转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kerrycode/p/4595797.html#undefined
在Linux系统中,为了避免主机时间因为在长时间运行下所导致的时间偏差,进行时间同步(synchronize)的工作是非常必要的。Linux系统下,一般使用ntp服务来同步不同机器的时间。NTP 是网络时间协议(Network Time Protocol)的简称,干嘛用的呢?就是通过网络协议使计算机之间的时间同步化。
系统时间与硬件时间
在展开Linux系统时间同步前,我们必须先了解一些概念:在一台计算机上我们有两个时钟:一个称之为硬件时间时钟(RTC Real Time Clock,又叫实时时钟),还有一个称之为系统时钟(System Clock)。
硬件时钟是指嵌在主板上的特殊的电路, 它的存在就是平时我们关机之后还可以计算时间的原因。RTC的英文全称是Real-Time Clock,翻译过来是实时时钟芯片. RTC是PC主板上的晶振及相关电路组成的时钟电路的生成脉冲主板上的晶振及相关电路组成的时钟电路的生成脉冲,RTC经过8254电路的变频产生一个频率较低一点的OS(系统)时钟TSC,系统时钟每一个cpu周期加一周期加一,每次系统时钟在系统初起时通过RTC初始化。8254本身工作也需要有自己的驱动时钟(PIT)
系统时钟就是操作系统的kernel所用来计算时间的时钟. 它从1970年1月1日00:00:00 UTC时间到目前为止秒数总和的值。在Linux下系统时间在开机的时候会和硬件时间同步(synchronization),之后也就各自独立运行了
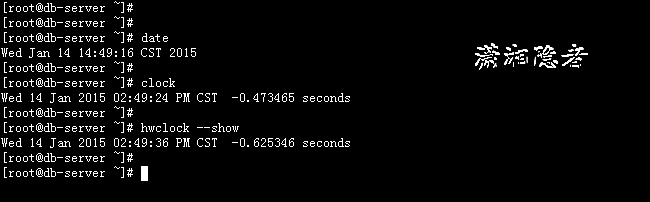
默认情况下,系统时间和硬件时间,并不会自动同步。在Linux运行过程中,系统时间和硬件时间以异步的方式运行,互不干扰。硬件时间的运行,是靠BIOS电池来维持,而系统时间,是用CPU tick来维持的。这也是系统时间长时间运行时会产生时间偏差的原因,我小时候有买过电子手表,那个时候的电子产品还相当不靠谱,电子手表走着走着就和新闻联播里面的时间对不上了,总会查那么几分钟甚至几十分钟,那个时候最苦恼的事情就是需要手动调整电子手表的时间,这也算是时间同步的一种吧!系统时间可以通过date命令查看,硬件时间可以通过clock或hwclock命令查看。我们来看看系统时间和硬件时间吧。
[root@db-server ~]# date
Wed Jan 14 14:49:16 CST 2015
[root@db-server ~]#
[root@db-server ~]# clock
Wed 14 Jan 2015 02:49:24 PM CST -0.473465 seconds
[root@db-server ~]#
[root@db-server ~]# hwclock --show
Wed 14 Jan 2015 02:49:36 PM CST -0.625346 seconds
[root@db-server ~]#
[root@db-server ~]#
如下所示,我们修改了系统时间,将时间修改为2015-01-14 08:00:00,然后我们查看硬件时间就可以发现,系统时间和硬件时间是异步运行。互补干扰。
[root@db-server ~]# date -s "2015-01-14 08:00:00"
Wed Jan 14 08:00:00 CST 2015
[root@db-server ~]# date
Wed Jan 14 08:00:02 CST 2015
[root@db-server ~]# clock
Wed 14 Jan 2015 02:52:54 PM CST -0.045672 seconds
[root@db-server ~]#
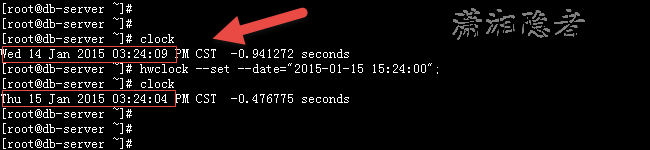
硬件时间的设置,可以用hwclock或者clock命令。其中,clock和hwclock用法相近,只用一个就行,只不过clock命令除了支持x86硬件体系外,还支持Alpha硬件体系。
设置硬件时间
[root@db-server ~]# clock
Wed 14 Jan 2015 03:24:09 PM CST -0.941272 seconds
[root@db-server ~]# hwclock --set --date="2015-01-15 15:24:00";
[root@db-server ~]# clock
Thu 15 Jan 2015 03:24:04 PM CST -0.476775 seconds
[root@db-server ~]#
[root@db-server ~]# clock --help
hwclock - query and set the hardware clock (RTC)
Usage: hwclock [function] [options...]
