无聊心情不好时就做~
第二个条件注意看清楚....
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){ int n, d, x; double e, tp; cin >> n >> e >> d; int may = 0, ab = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> x; int sum = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= x; j++) { cin >> tp; if(tp < e) sum ++; } if (sum > x / 2) { if(x > d) //看题看仔细,并不是sum > d ab ++; else may ++; } } printf("%.1f%% %.1f%%
",(double)may * 100 / n, (double)ab * 100 / n);} |
求队伍得分最高的 队伍编号和队伍总得分。队员编号无意义。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define MEM(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))using namespace std;int main(){ int max_res = -1; int max_pos = -1; int n, x, y, z; scanf("%d",&n); int mp[1010]; MEM(mp,0); while(n--) { scanf("%d-%d%d",&x, &y, &z); mp[x] += z; if(mp[x] > max_res) { max_res = mp[x]; max_pos = x; } } printf("%d %d
",max_pos,max_res);} |

无FUCK说
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){ string str; cin >> str; int P = 0, A = 0, T = 0, e = 0, s = 0, t = 0; for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) { if(str[i] == 'P')P++; else if(str[i] == 'A')A++; else if(str[i] == 'T')T++; else if(str[i] == 'e')e++; else if(str[i] == 's')s++; else if(str[i] == 't')t++; } while(P > 0 || A > 0 || T > 0 || e > 0 || s > 0 || t > 0) { if(P > 0) printf("P"),P--; if(A > 0) printf("A"),A--; if(T > 0) printf("T"),T--; if(e > 0) printf("e"),e--; if(s > 0) printf("s"),s--; if(t > 0) printf("t"),t--; }} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){ string bad, str; getline(cin,bad); // 不能用cin getline(cin,str); int op[150]; memset(op,0,sizeof(op)); for(int i = 0; i < bad.size(); i++) { op[bad[i]]++; if(bad[i] >= 'A' && bad[i] <= 'Z') op[tolower(bad[i])]++; } for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) { if(op[ str[i] ] == 0) { if(str[i] >= 'A' && str[i] <= 'Z' && op['+'] > 0) continue; else cout << str[i]; } } cout << endl;} |
13 是 tam 不是 tam tret,tam 是 13.....所以引发了格式问题,WA了一次,PE了一次,水题。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;string mp1[] = {"tret", "jan", "feb", "mar", "apr", "may", "jun", "jly", "aug", "sep", "oct", "nov", "dec"};string mp2[] = {"haha", "tam", "hel", "maa", "huh", "tou", "kes", "hei", "elo", "syy", "lok", "mer", "jou"};void solve1(string s){ int x = 0; for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) x = x * 10 + s[i] - '0'; int tp1, tp2; tp2 = x % 13; x /= 13; tp1 = x % 13; if(tp1 != 0) cout << mp2[tp1]; if(tp1 ==0) cout << mp1[tp2]; else if(tp2 != 0) cout << ' ' << mp1[tp2]; cout << endl;}void solve2(string s){ string tmp = ""; int sum = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) tmp += s[i]; for(int i = 0; i < 13; i++) { if(mp1[i] == tmp) sum += i; else if(mp2[i] == tmp) sum += 13 * i; } tmp = ""; for(int i = 4; i < s.size(); i ++) tmp += s[i]; for(int i = 0; i < 13; i++) { if(mp1[i] == tmp) sum += i; else if(mp2[i] == tmp) sum += 13 * i; } cout << sum << endl;}int main(){ int n; cin >> n; getchar(); while(n--) { string s; getline(cin,s); if(s[0] >= '0' && s[0] <= '9') solve1(s); else solve2(s); }}//代码 |
