水。。。。。。。。
Problem A: 第一个类
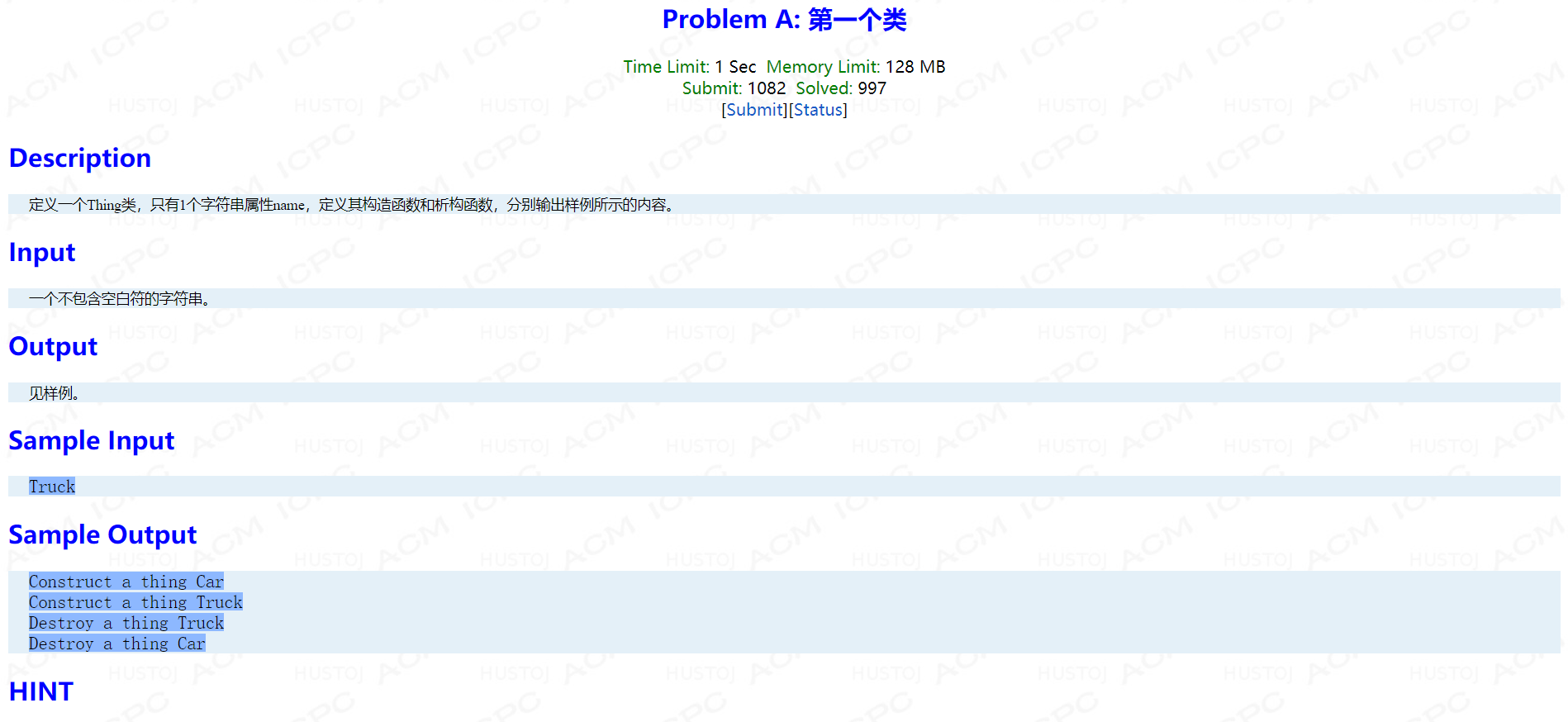
int main() { Thing A("Car"); string str; cin>>str; Thing B(str); return 0; }
考点:类的基本使用
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Thing { string name; public: Thing(string _name):name(_name){cout << "Construct a thing " << name << endl; } Thing(const Thing &b):name(b.name){cout << "Construct a thing " << name << endl;}; ~Thing() { cout << "Destroy a thing " << name << endl; } };
Problem B: 还会用继承吗?