Functions:
--help show this help
--show read hardware clock and print result
--set set the rtc to the time given with --date
--hctosys set the system time from the hardware clock
--systohc set the hardware clock to the current system time
--adjust adjust the rtc to account for systematic drift since
the clock was last set or adjusted
--getepoch print out the kernel's hardware clock epoch value
--setepoch set the kernel's hardware clock epoch value to the
value given with --epoch
--version print out the version of hwclock to stdout
Options:
--utc the hardware clock is kept in coordinated universal time
--localtime the hardware clock is kept in local time
--directisa access the ISA bus directly instead of /dev/rtc
--badyear ignore rtc's year because the bios is broken
--date specifies the time to which to set the hardware clock
--epoch=year specifies the year which is the beginning of the
hardware clock's epoch value
--noadjfile do not access /etc/adjtime. Requires the use of
either --utc or --localtime
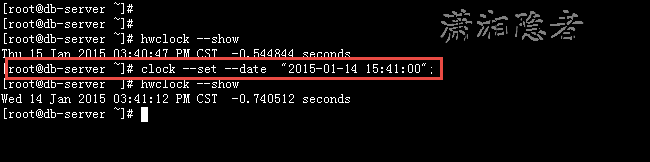
[root@db-server ~]# hwclock --show
Thu 15 Jan 2015 03:40:47 PM CST -0.544844 seconds
[root@db-server ~]# clock --set --date "2015-01-14 15:41:00";
[root@db-server ~]# hwclock --show
Wed 14 Jan 2015 03:41:12 PM CST -0.740512 seconds
[root@db-server ~]#
系统时间和硬件时间的同步
我们可以使用hwclock --systohc把系统时间设置成硬件时间,如下所示(我们先修改系统时间,手工造成系统时间与硬件时间不一致)
[root@db-server ~]# date -s "2015-01-14 15:53";
Wed Jan 14 15:53:00 CST 2015
[root@db-server ~]# date
Wed Jan 14 15:53:03 CST 2015
[root@db-server ~]# hwclock --systohc
[root@db-server ~]# date
Wed Jan 14 15:53:35 CST 2015
[root@db-server ~]# hwclock --show
Wed 14 Jan 2015 03:53:36 PM CST -0.149835 seconds
我们也可以把硬件时间设置成系统时间:运行以下命令即可
hwclock --hctosys
时间同步设置
网络时间协议NTP(Network Time Protocol)是用于互联网中时间同步的标准互联网协议。NTP的用途是把计算机的时间同步到某些时间标准。目前采用的时间标准是世界协调时UTC(Universal Time Coordinated)。NTP的主要开发者是美国特拉华大学的David L. Mills教授。关于NTP概念,深入的话,都足足可以讲一篇。我们暂且只是关注如何同步时间。要同步时间,就必须有一个精确地NTP Server,关于NTP Server可以参考NTP的官方网站http://www.pool.ntp.org,在这上面我们可以找到离我们城市最近的NTP Server
同步世界我们一般使用ntpd或ntpdate这两个命令,那ntpd与ntpdate在更新时间时有什么区别?ntpd不仅仅是时间同步服务器,它还可以做客户端与标准时间服务器进行同步时间,而且是平滑同步,并非ntpdate立即同步,在生产环境中慎用ntpdate,也正如此两者不可同时运行
一个是校准时间,一个是调整时间。也就是说ntpd在实际同步时间时是一点点的校准过来时间的,最终把时间慢慢的校正对。而ntpdate不会考虑其他程序是否会阵痛,直接调整时间。
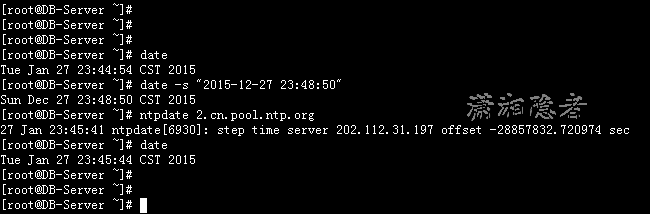
如下所示,我们首先修改系统时间,然后使用ntpdate命令同步系统时间。
[root@DB-Server ~]# date
Tue Jan 27 23:44:54 CST 2015
[root@DB-Server ~]# date -s "2015-12-27 23:48:50"
Sun Dec 27 23:48:50 CST 2015
[root@DB-Server ~]# ntpdate 2.cn.pool.ntp.org
27 Jan 23:45:41 ntpdate[6930]: step time server 202.112.31.197 offset -28857832.720974 sec
[root@DB-Server ~]# date
Tue Jan 27 23:45:44 CST 2015
但是如果cpu tick有问题,这类调整往往很难一次性解决问题,所以必须结合cron命令来彻底根治这个,例如下面cron命令。
*/30 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 192.168.7.161 1>/dev/null 2>&1
关于ntpd最好单独一章介绍一下如何配置ntpd。在此不做详细介绍。
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/suer0101/article/details/7868813
http://blog.csdn.net/sjx800688/article/details/7010979
http://hoya120.blog.163.com/blog/static/520294792010612103319272/
如果你真心觉得文章写得不错,而且对你有所帮助,那就不妨小小打赏一下吧,如果囊中羞涩,不妨帮忙“推荐"一下,您的“推荐”和”打赏“将是我最大的写作动力!
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接.