码云:https://gitee.com/SC_looker/wordcount.git
先明确任务内容,分为以下几点:
(1)分析、整理需求,提交PSP表格;
(2)编码实现,并在Github提交;
(3)设计测试用例,编写单元测试;
(4)撰写博客。
一、需求分析:
要求:统计文本文件的字符数、单词数、和行数。
输入格式说明:
wc.exe -c file.txt //返回文件 file.txt 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.txt //返回文件 file.txt 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.txt //返回文件 file.txt 的行数
输出格式说明:
保存在outfile.txt中
file1.txt, 字符数: 50
file1.txt, 单词数: 30
解题思路:
刚看到题目时,我打算写三个类,每个类分别统计数量,然后传到主函数,由主函数进行存取。由于我使用的是c++语言,所以可以使用fstream类。
在fstream类中,有一个成员函数open(),就是用来打开文件的,其原型是:
void open(const char* filename,int mode,int access);
参数:
- filename: 要打开的文件名
- mode: 要打开文件的方式
- access: 打开文件的属性
打开文件的方式在类ios(是所有流式I/O类的基类)中定义,常用的值如下:
- ios::app: 以追加的方式打开文件
- ios::ate: 文件打开后定位到文件尾,ios:app就包含有此属性
- ios::binary: 以二进制方式打开文件,缺省的方式是文本方式。两种方式的区别见前文
- ios::in: 文件以输入方式打开
- ios::out: 文件以输出方式打开
文本文件的读写
文本文件的读写很简单:用插入器(<<)向文件输出;用析取器(>>)从文件输入。
假设file1是以输入方式打开,file2以输出打开。示例如下:
file2<<"I Love You";//向文件写入字符串"I Love You"
int i;
file1>>i;//从文件输入一个整数值。
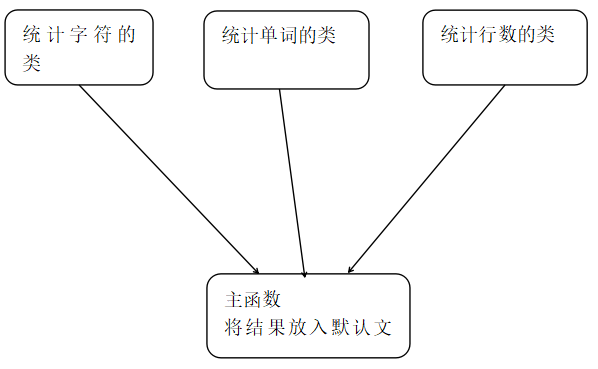
基本功能
- 支持 -c 统计字符数(char_count)
- 支持 -w 统计单词数(string_count)
- 支持 -l 统计总行数(line_count)
- 支持 -o 存入特定文件
拓展功能(待实现)
- 支持 -a 返回高级选项(代码行 空行 注释行)
- 支持 -s 递归处理符合条件的文件
二、基本功能模块:
一、实现字符数统计类
通过传参的方式将文件名以 (string filename)的方式传入类成员函数,利用fstream把文件以流的形式输出,把流输出到字符类型然后进行统计。
class CharCount
{
public:
int char_count(std::string infile)
{
std::fstream in;//文件读入流
in.open(infile, std::ios::in );//以读入打开,即如果不存在则打开失败
if (!in)
{
return -1;
}
while(!in.eof())
{
in>>c;
count++;
}
in.close();
return count;
}
private:
char c;
int count=-1;
};
二、实现单词数统计类
通过传参的方式将文件名以 (string filename)的方式传入类成员函数,利用fstream把文件以流的形式输出,把流输出到字符串类型然后进行统计,也可用getline(流,字符串变量,‘ ’)来统计,不过这种统计文件必须以空格结束,否则所统计的数少一。
class StringCount { public: int string_count(std::string infile) { std::fstream in;//文件读入流 in.open(infile, std::ios::in );//以读入打开,即如果不存在则打开失败 if (!in) { return -1; } while(1) { in>>s; count++; if(in.eof()) break; } in.close(); return count; } private: std::string s; int count=0; };
三、实现行数统计函数
通过传参的方式将文件名以 (string filename)的方式传入类成员函数,利用fstream把文件以流的形式输出,用getline(流,字符串变量,‘ ’)函数来统计,getline()以转行符结束。
class LineCount { public: int line_count(std::string infile) { std::fstream in;//文件读入流 in.open(infile, std::ios::in );//以读入打开,即如果不存在则打开失败 if (!in) { return -1; } while(!in.eof()) { getline(in,s,' '); count++; } in.close(); return count; } private: std::string s; int count=0; };
四、主函数模块:
调用类根据命令实现功能。
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { string Filename=argv[2]; if( !strcmp(argv[1],"-w"))//统计字符串 { StringCount ss; int count= ss.string_count(Filename); cout<<count<<endl; ofstream out; out.open("f:\m.txt",ios::app); out<<"文件名:"<<Filename; out<<",单词数:"<<count<<' ';//写入文件 out.close(); } if( !strcmp(argv[1],"-c"))//统计字符数 { CharCount cc; int count2= cc.char_count(Filename); cout<<count2<<endl; ofstream out; out.open("f:\m.txt",ios::app); out<<"文件名:"<<Filename; out<<",字符数:"<<count2<<' ';//写入文件 out.close(); } if( !strcmp(argv[1],"-l") )//统计行数 { LineCount ll; int count3= ll.line_count(Filename); cout<<count3<<endl; ofstream out; out.open("f:\m.txt",ios::app); out<<"文件名:"<<Filename; out<<",字符数:"<<count3<<' ';//写入文件 out.close(); } system("pause"); return 0; }
测试文件结果:
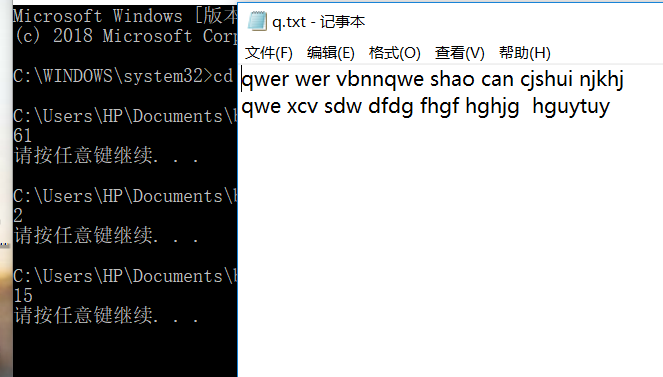

