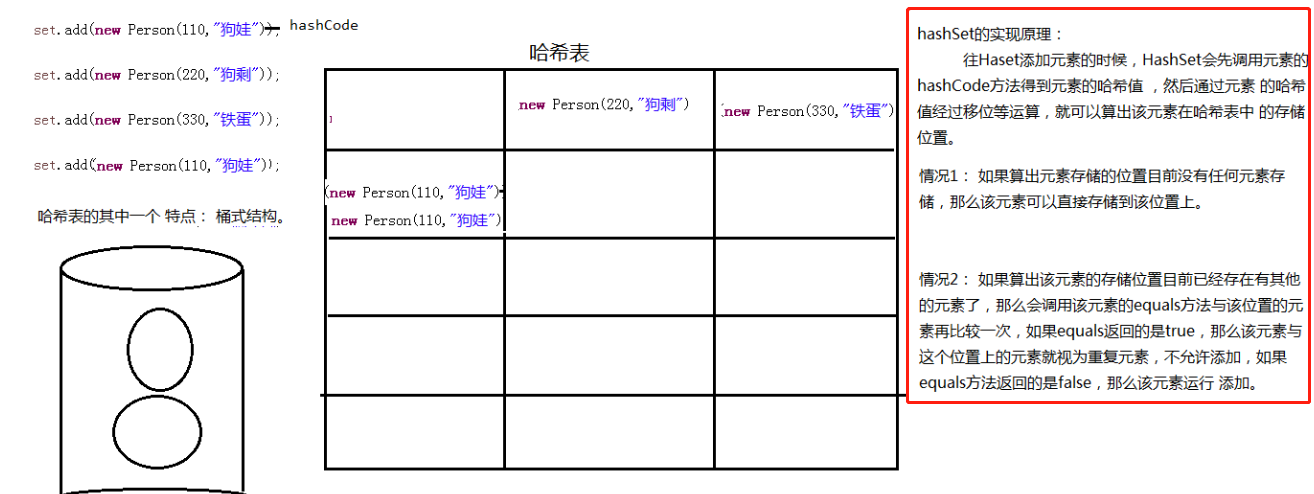
PS: 对象默认是单例的
package cn.itcast.a_hello; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; public class App2_bean { /** * 1) 对象创建: 单例/多例 * scope="singleton", 默认值, 即 默认是单例 【service/dao/工具类】 * scope="prototype", 多例; 【Action对象】 * * 2) 什么时候创建? * scope="prototype" 在用到对象的时候,才创建对象。 * scope="singleton" 在启动(容器初始化之前), 就已经创建了bean,且整个应用只有一个。 * 3)是否延迟创建 * lazy-init="false" 默认为false, 不延迟创建,即在启动时候就创建对象 * lazy-init="true" 延迟初始化, 在用到对象的时候才创建对象 * (只对单例有效) * 4) 创建对象之后,初始化/销毁 * init-method="init_user" 【对应对象的init_user方法,在对象创建爱之后执行 】 * destroy-method="destroy_user" 【在调用容器对象的destriy方法时候执行,(容器用实现类)】 */ @Test public void testIOC() throws Exception { // 得到IOC容器对象 【用实现类,因为要调用销毁的方法】 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/a_hello/applicationContext.xml"); System.out.println("-----容器创建-----"); // 从容器中获取bean User user1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User user2 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user1); System.out.println(user2); // 销毁容器对象 ac.destroy(); /*------User对象创建------ 创建对象之后,初始化 ------User对象创建------ -----容器创建----- cn.itcast.a_hello.User@53b32d7 cn.itcast.a_hello.User@53b32d7 IOC容器销毁,user对象回收!*/ } @Test public void test() throws Exception { // 容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/a_hello/applicationContext.xml"); System.out.println("-----容器创建完成-----"); User user1 = (User) ac.getBean("user1"); User user2 = (User) ac.getBean("user1"); User user3 = (User) ac.getBean("user1"); User user4 = (User) ac.getBean("user1"); System.out.println(user1==user2); System.out.println(user3==user2); /*------User对象创建------ 创建对象之后,初始化 ------User对象创建------ -----容器创建完成----- true true*/ } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- IOC容器的配置: 要创建的所有的对象都配置在这里 --> <bean id="user" class="cn.itcast.a_hello.User" init-method="init_user" destroy-method="destroy_user" scope="singleton" lazy-init="false"></bean> <bean id="user1" class="cn.itcast.a_hello.User" ></bean> </beans>
package cn.itcast.a_hello; public class User { private int id; private String name; public User() { super(); System.out.println("------User对象创建------"); } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void init_user() { System.out.println("创建对象之后,初始化"); } public void destroy_user() { System.out.println("IOC容器销毁,user对象回收!"); } }
PS: 注入方式
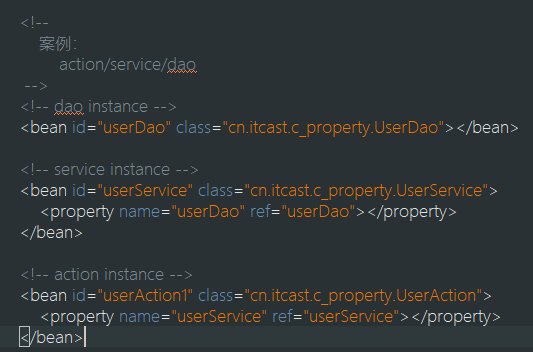
package cn.itcast.e_anno; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("userService") // userService加入ioc容器 public class UserService { // 会从IOC容器中找userDao对象,注入到当前字段 /* * <bean id="" class=""> * <property name="userDao" ref="userDao" /> @Resource相当于这里的配置 * </bean> */ @Resource(name = "userDao") private UserDao userDao; public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } public void save() { userDao.save(); } }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*****************************************************************************************


