Description
给定一个 (n) 个点、 (m) 条边的带权无向图,其中有 (s) 个点是加油站。
每辆车都有一个油量上限 (b) ,即每次行走距离不能超过 (b) ,但在加油站可以补满。
(q) 次询问,每次给出 (x,y,b) ,表示出发点是 (x) ,终点是 (y) ,油量上限为 (b) ,且保证 (x) 点和 (y) 点都是加油站,请回答能否从 (x) 走到 (y) 。
Input
第一行包含三个正整数 (n,s,m(2le sle nle 200000,1le mle 200000)) ,表示点数、加油站数和边数。
第二行包含 (s) 个互不相同的正整数 $c[1],c[2],cdots c[s] (1le c[i]le n) $ ,表示每个加油站。
接下来 (m) 行,每行三个正整数 (u[i],v[i],d[i](1le u[i],v[i]le n,u[i] e v[i],1le d[i]le 10000)) ,表示 (u[i]) 和 (v[i]) 之间有一条长度为 (d[i]) 的双向边。
接下来一行包含一个正整数 (q(1le qle 200000)) ,表示询问数。
接下来 (q) 行,每行包含三个正整数 (x[i],y[i],b[i](1le x[i],y[i]le n,x[i] e y[i],1<le b[i]le 2 imes 10^9)) ,表示一个询问。
Output
输出 (q) 行。第 (i) 行输出第i个询问的答案,如果可行,则输出 (mathrm{TAK}) ,否则输出 (mathrm{NIE}) 。
Sample
Sample Input
6 4 5
1 5 2 6
1 3 1
2 3 2
3 4 3
4 5 5
6 4 5
4
1 2 4
2 6 9
1 5 9
6 5 8
Sample Output
TAK
TAK
TAK
NIE
Solution
真是一道结论诡好题。
大家肯定知道,不是加油站的点是废点。那加油站点该怎么重新建图呢?
来看一个图。红点表示加油站,黑点是废点。
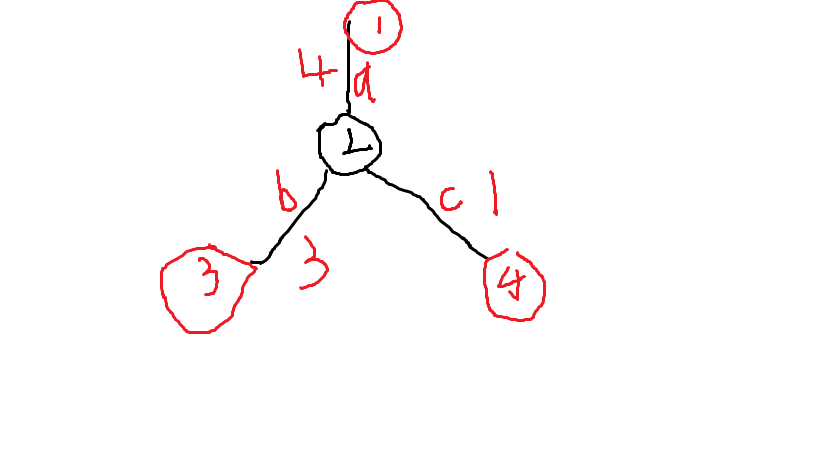
从 (1) 到 (3) 走简单路径会至少需要 (7) 的油量,而从 (1) 到 (4) 再到 (3) 则只需要准备 (5) 的油量就可以了。这是因为 $$c<a 且 c<b $$ 所以 $$c+b<a+b 且c+a<b+a$$ 于是我们就得到了结论
- 从当前节点到最近的加油站再到其它的加油站不会更差
那么就可以多源最短路,最小生成树判断连通性就可以了。
具体细节见代码。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 400011
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
inline int read() {
int x = 0, flag = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (!(ch ^ '-')) flag = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (isdigit(ch)) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); return x * flag;
}
int n, s, m, C[N], head[N], tot = 1, cnt, dis[N], near[N], fa[N];
int find(int x) { return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); }
queue<int> q;
bool inq[N], ans[N];
struct edge { int v, w, next; }e[N];
inline void add(int u, int v, int w) { e[++tot].v = v, e[tot].w = w, e[tot].next = head[u], head[u] = tot; }
struct edgeData {
int u, v, w;
edgeData(int _u = 0, int _v = 0, int _w = 0):u(_u), v(_v), w(_w) {}
bool operator < (const edgeData& b) const { return w < b.w; }
}edt[N];
struct query {
int id, S, T, d;
bool operator < (const query& b) const { return d < b.d; }
}qu[N];
void spfa() {
rep(i, 1, n) dis[i] = 0x7fffffff;
rep(i, 1, s) q.push(C[i]), inq[C[i]] = 1, dis[C[i]] = 0, near[C[i]] = C[i];
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop(), inq[u] = 0;
for (int i = head[u], v; i; i = e[i].next) if (dis[v = e[i].v] > dis[u] + e[i].w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + e[i].w, near[v] = near[u];
if (!inq[v]) q.push(v), inq[v] = 1;
}
}
rep(u, 1, n) for (int i = head[u], v; i; i = e[i].next) if (near[u] ^ near[v = e[i].v])
edt[++cnt] = edgeData(near[u], near[v], dis[u] + dis[v] + e[i].w);
sort(edt + 1, edt + 1 + cnt);
}
int main() {
n = read(), s = read(), m = read();
rep(i, 1, n) fa[i] = i;
rep(i, 1, s) C[i] = read();
rep(i, 1, m) { int u = read(), v = read(), w = read(); add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); }
spfa();
int q = read();
rep(i, 1, q) qu[i].S = read(), qu[i].T = read(), qu[i].d = read(), qu[i].id = i;
sort(qu + 1, qu + 1 + q);
int pos = 1;
rep(i, 1, q) {
while (pos <= cnt && edt[pos].w <= qu[i].d) {
int x = find(edt[pos].u), y = find(edt[pos].v);
if (x ^ y) fa[x] = y;
pos++;
}
ans[qu[i].id] = (find(qu[i].S) == find(qu[i].T));
}
rep(i, 1, q) puts(ans[i] ? "TAK" : "NIE");
return 0;
}