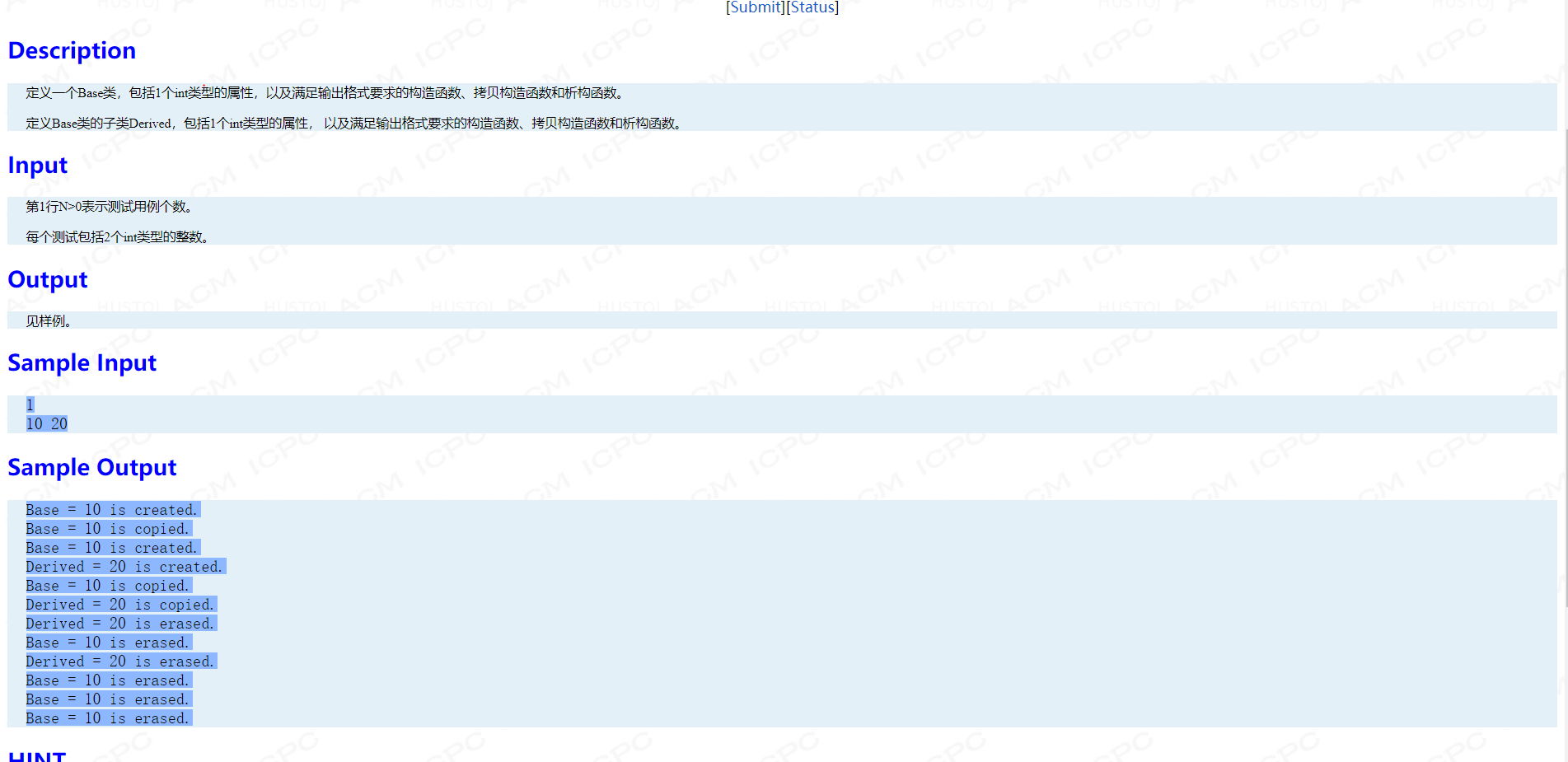
main函数:
int main() { int cases, data1, data2; cin>>cases; for (int i = 0; i < cases; i++) { cin>>data1>>data2; Base base1(data1), base2(base1); Derived derived1(data1, data2), derived2(derived1); } }
考点:类的继承,派生类拷贝构造函数的初始化
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Base { int num; public: Base(){}; Base(int _num):num(_num) { cout << "Base = " << num << " is created." << endl; } Base(const Base &b):num(b.num) { cout << "Base = " << num << " is copied." << endl; } ~Base() { cout << "Base = " << num << " is erased." << endl; } }; class Derived:public Base { int n; public: Derived(int _num,int _n):Base(_num),n(_n){ cout << "Derived = " << n << " is created." << endl; } Derived(const Derived&b):Base(b),n(b.n) { cout << "Derived = " << n << " is copied." << endl; } ~Derived() { cout << "Derived = " << n << " is erased." << endl; } };