PS: 事物也是基于aop实现的
【Spring】详解spring事务属性
----------------------------------------------------------
Redis分布式锁 ---Redis
redis分布式锁的作用及实现
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
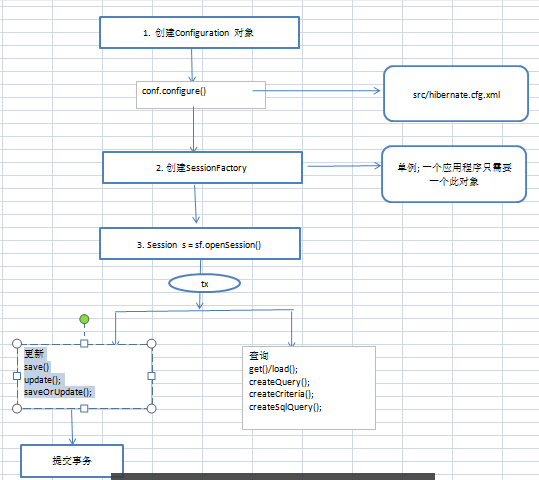





---------------------------------------------------------
Maven
----------------------------------------------------------------------


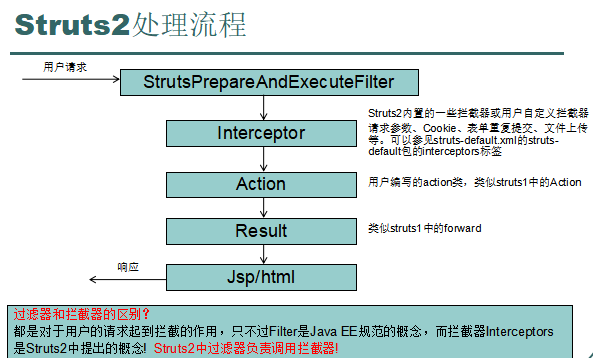
PS: 业务执行流程

PS: struts-defalut.xml详细解释
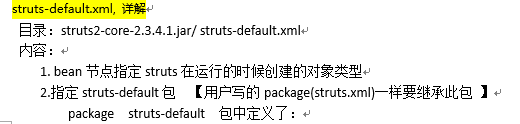


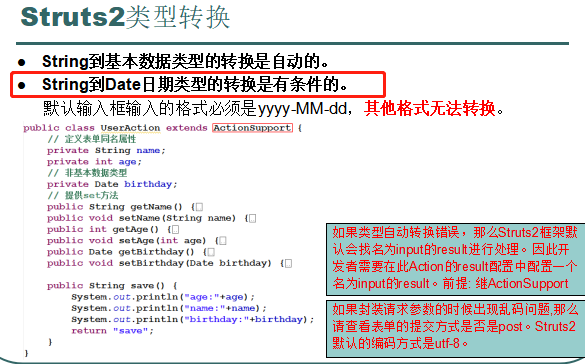
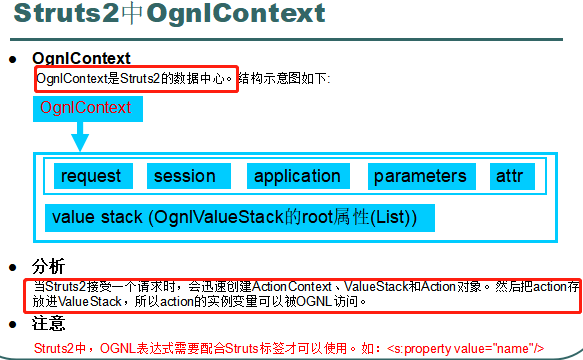
------------------------------------------------
泛型反射应用
PS: 编写baseDao
/** * 所有dao的公用的方法,都在这里实现 * @author Jie.Yuan * */ public class BaseDao<T>{ // 保存当前运行类的参数化类型中的实际的类型 private Class clazz; // 表名 private String tableName; // 构造函数: 1. 获取当前运行类的参数化类型; 2. 获取参数化类型中实际类型的定义(class) public BaseDao(){ // this 表示当前运行类 (AccountDao/AdminDao) // this.getClass() 当前运行类的字节码(AccountDao.class/AdminDao.class) // this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass(); 当前运行类的父类,即为BaseDao<Account> // 其实就是“参数化类型”, ParameterizedType Type type = this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass(); // 强制转换为“参数化类型” 【BaseDao<Account>】 ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType) type; // 获取参数化类型中,实际类型的定义 【new Type[]{Account.class}】 Type types[] = pt.getActualTypeArguments(); // 获取数据的第一个元素:Accout.class clazz = (Class) types[0]; // 表名 (与类名一样,只要获取类名就可以) tableName = clazz.getSimpleName(); } /** * 主键查询 * @param id 主键值 * @return 返回封装后的对象 */ public T findById(int id){ /* * 1. 知道封装的对象的类型 * 2. 