无FUCK说
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){ int n, m; cin >> n >> m; int mp[110][110]; for(int i = 1; i <= n + 2; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) scanf("%d",&mp[i][j]); for(int i = 3; i <= n + 2; i++) { int sum = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) sum += mp[1][j] * !(mp[2][j] ^ mp[i][j]); printf("%d
",sum); }} |
这题去年就做了,一直有2个测试点没过。因为精度丢失~
例如 -0.000001 得到的是 - 0.00 所以会出现 -0.00+-0.00i 这种错误的结果,正确应该是 0.00+0.00i
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){ double r1, r2, p1, p2, r, p, x, y; cin >> r1 >> p1 >> r2 >> p2; r = r1 * r2; p = p1 + p2; x = r * cos(p) + 0.0001;//防止精度丢失 y = r * sin(p) + 0.0001; printf("%.2f",x); if(y >= 0) printf("+"); printf("%.2fi
",y);} |
两个坑:1.并不包括边界 2.两个分数没说谁大谁小
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int gcd(int x,int y){ while(y != 0) { int tp = y; y = x % y; x = tp; } return x;}int main() { int n1, m1, n2, m2, k; scanf("%d/%d %d/%d %d", &n1, &m1, &n2, &m2, &k); if(n1 * m2 > n2 * m1) //坑1 { swap(n1, n2); swap(m1, m2); } int num = 1; bool flag = false; while(n1 * k >= m1 * num) num++; //边界不包括,所以用 >= while(n1 * k < m1 * num && m2 * num < n2 * k) // 边界不包括,所以用 < { if(gcd(num, k) == 1) { if(flag) printf(" "); flag = true; printf("%d/%d", num, k); } num++; }} |

好可怕,大模拟...注意爆int、爆ll
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#include <stdlib.h>typedef long long LL;using namespace std;LL gcd(LL x, LL y) { LL tmp; while(x % y != 0) { tmp = x % y; x = y; y = tmp; } return y;}string int_to_string(LL x,LL y) { char tmp[100]; string ans = ""; bool flag = false; //negative if((x * y) < 0) { flag = true; x = abs(x); y = abs(y); } LL gd = gcd(x, y); LL zi = x / gd; LL mu = y / gd; LL k = zi / mu; zi %= mu; if(k == 0 && zi == 0) return "0"; if(k > 0) { sprintf(tmp, "%lld", k); ans += tmp; if(zi > 0) ans += ' '; } if(zi > 0) { sprintf(tmp, "%lld", zi); ans += tmp; ans += '/'; sprintf(tmp, "%lld", mu); ans += tmp; } if(flag) { ans = "(-" + ans; ans += ")"; } return ans;}string solve(LL x1, LL y1, LL x2, LL y2, int op) { LL zi, mu; if(op == 0) { mu = y1 * y2 / gcd(y1, y2); zi = x1 * (mu / y1) + x2 * (mu / y2); } else if(op == 1) { mu = y1 * y2 / gcd(y1, y2); zi = x1 * (mu / y1) - x2 * (mu / y2); } else if(op == 2) { zi = x1 * x2; mu = y1 * y2; } else { zi = x1 * y2; mu = x2 * y1; if(mu == 0) return "Inf"; } string ans = int_to_string(zi, mu); return ans;}int main() { LL a1, a2, b1, b2; scanf("%lld/%lld", &a1, &b1); scanf("%lld/%lld", &a2, &b2); string a = int_to_string(a1, b1); string b = int_to_string(a2, b2); char mp[] = {'+','-','*','/'}; LL gd1 = gcd(a1, b1); LL gd2 = gcd(a2, b2); for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { cout << a << " " << mp[i] << " " << b << " = " << solve(a1/gd1, b1/gd1, a2/gd2, b2/gd2, i) << endl; //约分防止爆LL }} |

有上一题..这题直接A...