Problem C: 一切皆对象
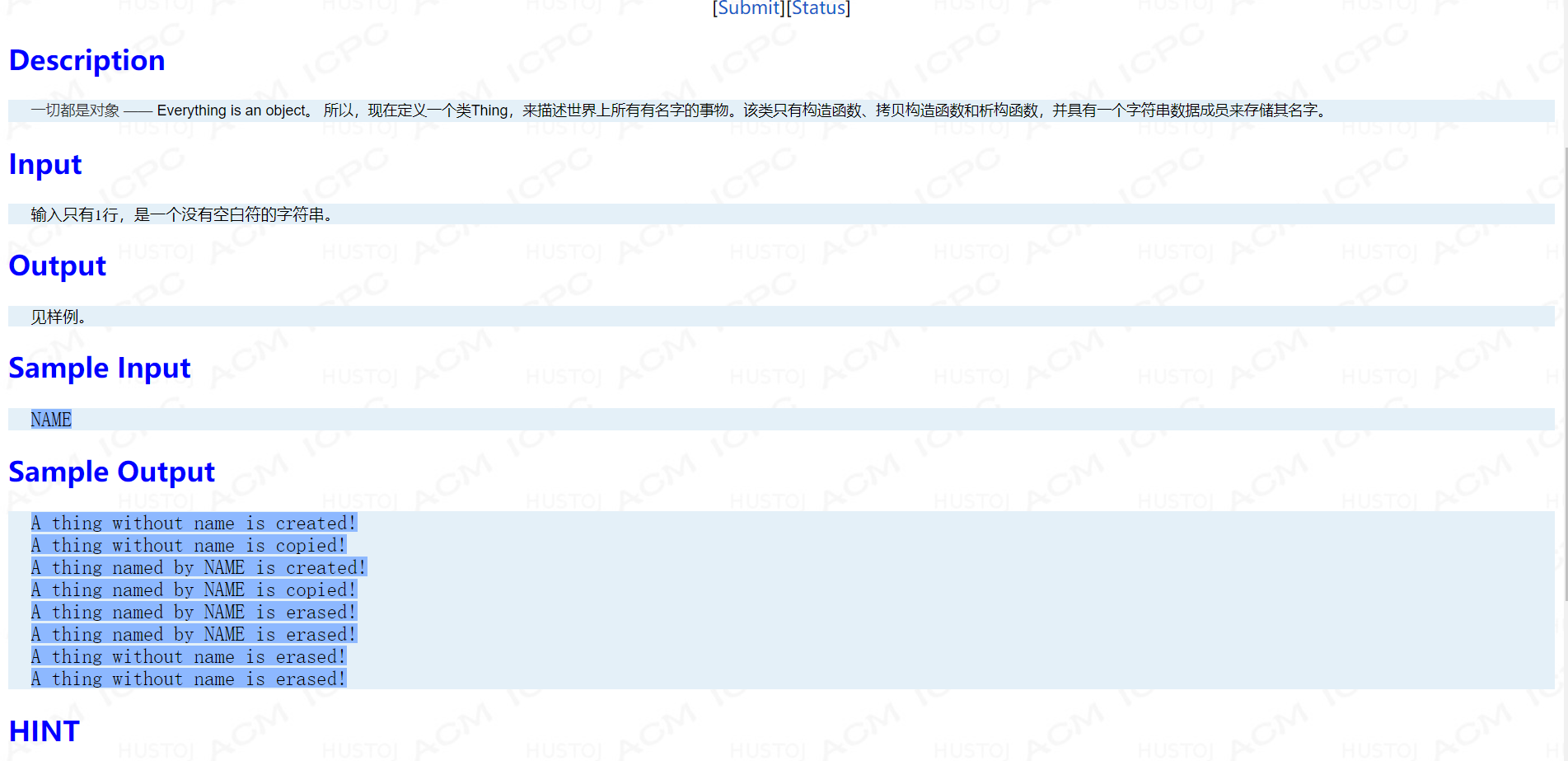
main 函数:
int main() { string name; Thing Thing1, Thing2(Thing1); cin>>name; Thing Thing3(name); Thing Thing4(Thing3); return 0; }
细节题,需要特判串为空的情况。
考点:类的基本使用
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Thing { string name; public: Thing() { cout << "A thing without name is created!" << endl; } Thing(string _name):name(_name) { if(name=="") cout << "A thing without name is created!" << endl; else cout << "A thing named by " << name << " is created!" << endl; } Thing(const Thing&b):name(b.name) { if(name=="") cout << "A thing without name is copied!" << endl; else cout << "A thing named by " << name << " is