表名【表名与对象名称一样, 且主键都为id】 * * 即, * ---》得到当前运行类继承的父类 BaseDao<Account> * ----》 得到Account.class */ String sql = "select * from " + tableName + " where id=? "; try { return JdbcUtils.getQuerrRunner().query(sql, new BeanHandler<T>(clazz), id); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } /** * 查询全部 * @return */ public List<T> getAll(){ String sql = "select * from " + tableName ; try { return JdbcUtils.getQuerrRunner().query(sql, new BeanListHandler<T>(clazz)); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
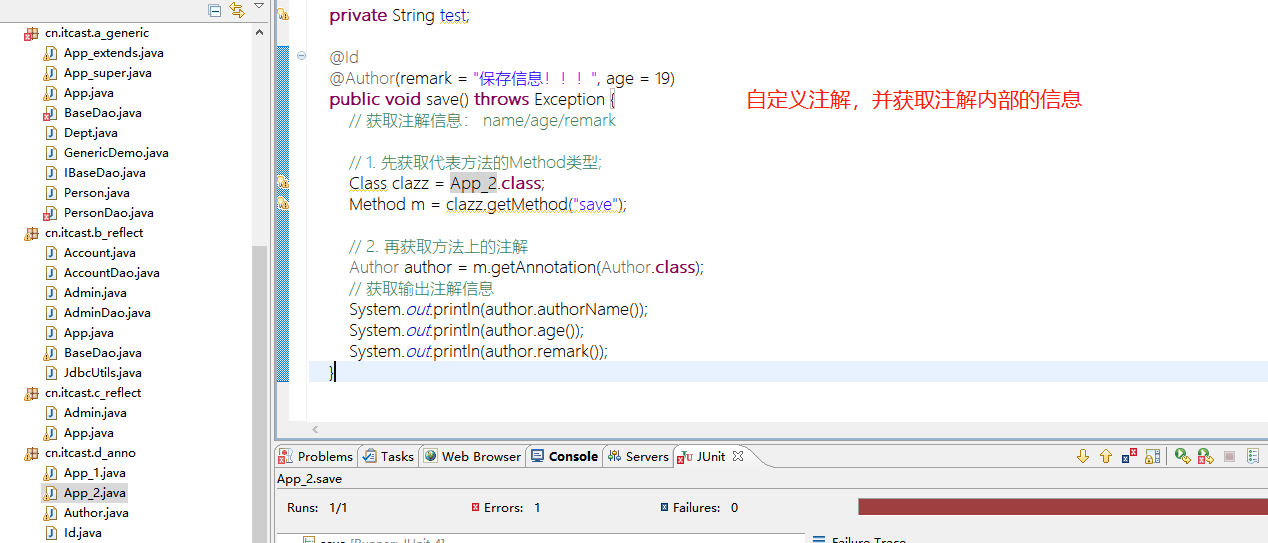
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------

javaweb学习总结(三十八)——事务
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------
Jsp
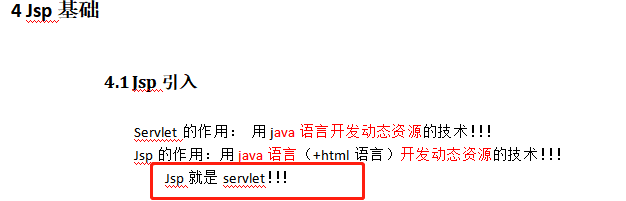









----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Servlet
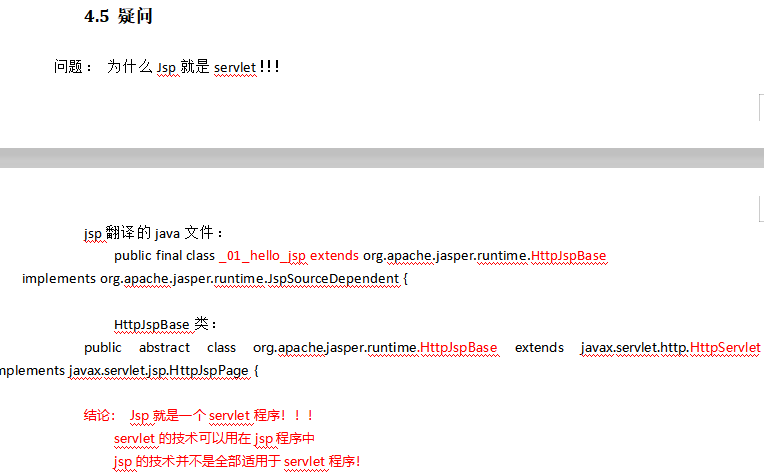
4.3 伪代码演示servlet的生命周期
Tomtcat内部代码运行:
1)通过映射找到到servlet-class的内容,字符串: gz.itcast.a_servlet.FirstServlet
2)通过反射构造FirstServlet对象
2.1 得到字节码对象
Class clazz = class.forName("gz.itcast.a_servlet.FirstServlet");
2.2 调用无参数的构造方法来构造对象
Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); ---1.servlet的构造方法被调用
3)创建ServletConfig对象,通过反射调用init方法
3.1 得到方法对象
Method m = clazz.getDeclareMethod("init",ServletConfig.class);
3.2 调用方法
m.invoke(obj,config); --2.servlet的init方法被调用
4)创建request,response对象,通过反射调用service方法
4.1 得到方法对象
Methodm m =clazz.getDeclareMethod("service",HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class);
4.2 调用方法
m.invoke(obj,request,response); --3.servlet的service方法被调用
5)当tomcat服务器停止或web应用重新部署,通过反射调用destroy方法
5.1 得到方法对象
Method m = clazz.getDeclareMethod("destroy",null);
5.2 调用方法
m.invoke(obj,null); --4.servlet的destroy方法被调用




