实验2-1 输入3个数,并按由大到小的顺序输出。
实验要求:
编写一个C程序,输入3个数,并按由大到小的顺序输出。

源码:
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
int a,b,c,t;
printf("请输入三个整数:");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
if(a<b){
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
if(b>c){
printf("%d\t%d\t%d\n",a,b,c);
}
else if(c>a){
printf("%d\t%d\t%d\n",c,a,b);
}
else{
printf("%d\t%d\t%d\n",a,c,b);
}
}

实验2-2 从键盘上输入x的值,并根据计算输出y的值
实验要求:从键盘上输入x的值,并根据计算输出y的值
提示:
- 使用数据函数需要#include <math.h>
- 开方函数:sqrt(x)
- 绝对值函数:fabs(x)
源码:
# include <stdio.h>
# include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
double x, y;
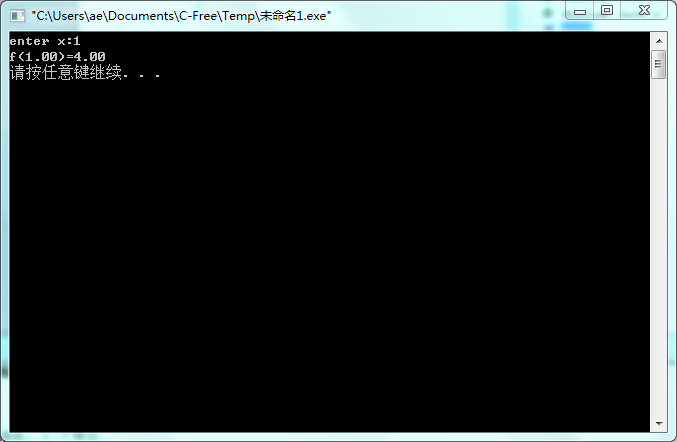
printf("enter x:");
scanf("%lf", &x);
if (x >4){
y = sqrt(x-4);
}
else if (x <-5){
y =fabs(x);
}
else{
y = x+3;
}
printf("f(%.2f)=%.2f\n",x,y);
return 0;
}
实验结果:


实验2-3从键盘上输入一个字母,如果是小写字母,将其转换成大写字母并输出。
实验要求:从键盘上输入一个字母,如果是小写字母,将其转换成大写字母并输出。
提示:
- 输入字符给变量c
char c;
方法一:c = getchar();
方法二:scanf("%c",&c);
- 输出字符变量c
方法一:putchar(c);
方法二:printf("%c",c);
程序源码#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char c;
printf("输入一个字母:");
scanf("%c",&c);
printf("%c\n",c-32);
}
运行结果抓图

实验2-4从键盘上输入x的值,并根据计算输出y的值
实验要求:从键盘上输入x的值,并根据计算输出y的值
程序源码
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float x,y;
scanf("%f",&x);
if(x<1)
y=x;
else if(x>=1 && x<10)
y=2*x-1;
else
y=3*x-11;
printf("%f",y);
return 0;
}
运行结果抓图



实验2-5 给出一个百分制的成绩,要求出成绩等级’A’、’B’、’C’、’D’、’E’,其中90分以上输出’A’,80~89输出’B’,70~79输出’C’,60~69输出’D’,60分以下输出’E’。
实验要求:
给出一个百分制的成绩,要求出成绩等级’A’、’B’、’C’、’D’、’E’,其中90分以上输出’A’,80~89输出’B’,70~79输出’C’,60~69输出’D’,60分以下输出’E’。
提示:
本实验要求同学们采用两种方法来完成:
方法一:使用if语句完成
方法二:使用switch语句完成。
程序源码
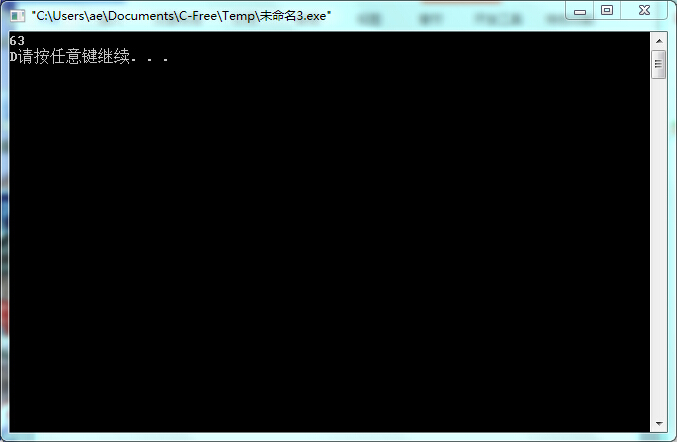
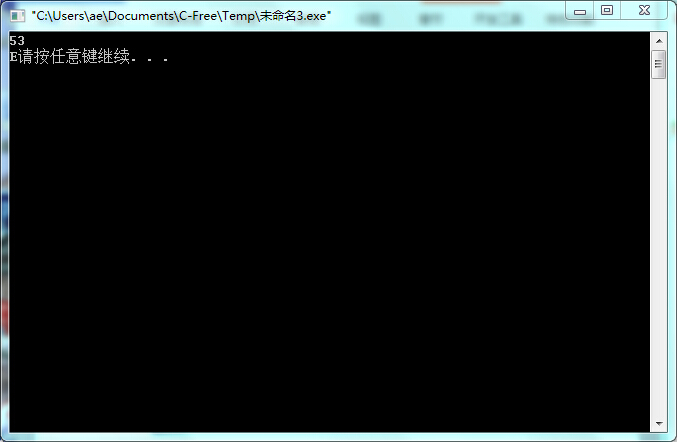
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float a;
scanf("%f",&a);
if(a>=90)
printf("A");
else if(a>=80 && a<90)
printf("B");
else if(a>=70 && a<80)
printf("C");
else if(a>=60 && a<70)
printf("D");
else
printf("E");
return 0;
}
运行结果抓图



实验心得
每个语言程序都有自己的独特的特点,都需要我们细心的去完成,虽然各不相同,但还是会有一些相似之处值得我们去和其他程序去参考,只要我们足够细心,有耐心,大脑思路清晰,就一定能够完成程序的设计。对于我来说可能还是不太熟悉,希望以后会慢慢的更加了解。