三、测试用例:
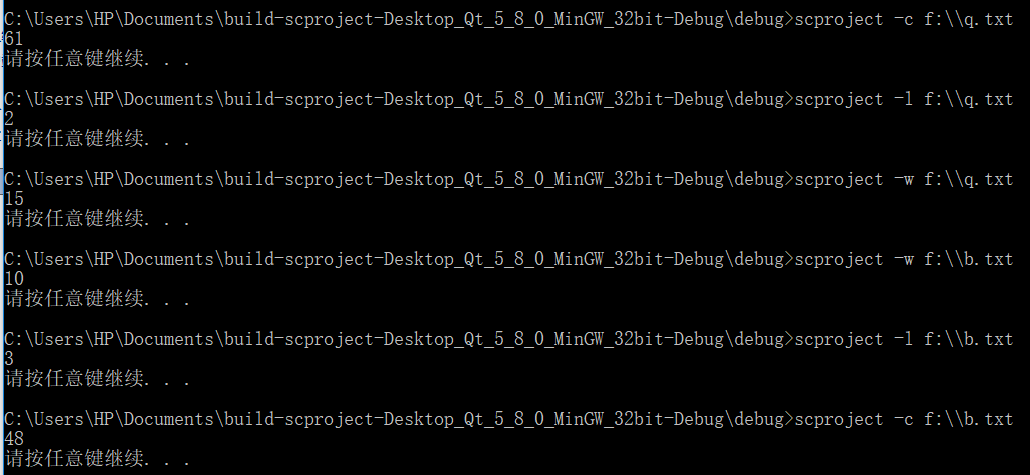

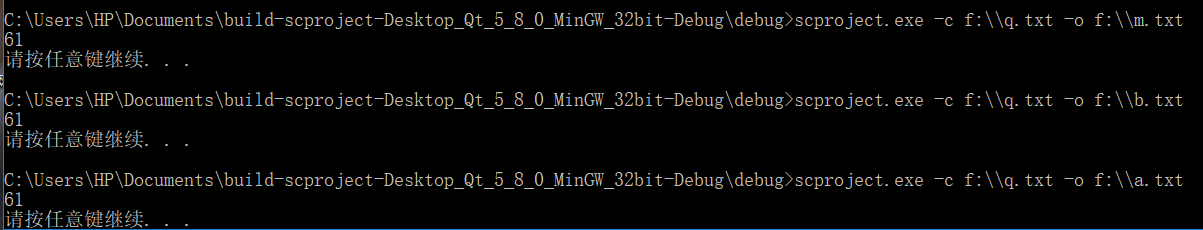

文件:

可执行文件
总结:
这个任务,我使用的是c++,由于c++是早些时候学习过的然后之后是没在使用过,这次机会我重新复习一次,这个项目让我学到了很多东西,我从不懂如何写代码到一步步实现功能,这次的代码我是使用的绝对路径,我实现了要求的基本功能,也清楚了qt生成的可执行文件是与原先代码所分离开的,刚开始一直找不到可执行文件,后来通过上网查询,要在path添加路径才能使用exe文件,也了解到从命令行写入的参数在代码中如何读取。本次的项目还有很多不足的地方还需要加以改善,比如把绝对路径改为相对路径。可以存到指定目录的,更多功能还待提高。
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/Rasin_Wu/article/details/79048094?utm_source=copy
首先完成PSP表格,对自己所做的项目进行大致的规划
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (小时) |
实际耗时 (小时) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
48 |
38 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
48 |
38 |
|
Development |
开发 |
21 |
20 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
3 |
4 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
2 |
3 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
2 |
2 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
1 |
1 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
4 |
3 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
4 |
4 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
3 |
2 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
2 |
2 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
7 |
5 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
3 |
3 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
2 |
1 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
2 |
1 |
|
合计 |
28 |
25 |