--------Cookie---------------------------------------



4.3 Session原理



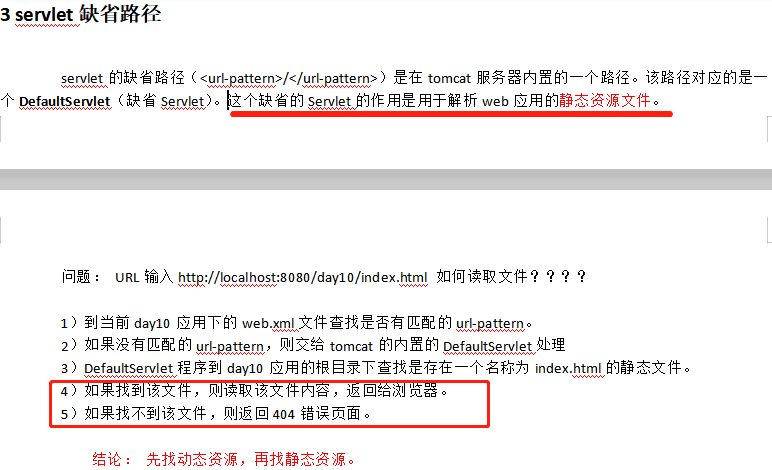
------------------------------------路径问题
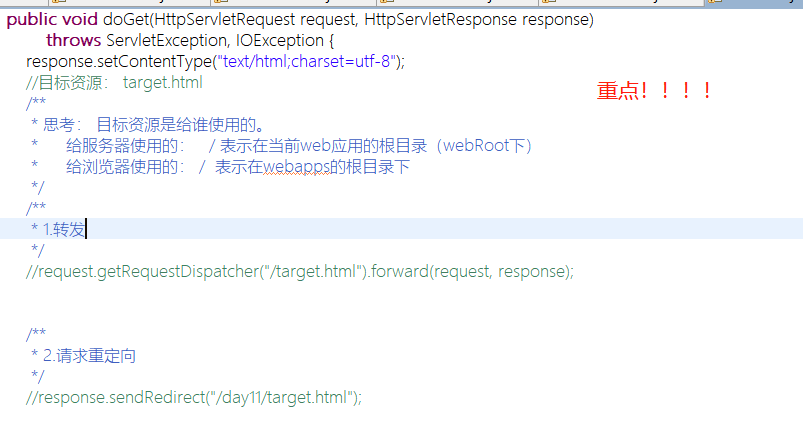
package gz.itcast.b_resource; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * 读取web应用下的资源文件(例如properties) * @author APPle */ public class ResourceDemo extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { /** * . 代表java命令运行目录。java运行命令在哪里?? 在tomcat/bin目录下 * 结论: 在web项目中, . 代表在tomcat/bin目录下开始,所以不能使用这种相对路径。 */ //读取文件。在web项目下不要这样读取。因为.表示在tomcat/bin目录下 /*File file = new File("./src/db.properties"); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);*/ /** * 使用web应用下加载资源文件的方法 */ /** * 1. getRealPath读取,返回资源文件的绝对路径 */ /*String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties"); System.out.println(path); File file = new File(path); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);*/ /** * 2. getResourceAsStream() 得到资源文件,返回的是输入流 */ InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties"); Properties prop = new Properties(); //读取资源文件 prop.load(in); String user = prop.getProperty("user"); String password = prop.getProperty("password"); System.out.println("user="+user); System.out.println("password="+password); } }
---------------------------------