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#include <stdlib.h>typedef long long LL;using namespace std;LL gcd(LL x, LL y) { LL tmp; while(x % y != 0) { tmp = x % y; x = y; y = tmp; } return y;}LL lcm(LL x, LL y) { LL tmp; LL a = x, b = y; while(x % y != 0) { tmp = x % y; x = y; y = tmp; } return a * b / y;}string int_to_string(LL x,LL y) { char tmp[100]; string ans = ""; bool flag = false; //negative if((x * y) < 0) { flag = true; x = abs(x); y = abs(y); } LL gd = gcd(x, y); LL zi = x / gd; LL mu = y / gd; LL k = zi / mu; zi %= mu; if(k == 0 && zi == 0) return "0"; if(k > 0) { sprintf(tmp, "%lld", k); ans += tmp; if(zi > 0) ans += ' '; } if(zi > 0) { sprintf(tmp, "%lld", zi); ans += tmp; ans += '/'; sprintf(tmp, "%lld", mu); ans += tmp; } if(flag) { ans = "-" + ans; } return ans;}int main() { LL a, b; int n; cin >> n; LL zi = 0; LL mu = 1; while(n--) { scanf("%lld/%lld", &a, &b); int lm = lcm(b,mu); zi = zi * (lm / mu); zi += a * (lm / b); mu = lm; int gd = gcd(zi, mu); zi /= gd; mu /= gd; } cout << int_to_string(zi, mu) << endl;} |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main() { int n, cnt = 0; char a[50], b[50]; double temp, sum = 0.0; cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%s", a); sscanf(a, "%lf", &temp); //从一个字符串中读进与指定格式相符的数据 sprintf(b, "%.2lf",temp); //字符串格式化命令,主要功能是把格式化的数据写入某个字符串中 int flag = 0; for(int j = 0; j < strlen(a); j++) { if(a[j] != b[j]) { flag = 1; } } if(flag || temp < -1000 || temp > 1000) { printf("ERROR: %s is not a legal number
", a); continue; } else { sum += temp; cnt++; } } if(cnt == 1) { printf("The average of 1 number is %.2lf", sum); } else if(cnt > 1) { printf("The average of %d numbers is %.2lf", cnt, sum / cnt); } else { printf("The average of 0 numbers is Undefined"); } return 0;} |
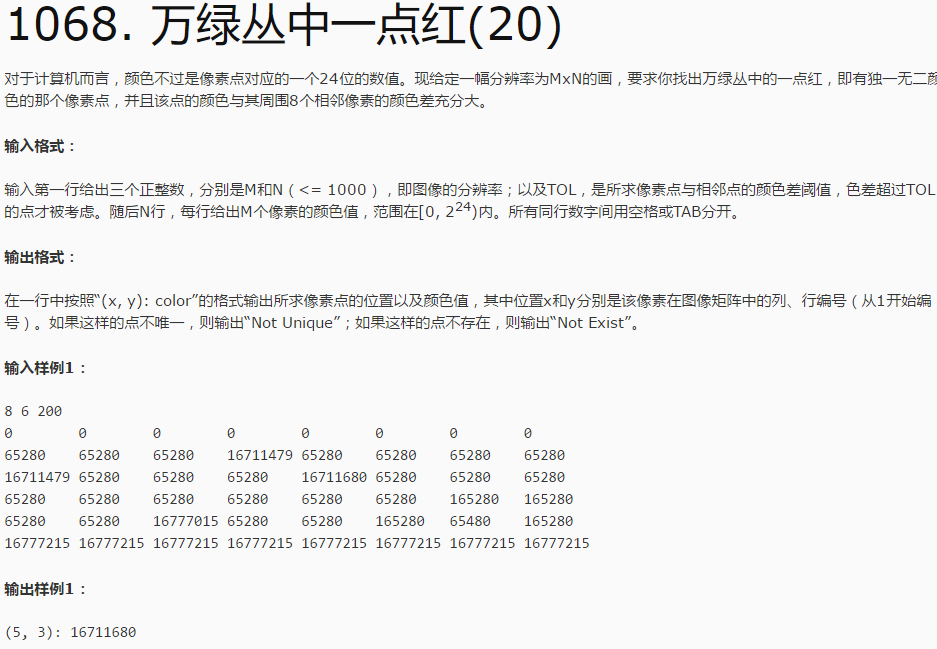
两个坑,如注释
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int mp[1100][1100];map<int, int> check;int main() {// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); int m, n, tol; check.clear(); scanf("%d%d%d",&m, &n, &tol); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { scanf("%d", &mp[i][j]); check[mp[i][j]]++; //独一无二 } } int fx[] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1}; int fy[] = {1, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1}; int i, j, k; vector< pair<int,int> > ans; for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(j = 1; j <= m; j++) { if(check[mp[i][j]] != 1) continue; for(k = 0; k < 8; k++) { int x = i + fx[k]; int y = j + fy[k]; if(x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > m) continue;//边界也可以是万绿丛中一点红 if( abs(mp[i][j] - mp[x][y]) <= tol ) break; } if(k == 8) ans.push_back( make_pair(i,j) ); } } if(ans.size() == 0) puts("Not Exist"); else if(ans.size() > 1) puts("Not Unique"); else printf("(%d, %d): %d", ans[0].second, ans[0].first, mp[ans[0].first][ans[0].second]);} |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main() { int m, n, s; cin >> m >> n >> s; set<string>st; vector<string>vec; string a; while(m--) { cin >> a; vec.push_back(a); } if(vec.size() <= s - 1) { puts("Keep going..."); return 0; } for(int i = s - 1; i < vec.size(); i = i+n) { if( st.find(vec[i]) == st.end() ) { st.insert(vec[i]); cout << vec[i] << endl; } else i -= (n - 1); //经过 i = i + n 之后,则变成了下一个 } return 0;} |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define scf0(a) scanf("%s",&a)#define scf1(a) scanf("%d",&a)#define scf2(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)#define scf3(a,b,c) scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)#define MEM(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))#define pii pair<int,int>#define pdd pair<double,double>#define LL long longusing namespace std;struct Node{ int data, next;}node[100100];int main() { int add0, n, k, add, data, next; scf3(add0, n, k); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scf3(add, data, next); node[add].data = data; node[add].next = next; } vector<int>vec; while(add0 != -1) { vec.push_back(add0); add0 = node[add0].next; } int t = vec.size() / k; //注意要vec.size / k,因为可能中途某些结点用不到,所以是小于等于N的 for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) //是每k个结点反转 reverse(vec.begin() + i*k, vec.begin() + (i + 1)*k); for(int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { if( i < vec.size() - 1) printf("%05d %d %05d
", vec[i], node[vec[i]].data, vec[i+1]); else printf("%05d %d -1
", vec[i], node[vec[i]].data); }} |

模拟。注意scanf字符的用法...
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define scf0(a) scanf("%s", a)#define scf1(a) scanf("%d",&a)#define scf2(a, b) scanf("%d%d",&a, &b)#define scf3(a, b, c) scanf("%d%d%d",&a, &b, &c)#define MEM(a,b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))using namespace std;struct Node { int no, wa, sco; vector<char>ans;}node[110];bool cmp(const Node &a, const Node &b) { if(a.wa == b.wa) return a.no < b.no; else return a.wa > b.wa;}int main() { int n, m; int a, b, c; char x, y; MEM(node, 0); scf2(n, m); getchar(); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { scf3(a,b,c); node[i].no = i; node[i].sco = a; getchar(); while(c--) { scanf("%c%*c", &y); (node[i].ans).push_back(y); } } int tot[1010]; //sco of student MEM(tot, 0); vector<char>tp; for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { scanf("(%d%*c", &a); tp.clear(); while(a--) { scanf("%c%*c", &y); tp.push_back(y); } getchar();//读取空格/回车 if( tp.size() != (node[i].ans).size() ) { node[i].wa++; continue; } sort( tp.begin(), tp.end() ); int k; for(k = 0; k < tp.size(); k++) { if(tp[k] != node[i].ans[k]) break; } if(k == tp.size()) tot[j] += node[i].sco; else node[i].wa++; } } for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) cout << tot[j] << endl; sort(node+1, node+m+1, cmp); if(node[1].wa == 0) { puts("Too simple"); return 0; } cout << node[1].wa; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { if(node[i].wa == node[1].wa) cout << ' ' << node[i].no; else break; } cout << endl;} |