copied!" << endl; } ~Thing() { if(name=="") cout << "A thing without name is erased!" << endl; else cout << "A thing named by " << name << " is erased!" << endl; } };
Problem D: 给我一台计算机吧!
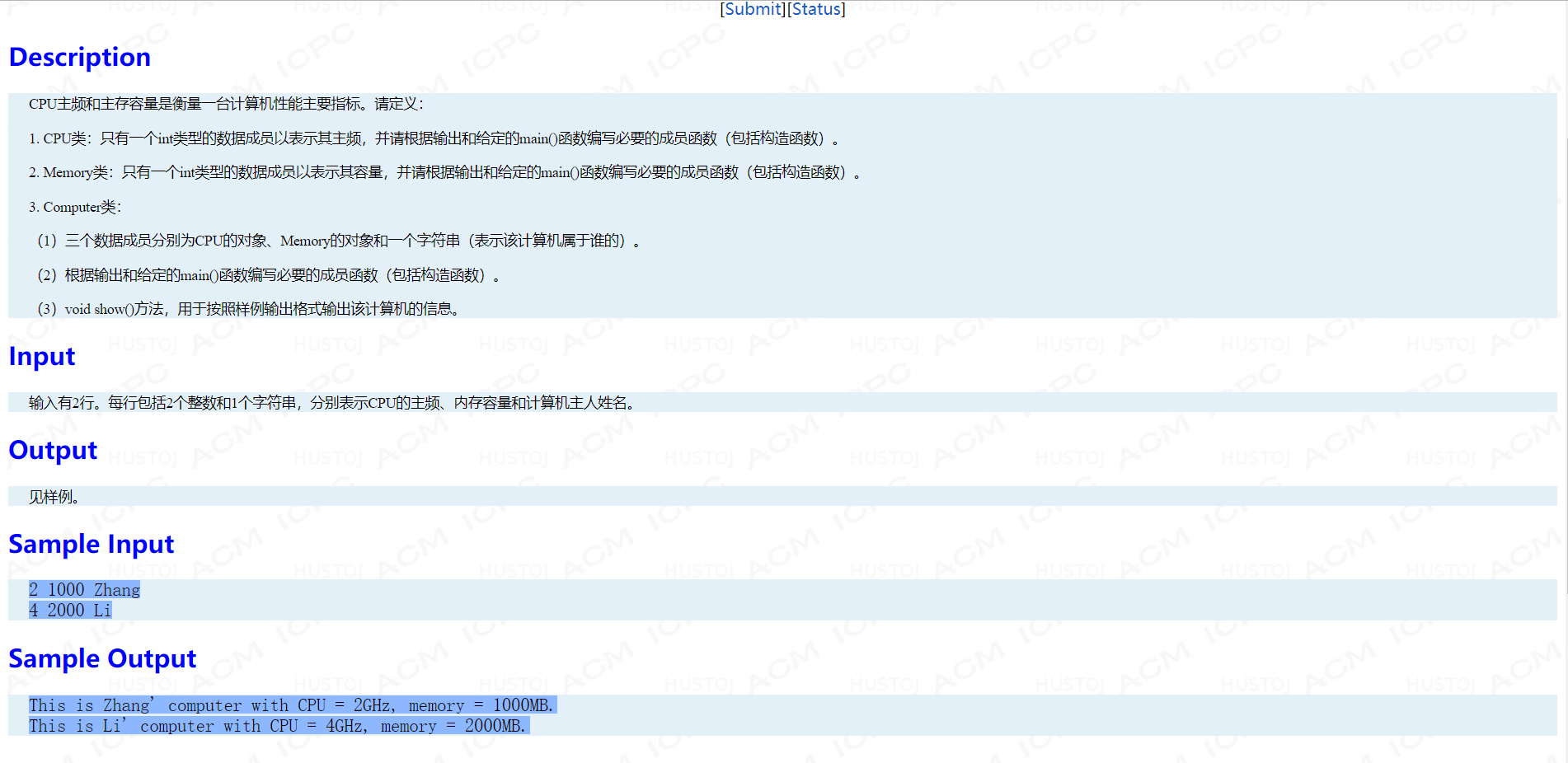
main函数:
int main() { int c, m; string n; cin>>c>>m>>n; CPU cpu(c); Memory mem(m); Computer com1(cpu, mem, n); cin>>c>>m>>n; Computer com2(c, m, n); com1.show(); com2.show(); return 0; }
考点:类的组合
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class CPU { friend class Computer; int hz; public: CPU(int _hz):hz(_hz){} CPU(const CPU &b):hz(b.hz){} }; class Memory { friend class Computer; int val; public: Memory(int _val):val(_val){} Memory(const Memory &b):val(b.val){}; }; class Computer { CPU c; Memory m; string name; public: Computer(CPU _c, Memory _m,string _name):c(_c),m(_m),name(_name) { } void show() { cout << "This is " << name << "' computer with CPU = " << c.hz << "GHz, memory = " << m.val << "MB." << endl; } };
Problem E: 模板是个好东西

main函数:
int main() { string n; int x, y, d; char c; cin>>n; cin>>x>>y>>d; cin>>c; Point p(x, y); Data<char> aChar(c); Data<int> anInt(d); Data<Point> aPoint(p); Data<string> aString(n); aChar.show(); anInt.show(); aString.show(); aPoint.show(); return 0; }
考点:类模板加输出运算符重载
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Point { int x,y; public: Point():x(0),y(0){}; Point(int _x,int _y):x(_x),y(_y){} friend ostream &operator << (ostream &os,Point &b) { os << b.x << ' ' << b.y << endl; return os; } }; template <class T> class Data { T a; public: Data(T _a):a(_a){}; void show() { cout << a << endl; } };