PS: 就是window、screen这些东西


---------------Request和Response-------------------------------------------------
(13)javaWeb中HttpServletRequest详解
javaweb学习总结(七)——HttpServletResponse对象(一)
--------------------------------------



package cn.itcast.path; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; /* 如果经常会发生变化的数据我们可以定义在配置文件上。 比如说:数据库的用户名与密码。 配置文件的路径应该如何写 呢? 绝对路径:一个文件的完整路径信息。一般绝对路径是包含有盘符 的。 绝对路径的缺陷: 因为绝对路径是有盘符开头的,有些系统是没有盘符的。 相对路径: 相对路径是相对于当前程序的路径。当前路径就是执行java命令的时候,控制台所在的路径。 类文件路径 :类文件路径就是使用了classpath的路径找对应的资源文件。 如果需要使用到类文件路径首先先要获取到一个Class对象。 */ public class DBUtil { static Properties properties ; static{ try { properties = new Properties(); //去加载配置文件 / Class clazz = DBUtil.class; InputStream inputStream = clazz.getResourceAsStream("/cn/itcast/path/db.properties"); // "/"代表了Classpath的路径。 getResourceAsStream 该方法里面使用的路径就是使用了类文件路径。 properties.load(inputStream);///day01/src/cn/itcast/path/db.properties } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("当前路径:"+ new File(".").getAbsolutePath() ); System.out.println("用户名:"+ properties.getProperty("userName")+" 密码:"+properties.getProperty("password")); } }
------------------------------------------------------------------
PS: 反射操作过于麻烦------》内省操作

beanUtils的用法,设置属性,复制属性
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
package cn.itcast.input; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; /* File类: 用于描述一个文件或者文件夹的。 通过File对象我们可以读取文件或者文件夹的属性数据,如果我们需要读取文件的内容数据,那么我们需要使用IO流技术。 IO流(Input Output) IO流解决问题: 解决设备与设备之间的数据传输问题。 内存--->硬盘 硬盘--->内存 IO流技术: IO流分类: 如果是按照数据的流向划分: 输入流 输出流 如果按照处理的单位划分: 字节流: 字节流读取得都是文件中二进制数据,读取到二进制数据不会经过任何的处理。 字符流: 字符流读取的数据是以字符为单位的 。 字符流也是读取文件中的二进制数据,不过会把这些二进制数据转换成我们能 识别的字符。 字符流 = 字节流 + 解码 输入字节流: --------| InputStream 所有输入字节流的基类 抽象类 ------------| FileInputStream 读取文件数据的输入字节流 使用FileInputStream读取文件数据的步骤: 1. 找到目标文件 2. 建立数据的输入通道。 3. 读取文件中的数据。 4. 关闭 资源. */ public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { readTest4(); } //方式4:使用缓冲数组配合循环一起读取。28 public static void readTest4() throws IOException{ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //找到目标文件 File file = new File("D:\a.txt"); //建立数据的输入通道 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); //建立缓冲数组配合循环读取文件的数据。 int length = 0; //保存每次读取到的字节个数。 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; //存储读取到的数据 缓冲数组 的长度一般是1024的倍数,因为与计算机的处理单位。 理论上缓冲数组越大,效率越高 while((length = fileInputStream.read(buf))!=-1){ // read方法如果读取到了文件的末尾,那么会返回-1表示。 System.out.print(new String(buf,0,length)); } //关闭资源 fileInputStream.close(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("读取的时间是:"+ (endTime-startTime)); //446 } //方式3:使用缓冲 数组 读取。 缺点: 无法读取完整一个文件的数据。 12G public static void readTest3() throws IOException{ //找到目标文件 File file = new File("D:\a.txt"); //建立数据的输入通道 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); //建立缓冲字节数组,读取文件的数据。 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; //相当于超市里面的购物车。 int length = fileInputStream.read(buf); // 如果使用read读取数据传入字节数组,那么数据是存储到字节数组中的,而这时候read方法的返回值是表示的是本次读取了几个字节数据到字节数组中。 System.out.println("length:"+ length); //使用字节数组构建字符串 String content = new String(buf,0,length); System.out.println("内容:"+ content); //关闭资源 fileInputStream.close(); } //方式2 : 使用循环读取文件的数据 public static void readTest2() throws IOException{ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //找到目标文件 File file = new File("D:\a.txt"); //建立数据的输入通道 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); //读取文件的数据 int content = 0; //声明该变量用于存储读取到的数据 while((content = fileInputStream.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)content); } //关闭资源 fileInputStream.close(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("读取的时间是:"+ (endTime-startTime)); //446 } //读取的方式一缺陷: 无法读取完整一个文件 的数据. public static void readTest1() throws IOException{ //1. 找到目标文件 File file = new File("D:\a.txt"); //建立数据的输入通道。 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); //读取文件中的数据 int content = fileInputStream.read(); // read() 读取一个字节的数据,把读取的数据返回。 System.out.println("读到的内容是:"+ (char)content); //关闭资源 实际上就是释放资源。 fileInputStream.close(); } }

总结:
字节流: 每次读取一个字节,可以读取任何文件
InputStream--》FileInputStream-->(为了提高读取效率)BufferInputStream
OutputStream也是同理
字符流:每次读取一个字符,只能读取文本文件(他的出现就是为了解决字节读取中文字符时出现的乱码,因为中文字符不是一个字节)
Reader --> FileReader --> BufferFileReader(为了提高读取效率而出现的)
Writer同理
Java设计模式----装饰器模式




