流的原理
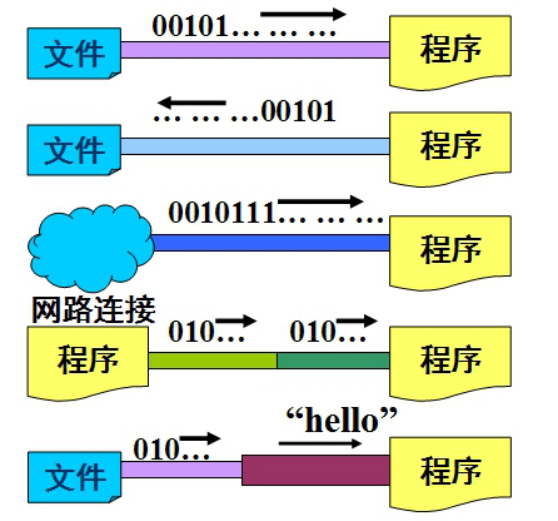
1) 在 Java 程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流”
(stream) 方式进行;
2) J2SDK 提供了各种各样的“流”类,用以获取不同种类的
数据;程序中通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
3) Java 的流类型一般位于 java.io 包中
IO流基本概念:----->https://www.cnblogs.com/oubo/archive/2012/01/06/2394638.html
文件字节流
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
使用 FileInputStream 读取文件内容
1) abstract int read( ); //一次读取一个字节,读到文件末尾为-1
2) int read( byte b[ ] ); //从该输入流读取最多 b.length个字节的数据为字节数组。
3) int read( byte b[ ], int off, int len );
4) int available( ); //估算文件字节数
5) close( ); //关闭文件输入流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(new File("D:\test.txt")); //在此之前"D:\test.txt"不存在则new File(path)
如果"D:\test.txt"已经存在,则不需new,直接FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt");即可

1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class TestInpuStream { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 //(1)数据源与应用程序之间搭建管道 9 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(new File("D:\test.txt")); 10 //(2)从数据源开始向程序中读数据 11 int count=fis.available(); 12 System.out.println("文件中大概有"+count+"个字节"); 13 14 //中转站比较小,一次读一个字节 15 //System.out.println(fis.read()); //读取一个字节 16 //System.out.println(fis.available()); //文件中还有多少字节未读取 17 18 int buf=0;//存储读到的字节 19 int i=0; 20 while((buf=fis.read())!=-1){ 21 i++; 22 System.out.print((char)buf); 23 } 24 //(3)关闭 25 fis.close(); 26 System.out.println(i); 27 } 28 }

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 public class TestInputStream2 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 6 //(1)搭桥 7 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"); 8 //(2)创建大一些的中转站 9 byte [] buf=new byte[1024]; 10 int len=0;//用于存储每次读到的实际字节 11 int i=0; 12 while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){ 13 i++; 14 //借助String类构造方法 15 System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len)); 16 } 17 //(3)关闭 18 fis.close(); 19 System.out.println(i); 20 } 21 }
使用 FileOutputStream 写内容到文件
1) abstract void write( int b ); //一次写一个字节
2) void write( byte b[ ] ); //将 b.length个字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流。
3) void write( byte b[ ], int off, int len );
4) void flush( );//刷新缓冲区
5) void close( ); //关闭

