优于别人,并不高贵,真正的高贵,应该是优于过去的自己。
—— 海明威 《真实的高贵》
ps:算是手速场吧,没有像上场那么自闭,看来喊喊rank1还是有用的,嘻嘻。
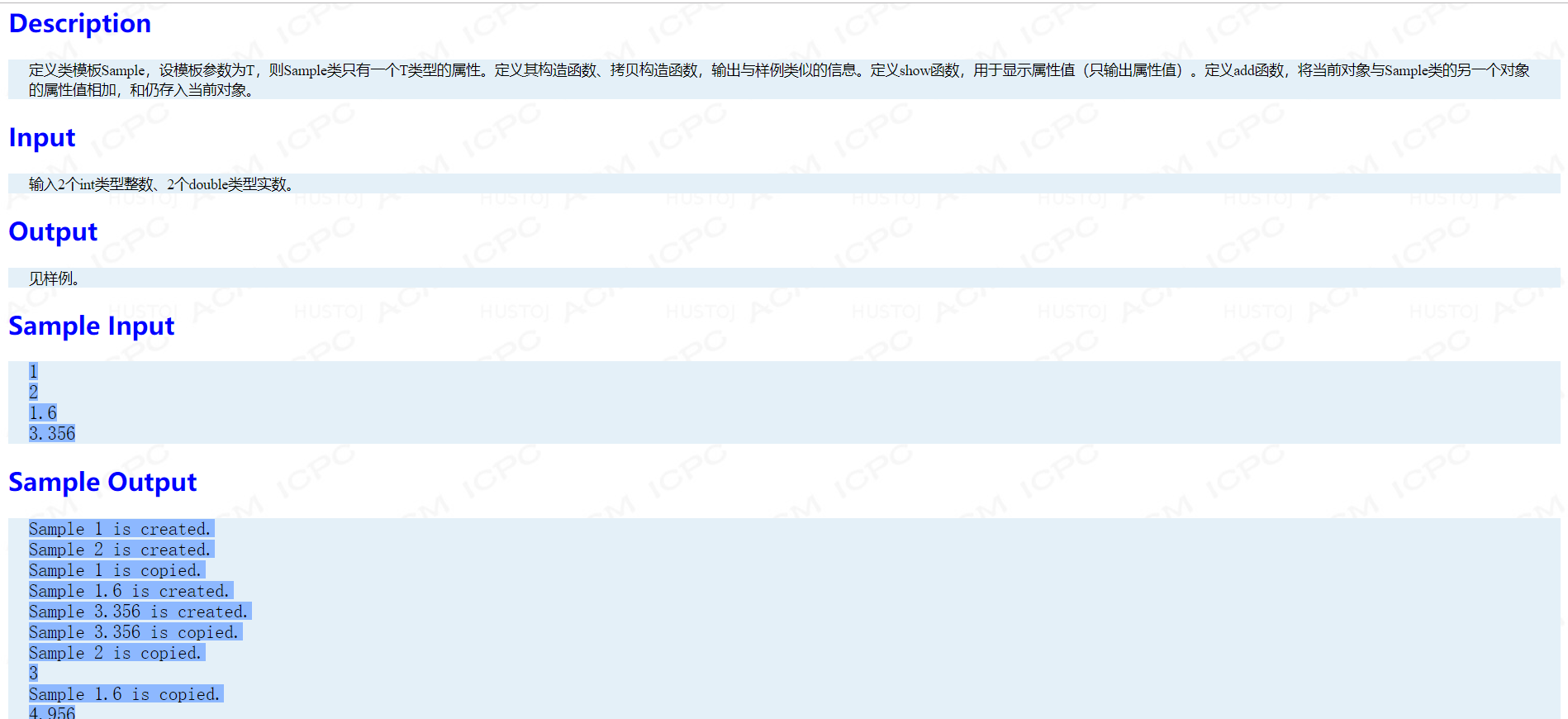
Problem A: 第一个类
main函数:
int main() { Thing A("Car"); string str; cin>>str; Thing B(str); return 0; }
水。。。。。。。。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Thing { string name; public: Thing(string _name):name(_name){cout << "Construct a thing " << name << endl; } ~Thing() { cout << "Destroy a thing " << name << endl; } };
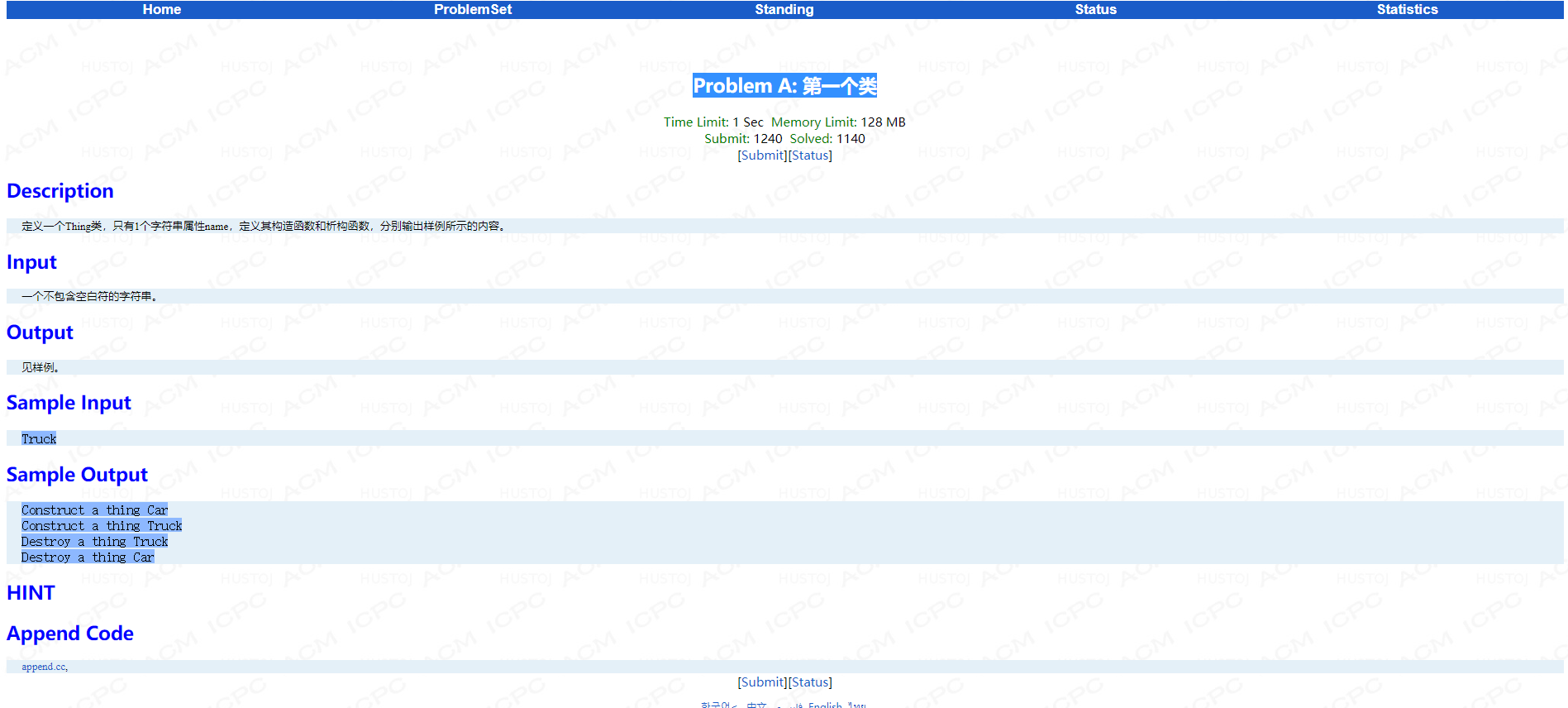