编码、解码
// 编码操作与解码操作。 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String value = System.getProperty("file.encoding"); System.out.println("系统默认的编码为 " + value); String str = "中"; // 编码操作 byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); byte[] bytes2 = str.getBytes("gbk");// d6d0 byte[] bytes3 = str.getBytes("utf-8");// e4b8ad System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); // [-42, -48] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2));// [-42, -48] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes3));// [-28, -72, -83] // 解码操作 // 编码gbk,解码utf-8乱码。 String str2 = new String(bytes2, "utf-8"); System.out.println(str2); // 编码utf-8 解码gbk,乱码 str2 = new String(bytes3, "gbk"); System.out.println(str2); // gbk兼容gb2312所以,没有问题。 str = new String("中国".getBytes("gb2312"), "gbk"); System.out.println(str); }
系统默认的编码为 GBK
[-42, -48]
[-42, -48]
[-28, -72, -83]
??
涓?
中国

/*
字节流
输入字节流:
-----------| InputStream 所有输入字节流的基类 抽象类
-----------------| FileInputStream 读取文件数据的输入字节流
-----------------| BufferedInputStream 缓冲输入字符流 该类出现的目的是为了提高读取文件 数据的效率。 这个类其实只不过是在内部维护了一个8kb的字节数组而已。
输出字节流:
-----------| OutputStream 所有输出字节流的基类。 抽象类。
----------------| FileOutputStream 向文件输出数据的输出字节流
----------------| BufferedOutputStream 缓冲输出字节流 该类出现的目的也是为了提高向文件写数据的效率。 这个类的也只不过是在内部维护了一个8kb的字节数组而已。
字符流 : 字符流 = 字节流 + 编码(解码)
输入字符流:
---------| Reader 所有输入字符流的基类。 抽象类。
----------------| FileReader 读取文件数据的输入字符流。
----------------| BufferedReader 缓冲输入字符流 该类出现的目的是为了提高读取文件数据的效率与拓展FileReader的(readLine)功能。 这个类的也只不过是在内部维护了一个8kb的字符数组而已。
输出字符流:
---------| Writer 所有输出字符流的基类。 抽象类
----------------| FileWriter 向文件输出数据的输出字符流
----------------| BufferedWriter 缓冲输出字符流 该类出现的目的是为了提高写文件数据的效率与拓展FileWriter的(newLine)功能.
----------------------------------------
-------------------
Runnable和Thread区别和比较 重点是比较static tickets
---------------------------------------------------------------------

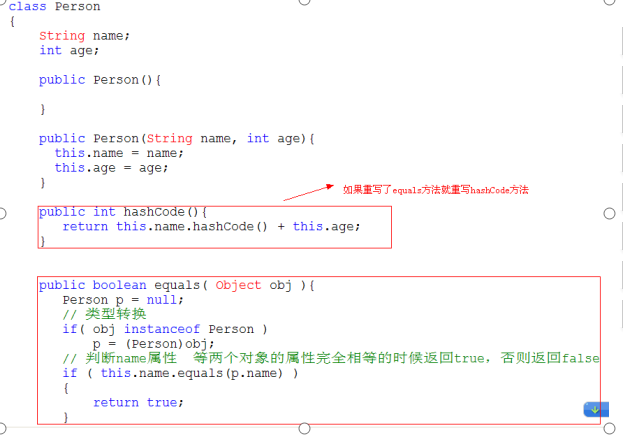
PS: 也就是实现equals 必须实现hashcode方法(计算内存地址)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

PS: 也就是在存在继承关心的时候,子类加载时,子类构造函数中如果没有指定,都会加载父类无参构造函数,
如果指定了会加载父类构造函数
/* 疑问: 为什么要调用父类的构造方法啊?这样子做的意义在那? 调用父类 的构造方法是可以初始化从父类继承下去的属性的。 */ class Fu{ int x = 10; String name; public Fu(String name){ this.name = name; System.out.println("Fu类d带参的构造方法..."); } public Fu(){ System.out.println("Fu类无参的构造方法..."); } } class Zi extends Fu{ int x = 20; public Zi(String name){ //super(name); //指定调用父类一个参数的构造函数。 } public void print(){ System.out.println("x1 = "+ x); } } class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Zi z = new Zi("大头儿子"); System.out.println("name= "+z.name); } }
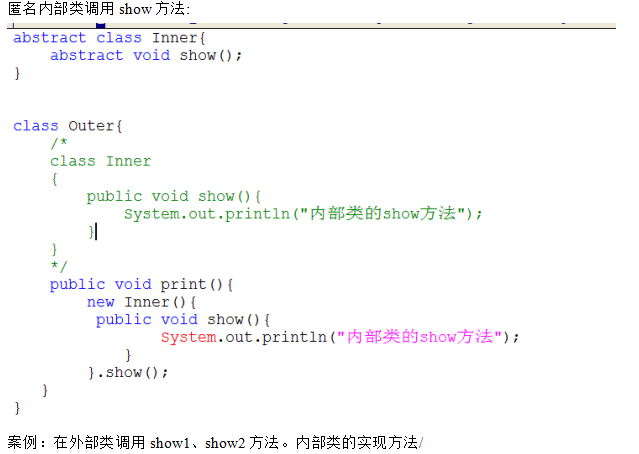
--------匿名内部类