1 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 public class TestFileOutputStream { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //(1)搭桥 8 FileOutputStream fos=null; 9 try { 10 fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt",true);//如果有true这个参数则写入方式为追加,前提是有这个文件 11 //(2)写数据,一次写一个字节 12 //fos.write(97); 13 //(2)一次写多个字节 14 byte [] buf="helloworld".getBytes();//使用平台的默认字符集将此 String编码为字节序列,将结果存储到新的字节数组中。 15 fos.write(buf); 16 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 17 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } catch (IOException e) { 20 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 }finally{ 23 //(3)关闭 24 try { 25 if(fos!=null){ 26 fos.close(); 27 } 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 }
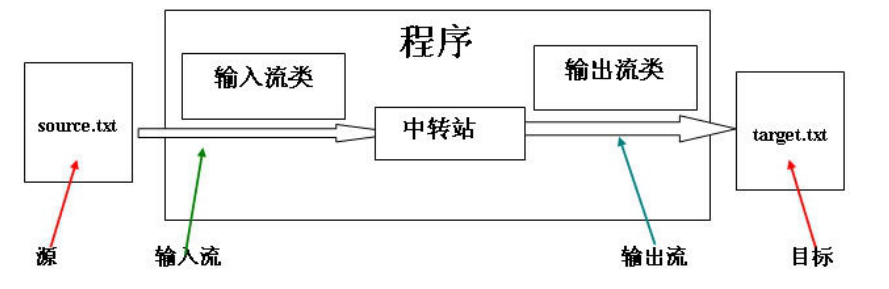
使用字节流实现文件复制
文件复制的原理
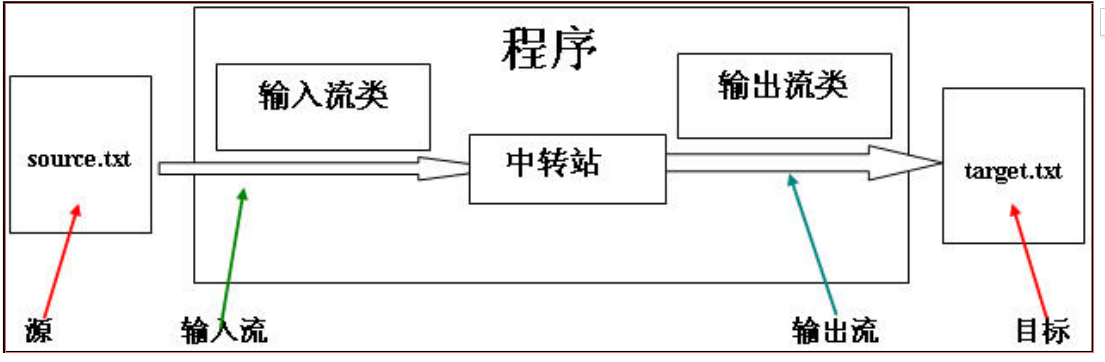
文件复制的代码实现
1.没经过异常处理前的代码

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 4 public class TestFileCopy { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //数据源是文件 8 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"); 9 //目的地 10 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\tager.txt"); 11 12 int b = 0;//用于存储读到的字节,中转站 13 while( (b = fis.read()) != -1 ) { 14 //写入文件 15 fos.write(b); 16 } 17 //关闭 18 fos.close(); 19 fis.close(); 20 } 21 }
2.经过异常处理的代码:选中要处理的代码块(7~16行),按住Alt+Shift+Z,选第一个添加try/cath,写个finally把关闭io流放到里面去,在finally还要处理关闭io异常
先分别为两个关闭io流添加try/cath,在try中添加判断,如果io流不为null再关闭(为null会抛出一个空指针异常), 每次只读一个字节太费io,改为一次读字节数组个字节

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class TestFileCopy { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //数据源是文件 10 FileInputStream fis = null; 11 //目的地 12 FileOutputStream fos = null; 13 try { 14 fis = new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"); 15 fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\tager.txt"); 16 byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//中转站 17 int len = 0;//用于存储每次读到的字节个数 18 while( ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1)) { 19 fos.write(buf,0,len); 20 } 21 /*int b = 0;//用于存储读到的字节,中转站 22 while( (b = fis.read()) != -1 ) { 23 //写入文件 24 fos.write(b); 25 }*/ 26 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 27 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } catch (IOException e) { 30 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 }finally {//无论程序是否产生异常,最后io都要关闭 33 //关闭 34 try { 35 if(fos != null) { 36 fos.close(); 37 } 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 try { 43 if(fis != null) { 44 fis.close(); 45 } 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 }
文件字符流
Reader/Writer
使用 Reader 读取文件内容
1) int read( );
2) int read( char [ ]cbuf );
3) int read( char [ ]cbuf, int off, int len ); //将字符读入数组的一部分 cbuf目标缓冲区 off开始存储字符的偏移量 len要读取的最大字符数
4) int available( );
5) close( );

1 import java.io.FileReader; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 public class TestFileReader { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 6 //(1)搭桥 7 FileReader reader=new FileReader("D:\test.txt"); 8 //(2)读取 9 //int b=reader.read(); //读到的字符的int类型数据 10 //System.out.println((char)b); 11 /*int b=0;//用于存储每次读到的字符数据的整数值 12 while((b=reader.read())!=-1){ 13 System.out.println((char)b); 14 }*/ 15 char [] cbuf=new char[1024]; 16 int len=0;//用于存储读到的字符的个数 17 while((len=reader.read(cbuf))!=-1){ 18 System.out.println(new String(cbuf,0,len)); 19 } 20 //(3)关闭 21 reader.close(); 22 } 23 }
使用 Writer 写内容到文件
1) void write( int c );
2) void write( char[]cbuf);
3) abstract void write( char [ ]cbuf, int off, int len ); //cbuf缓冲区 off从中开始编写字符的偏移量 要写入的 len数
4) void write(String str); //直接把字符串str写入
5) abstract void flush( ); //刷新缓冲区
6) void close( );