Problem B: 建造一间教室
main函数:
int main() { int nl, nc; int w; string color; cin>>w>>color; Light light(w); Chair chair(color); cin>>nl>>nc; cin>>w>>color; ClassRoom room(nl, nc, w, color); return 0; }
半水吧,就一个坑点,chair类的析构也输出created,还好测了遍样例,手动狗头。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Light { int w; public: Light(int _w):w(_w) { printf("A %dw light is created. ",w); } ~Light() { printf("A %dw light is erased. ",w); } }; class Chair { string co; public: Chair(string _co):co(_co) { cout << "A " << co << " chair is created." << endl; } ~Chair() { cout << "A " << co << " chair is created." << endl; } }; class ClassRoom { Light li;Chair ch; int n_c; int n_l; public: ClassRoom(int _c,int _l,int _li,string _ch):n_c(_c),n_l(_l),li(_li),ch(_ch) { printf("A classroom having %d lights and %d chairs is created. ",n_c,n_l); } ~ClassRoom() { printf("A classroom having %d lights and %d chairs is erased. ",n_c,n_l); } };
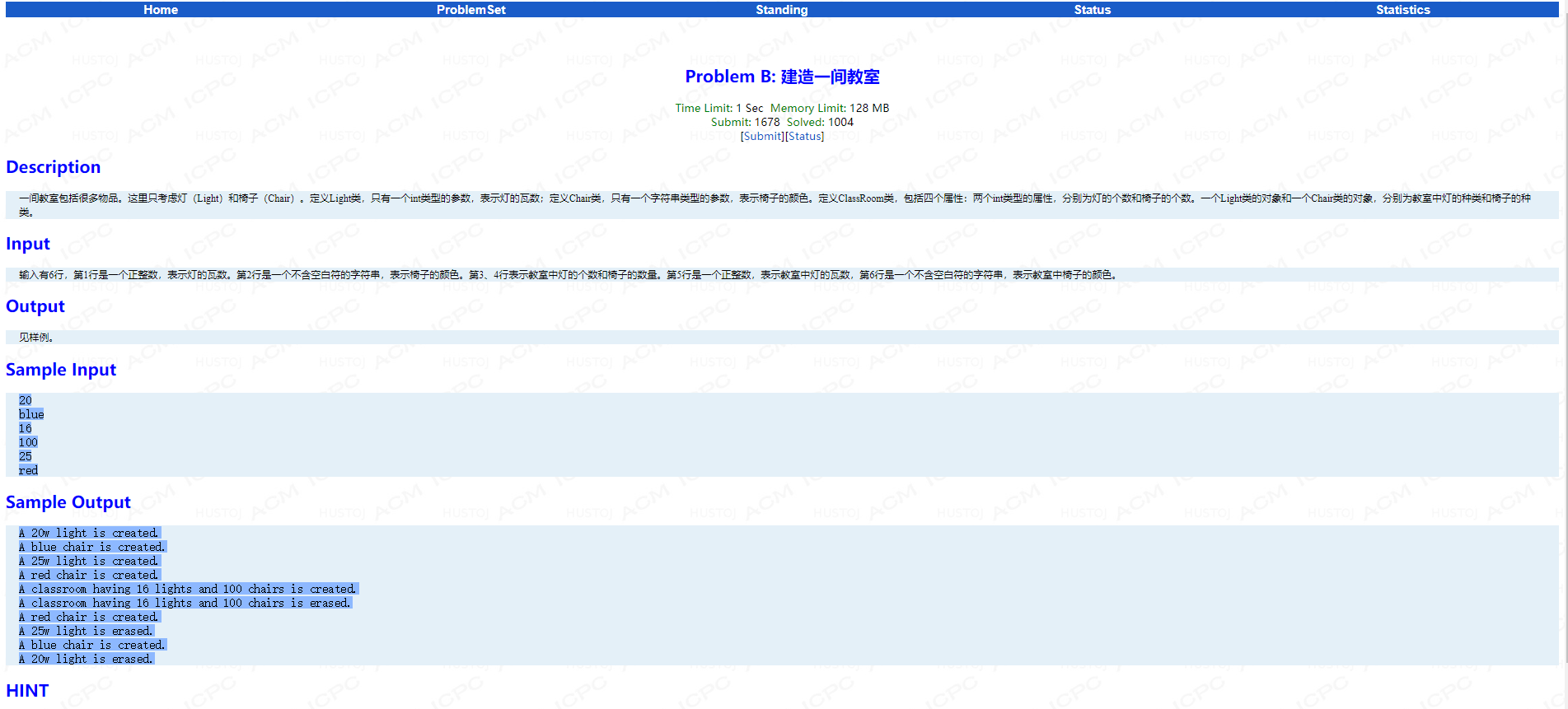
Problem C: 是否回文数?