--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.union和unionall
uion会过滤元素并且排序,unionAll只是合并排序
2.如果日志满了会怎么办?
只能查询,不能插入和备份
3.
1. == , equals, hashcode()
PS: 如果数据类型是基本类型,==就算是比较值;如果类型是应用类型,就是比较内存地址。
在没有覆盖的情况下, == 和 equals是一样的。
PS:equals判断两个对象相等
PS:hashcode也是判断对象是否相等, 按照使用原则,最好同时覆盖。
hashcode不对,equals一定不对;equals不对,hashcode不一定对

0.值传递和引用传递





1.关于构造函数

2. Java clone返回的是新对象的引用
3.继承

4.Override 和 overwrite 两者是多态的表现
5.内部类分为 1. 静态 2.成员 3.局部 4.匿名



5.finalize方法

6.static的关键作用
1.成员变量
2.静态方法,不用创建直接引用
3.静态代码块:初始化的时候使用
4.内部类
7.---volatile--


8.char 是 2个字节
9. -------------不可变类
PS: 也就是 在它创建出来以后整个生命周期内,他的成员变量都不可以再修改了


10. 判断 字符串中 是否有中文字符
11.
PS:此图说明为了说明括号的提取问题
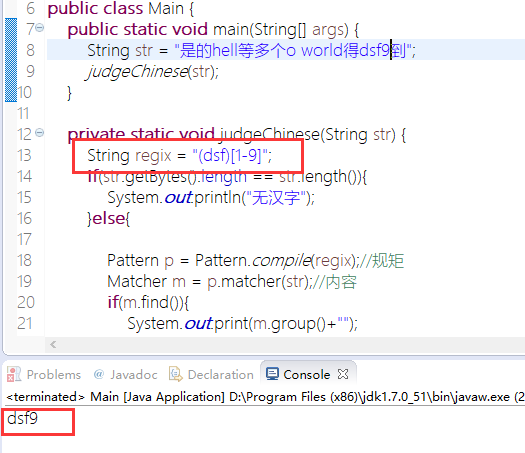
正则表达式的() [] {}有不同的意思。 () 是为了提取匹配的字符串。表达式中有几个()就有几个相应的匹配字符串。 (s*)表示连续空格的字符串。 []是定义匹配的字符范围。比如 [a-zA-Z0-9] 表示相应位置的字符要匹配英文字符和数字。[s*]表示空格或者*号。 {}一般用来表示匹配的长度,比如 s{3} 表示匹配三个空格,s[1,3]表示匹配一到三个空格。 (0-9) 匹配 '0-9′ 本身。 [0-9]* 匹配数字(注意后面有 *,可以为空)[0-9]+ 匹配数字(注意后面有 +,不可以为空){1-9} 写法错误。 [0-9]{0,9} 表示长度为 0 到 9 的数字字符串。
package net.jcip.examples; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "是的hell等多个o world得到"; judgeChinese(str); } private static void judgeChinese(String str) { String regix = "[u4e00-u9fa5]"; if(str.getBytes().length == str.length()){ System.out.println("无汉字"); }else{ Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regix);//规矩 Matcher m = p.matcher(str);//内容 if(m.find()){ System.out.print(m.group()+""); } } } }
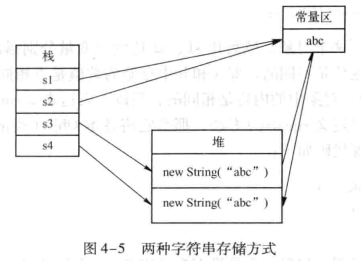
1. String


1.异常处理

PS:他会在 return之前执行



1. java 语言


PS: 程序的运行,都跟java VM有着很深的关系
2. Java加载类的原理:动态加载;显示加载和隐式加载


11. GC 垃圾回收






PS: ------------Java 内存泄露问题 -----------------



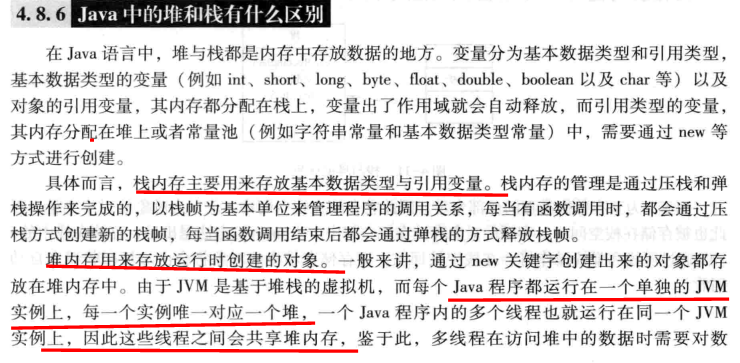
PS: Java 堆栈------------------多线程会共享堆内存
--------------------集合
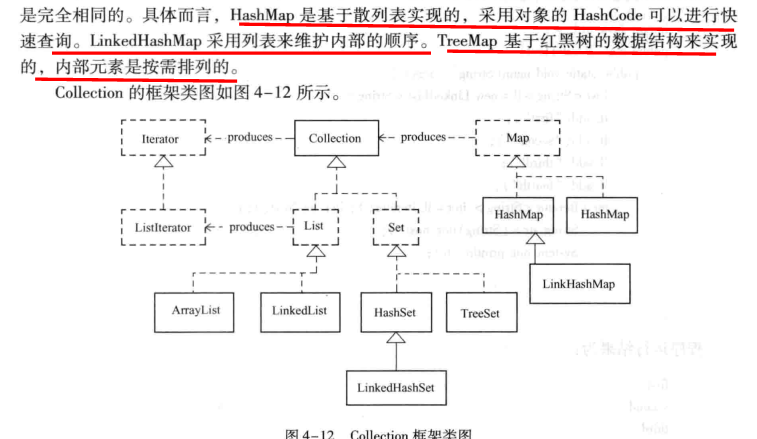
----------ArrayList ,LinkedList,Vector

