 t1.setPriority(java.lang.Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 18 t2.setPriority(java.lang.Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 19 t3.setPriority(java.lang.Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); 20 t1.start(); 21 t2.start(); 22 t3.start(); 23 } 24 }
执行结果为:可以知道主方法的优先级为中等优先级,最先执行的为B(最高优先级),然后是C(中等优先级),最后才是C(最低优先级)
5 线程B,x = 0 线程C,x = 0 线程B,x = 1 线程C,x = 1 线程A,x = 0 线程A,x = 1
七、线程的同步
线程的同步与死锁是为了解决多个线程同时共享一个资源时所需要的手段,如买票系统,当不存在线程的同步与死锁时,其实现如下:
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private int ticket = 10;// 共10张票 3 @Override 4 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 5 for (int x= 0; x < 20; x++) { 6 if (this.ticket > 0){//还剩有票 7 try{ 8 java.lang.Thread.sleep(200);// 模拟网络延迟 9 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName() + 13 "卖票,ticket = " + this.ticket--); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 public class TestRunnable { 19 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 20 MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(); 21 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子A").start(); 22 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子B").start(); 23 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子C").start(); 24 } 25 }
执行结果:
票贩子A卖票,ticket = 10 票贩子C卖票,ticket = 8 票贩子B卖票,ticket = 9 票贩子A卖票,ticket = 7 票贩子B卖票,ticket = 5 票贩子C卖票,ticket = 6 票贩子A卖票,ticket = 4 票贩子B卖票,ticket = 3 票贩子C卖票,ticket = 2 票贩子A卖票,ticket = 1 票贩子B卖票,ticket = 0 票贩子C卖票,ticket = -1
可知票数会出现负数的情况,明显不符合实际情况,这种情况称之为不同步操作
为了解决上述情况,需要对线程进行同步,线程同步也就是不允许线程一起进入方法中执行,而是按照顺序一个个进入执行,详细解释如下图:
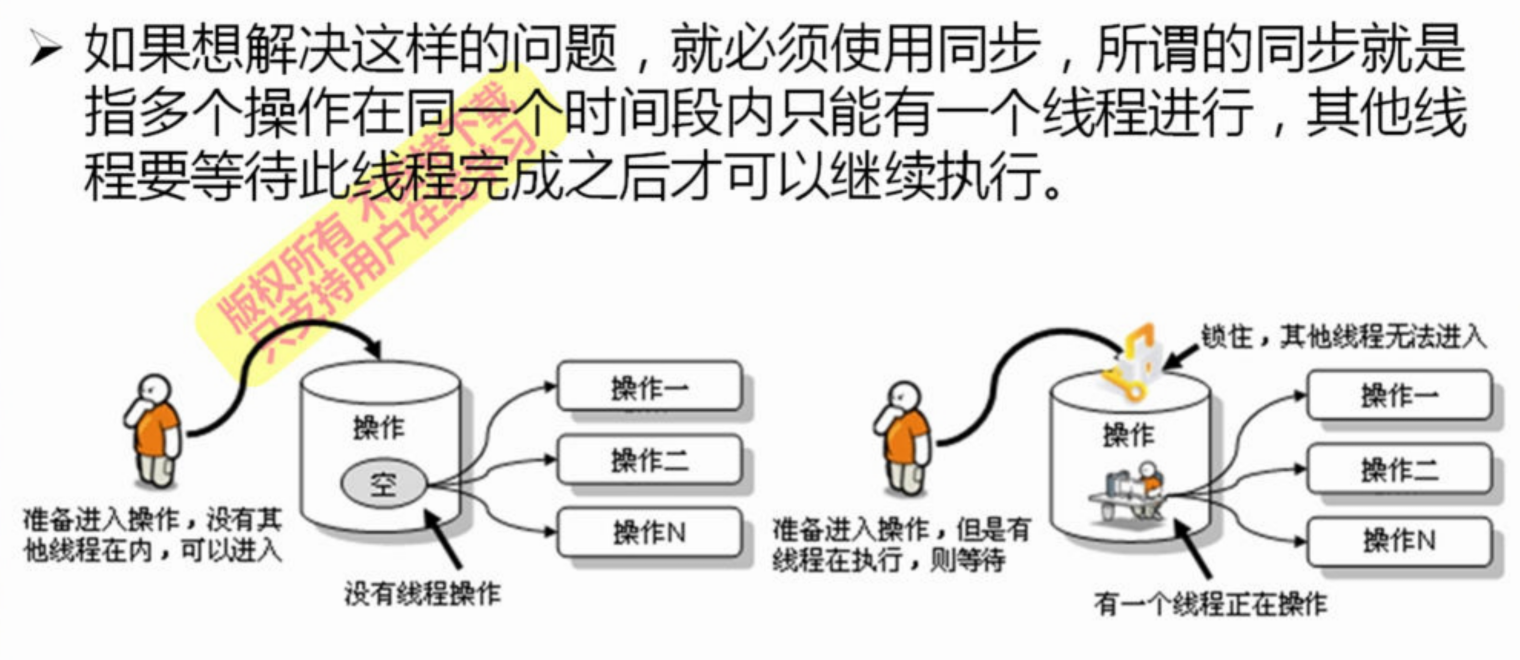
为了实现上述功能,可以使用synchronized关键字来实现,共有两个模式:同步代码块、同步方法
1、同步代码块
使用同步代码块必须设置一个要锁定的对象,一般锁定的对象是当前对象:this,实现如下:
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private int ticket = 1000;// 一共需要卖出去的票 3 @Override 4 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 5 for (int x= 0; x < 2000; x++) { 6 //在同一时刻,只允许一个线程进入并操作,其他线程需要等待 7 synchronized (this){//为程序逻辑上锁 8 if (this.ticket > 0){//还剩有票 9 try{ 10 java.lang.Thread.sleep(200);// 模拟网络延迟 11 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName() + 15 "卖票,ticket = " + this.ticket--); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 public class TestRunnable { 22 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 23 MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(); 24 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子A").start(); 25 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子B").start(); 26 new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子C").start(); 27 } 28 }
该方法是在方法中通过synchronized关键字来进行拦截,也就是仍然有多个线程进入方法,而后在方法中拦截排序。
2、同步方法
1 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 private int ticket = 1000;// 一共需要卖出去的票 3 @Override 4 public void run() {//所有的线程从此处执行 5 for (int x = 0; x < 2000; x++) { 6 this.sale();//调用方法 7 } 8 } 9 public synchronized void sale(){ 10 if (this.ticket > 0){//还剩有票 11 try{ 12 java.lang.Thread.sleep(200);// 模拟网络延迟 13 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 System.out.println(java.lang.Thread.currentThread().getName() + 17 "卖票,ticket = " + this.ticket--); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 public class TestRunnable { 23 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 24 MyRunnable mt = new MyRunnable(); 25 java.lang.Thread t1 = new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子A"); 26 java.lang.Thread t2 = new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子B"); 27 java.lang.Thread t3 = new java.lang.Thread(mt,"票贩子C"); 28 t1.setPriority(java.lang.Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//设置优先级为最低 29 t1.start(); 30 t2.start(); 31 t3.start(); 32 } 33 }
同步方法相当于同步代码块执行速度会慢一些
八、线程的死锁
同步的含义是一个线程等待另一个线程执行完毕后才可以执行,但是若所有的线程都在彼此等待,那么就会造成死锁。死锁一旦出现后就会造成整个程序实际上的中断,因此过多的同步会容易造成死锁,因此增加同步要谨慎。
九、生产者消费者模型
生产者和消费者要用到多线程前面的所有知识,例如需要用到多线程来实现生产者的产生和消费者的消耗的同时发生;用到synchronized来解决生产者消费者中不同步的问题。此外,还需要解决重复进行取出(get)、设置(set)的操作,需要增加等待唤醒机制,其使用的方法如下:
|
NO. |
方法 |
类型 |
描述 |
|
1 |
Public final void wait() throws InterruptedException |
普通 |
等待、死等(无限期等待) |
|
2 |
Public final void notify() |
普通 |
唤醒第一个等待线程 |
|
3 |
Public final void notifyAll() |
普通 |
唤醒全部等待线程,优先级高的线程可能优先执行 |
实现代码如下:
1 class Provider implements Runnable{//生产者 2 private Data data; 3 public Provider(Data data){ 4 this.data = data; 5 } 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 for (int x = 0; x < 50; x++){ 9 if (x % 2 == 0){ 10 this.data.set("老李","是个好人"); 11 }else { 12 this.data.set("民族败类","老方"); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 class Consumer implements Runnable{//消费者 18 private Data data; 19 public Consumer(Data data) { 20 this.data = data; 21 } 22 @Override 23 public void run() { 24 for (int x = 0; x < 50; x++){ 25 this.data.get(); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 class Data{//中转站,负责数据保存 30 private String title; 31 private String note; 32 //flag=true表示允许生产但不允许消费 33 //flag=false表示不允许生产允许消费 34 private boolean flag = true; 35 public synchronized void get() { 36 if (this.flag == false){//已经生产了不允许重复生产,需要等待 37 try { 38 super.wait();//等待 39 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 try { 44 java.lang.Thread.sleep(10); 45 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 System.out.println(this.title + " = " +this.note); 49 this.flag = false;//表示已经生产过,不允许生产 50 super.notify();//唤醒等待线程 51 } 52 public synchronized void set(String title,String note){ 53 if (this.flag == true){//表示不允许取走 54 try { 55 super.wait(); 56 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 } 59 } 60 this.title = title; 61 try { 62 java.lang.Thread.sleep(50); 63 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 this.note = note; 67 this.flag = true;//允许生产 68 super.notify(); 69 } 70 } 71 public class TestDemo { 72 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 73 Data data = new Data(); 74 new java.lang.Thread(new Provider(data)).start(); 75 new java.lang.Thread(new Consumer(data)).start(); 76 } 77 }
在上述代码中,首先设置Provider作为生产者,用来设置数据提供数据,Consumer作为消费者,用来将生产的数据显示出来,而Data类则是用来保存生产者生产的数据,提供中转的作用。在Data类中,为了让生产者和消费者两个类之间的操作能够同步,使用synchronized来进行锁止,来防止生产者和消费者同时执行;此外,为了防止有多余的设置取出操作,通过设置flag参数来进行限制,当生产者生产了后不允许生产者再次生产,必须等待消费者消费后修改flag参数方可唤醒生产者再次生产,此时消费者进行等待。
wait和sleep的区别在于:wait是Object类中的方法,只能通过notify()、notifyAll()来进行唤醒;sleep是Thread中的方法,只能等待一段时间后自动唤醒。