1 import java.io.FileWriter; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 public class TestWriter { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 //创建对象 7 FileWriter writer=null; 8 try { 9 writer = new FileWriter("D:\b.txt"); 10 //写数据 11 writer.write("你好吗?");//写到了缓冲区中, 12 writer.flush(); //刷新缓冲区,如不刷新则需关闭才能写入 13 } catch (IOException e) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 }finally{ 17 //关闭 18 try { 19 if(writer!=null){ 20 writer.close(); 21 } 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 }
缓冲字节流
BufferedInputStream / BufferedOutputStream
FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 是节点流

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class Filecopy { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 9 //数据源 10 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("F:\java学习\【API】jdk api 1.8_google.CHM"); 11 //目的地 12 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("F:\java学习\【API】jdk api 1.8_google2.CHM"); 13 //读数据和写数据 14 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 15 byte [] buf = new byte[1024];//中转站 16 int len = 0; 17 while( (len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) { 18 fos.write(buf, 0, len); 19 fos.flush();//手动刷新缓冲区 20 } 21 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 22 System.out.println("文件复制一共用了"+(end-start)+"毫秒");//文件复制一共用了1143毫秒 23 //关闭 24 fos.close(); 25 fis.close(); 26 } 27 }
文件大小41M,用节点流在本机(机子性能较差)跑为1143毫秒。
BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream 是处理流(包装
流)
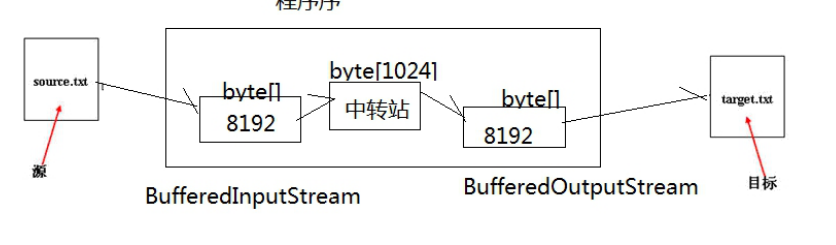
1) 读文件和写文件都使用了缓冲区,减少了读写次数,从而
提高了效率
2) 当创建这两个缓冲流的对象时时,会创建了内部缓冲数组,
缺省使用 32 字节大小的缓冲区.
3) 当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直
接访问缓冲区
4) 当写入数据时,首先写入缓冲区,当缓冲区满时,其中的
数据写入所连接的输出流。使用方法 flush()可以强制将缓
冲区的内容全部写入输出流
5) 关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反.只要关闭高层流即可,
关闭高层流其实关闭的底层节点流
6) Flush 的使用:手动将 buffer 中内容写入文件

1 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 2 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 3 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 public class TestCopy { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 12 //数据源 13 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("F:\java学习\【API】jdk api 1.8_google.CHM"); 14 //目的地 15 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("F:\java学习\【API】jdk api 1.8_google2.CHM"); 16 17 /* 18 * 使用缓冲流 19 */ 20 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 21 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 22 23 //读数据和写数据 24 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 byte [] buf = new byte[1024];//中转站 26 int len = 0; 27 while( (len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) { 28 bos.write(buf, 0, len); 29 bos.flush();//手动刷新缓冲区 30 } 31 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 32 System.out.println("文件复制一共用了"+(end-start)+"毫秒");//文件复制一共用了863毫秒 33 //关闭 34 bos.close(); 35 bis.close(); 36 } 37 }
同样的文件用缓冲流(处理流)时间为863
缓冲字符流
BufferedReader
readLine() 读取一个文本行的数据
BufferedWriter
newLine();写入一个行分隔符。

1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileReader; 5 import java.io.FileWriter; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 8 public class TestBuffered { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 //缓冲字符流 12 BufferedReader br = null; 13 BufferedWriter bw = null; 14 try { 15 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\a.txt")); 16 bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\copya.txt")); 17 String line = null;//用于存储读到的字符串 18 while( (line = br.readLine()) != null) { 19 bw.write(line); 20 bw.newLine(); 21 bw.flush(); 22 } 23 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 24 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 }finally { 30 try { 31 if(bw != null) { 32 bw.close(); 33 } 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 try { 39 if(br != null) { 40 br.close(); 41 } 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 }
纯文本使用字符流,提高读取效率和写入效率使用缓冲字符流,其他情况都可使用字节流来完成