main函数:
int main() { Data data; int v; while (cin>>v) { data.setValue(v); if (data.isPalindrome()) cout<<"Yes"<<endl; else cout<<"No"<<endl; } return 0; }
重点应该是在isPalindrome函数的设计的吧,基本思路应该是先取个abs,然后转化为字符串看是否对称的吧。
way1 : 使用sprintf 函数将数字转化为字符串 sprintf(要转入的字符数组s,格式控制符,转出的数字);
way2: 使用STL库中的反转函数 reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
ac代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Data { int v; public: Data(){} void setValue(int x){v =x;} bool isPalindrome()// way 1 { int d = v; d = abs(d); char s[20]; sprintf(s,"%d",d); int len = strlen(s); for(int i = 0,j=len-1;i<=j;i++,j--) if(s[i]!=s[j]) return false; return true; } bool isPalindrome()// way 2 { int d = abs(v); string s,s1; while(d) { s+=(d%10+'0'); d/=10; } s1 = s; int len = s.size(); reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end()); for(int i = 0;i<=(len+1)/2;i++) if(s[i]!=s1[i]) return false; return true; } };
Problem D: Base与Derived
main函数:
int main() { int a, b; cin>>a>>b; Base base(a); Derived derived(a, b); return 0; }
水,细节题,析构输出created 。。。。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Base { int b; public: Base(int _b):b(_b) { printf("Base %d is created. ",b); } ~Base() { printf("Base %d is created. ",b); } }; class Derived:public Base { int d; public: Derived(int _b,int _d):Base(_b),d(_d) { printf("Derived %d is created. ",d); }; ~Derived () { printf("Derived %d is created. ",d); } };
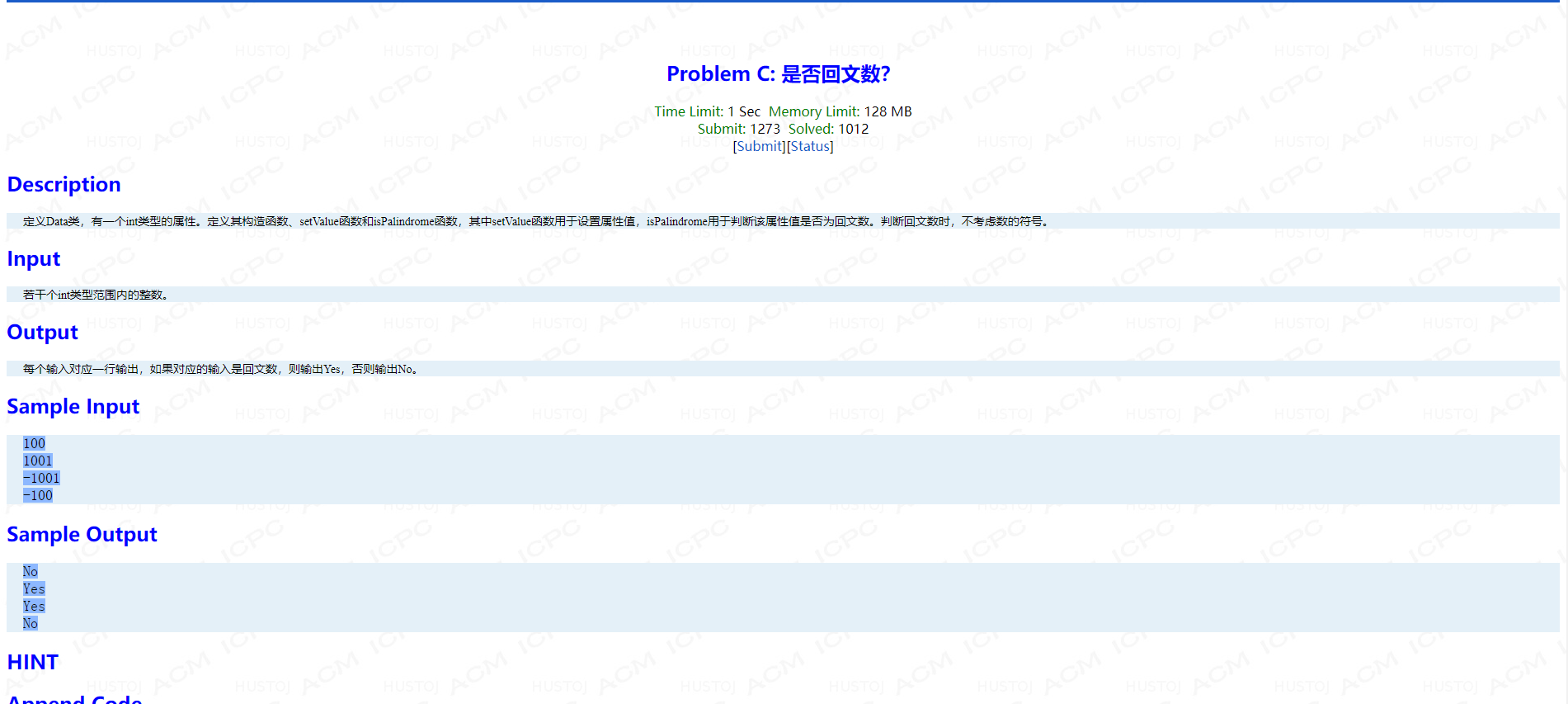
Problem E: 类模板Sample
main函数:
int main() { int a, b; double c, d; cin>>a>>b>>c>>d; Sample<int> s1(a), s2(b), s3(s1); Sample<double> s4(c), s5(d), s6(s5); s1.add(s2); s1.show(); s5.add(s4); s5.show(); return 0; }
类模板
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class Sample
{
T num;
public:
Sample(T _num):num(_num)
{
cout << "Sample " << num << " is created." << endl;
}
template <class T1>
Sample(Sample<T1> &b)
{
num = b.num;
cout << "Sample " << num << " is copied." << endl;
}
void show()
{
cout << num << endl;
}
template <class T1>
void add(Sample<T1> b)
{
num+=b.num;
}
};