----------------------------PS:线程

--------------PS:同步----

------------PS: 实现线程的方法
1.继承Thread
2.实现Runnable接口
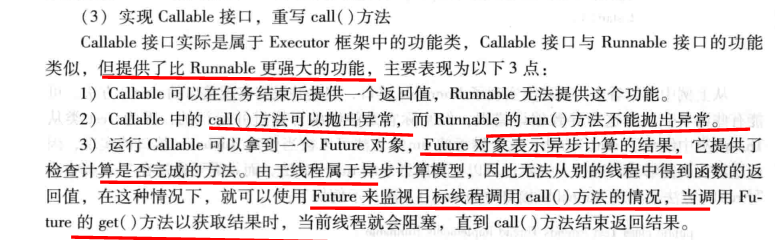
PS: 多线程实现同步的的方法



-----------PS:线程结束的方式------
PS:
Thread.stop;会丢失锁,
Thread.suspend 会 不释放索,推荐使用下面两个方法


PS:

Ps: 守护线程---只有守护线程的时候,程序是可以退出的






-----------------------------Servlet

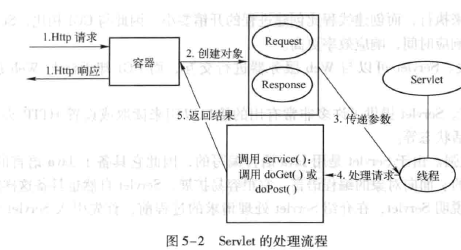
------生命周期

11.JSP的内置对象
PS: request ,response,session,allplication,page(this页面),pageContext(提供访问有的对象),exception,out,config(获取服务器的配置信息,传递给servlet)

12.会话跟踪技术有4种;
page。seesion,application,request
13. 开发时候需要的注意的事情?
1、尽量少使用继承
2、尽可能使用数据库连接池
3.经常使用的servlet和jsp最好缓存起来
4.Sql语句优化
=====数据库 三 范式
1.每一个字段都是独立的个体
2.每个表字段,都和这个表有关系
3.非主键属性不存在传递关系
一、 文件路径
1.1. 绝对路径
以根目录或某盘符开头的路径(或者说完整的路径)
例如:
l c:/a.txt (Windows操作系统中)
l c:/xxx/a.txt (Windows操作系统中)
l /var/xx/aa.txt (Linux操作系统中)
绝对路径的问题: 比如C:abca.properties文件路径,该路径在windows上执行没有 问题,但是如果把该项目移动到linux上面执行 ,该路径就会出现问题了,因为在linux上面没有c盘的,只有根目录。
1.2. 相对路径
相对于当前路径的一个路径。例如当前文件夹为c:/abc时:相对路径a.txt表示c:/abc/a.txt,相对路径xx/a.txt = c:/abc/xx/a.txt
l . 表示当前文件夹
l .. 表示上级文件夹
相对路径存在的问题:相对路径是相对于目前执行class文件的时候,控制台所在的路径,这样子也会导致出现问题。
1.3. Java程序中的相对路径
在Java程序中使用File时写相对路径,是指相对于执行java命令时当前所在的文件夹。
测试代码:
在命令行中使用cd命令切换到不同的路径下试试,可以看到以上所说的效果。
在Eclipse中,当前路径是工程的根目录。
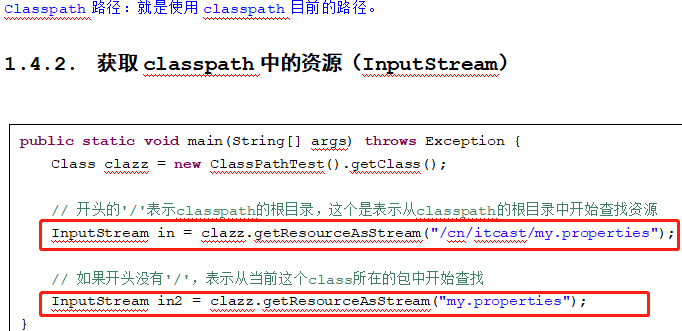
1.4. classpath路径
1.4.1. classpath路径说明
在Java程序中,一般情况下使用绝对路径还是相对路径都不太合适,因为Java程序的jar包所放的位置不确定,执行java程序时当前的路径也不确定,所以不合适。一般在Java程序中我们会把资源放到classpath中,然后使用classpath路径查找资源。
Classpath路径:就是使用classpath目前的路径。