题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4940
Destroy Transportation system
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 21 Accepted Submission(s): 17
Problem Description
Tom is a commander, his task is destroying his enemy’s transportation system.
Let’s represent his enemy’s transportation system as a simple directed graph G with n nodes and m edges. Each node is a city and each directed edge is a directed road. Each edge from node u to node v is associated with two values D and B, D is the cost to destroy/remove such edge, B is the cost to build an undirected edge between u and v.
His enemy can deliver supplies from city u to city v if and only if there is a directed path from u to v. At first they can deliver supplies from any city to any other cities. So the graph is a strongly-connected graph.
He will choose a non-empty proper subset of cities, let’s denote this set as S. Let’s denote the complement set of S as T. He will command his soldiers to destroy all the edges (u, v) that u belongs to set S and v belongs to set T.
To destroy an edge, he must pay the related cost D. The total cost he will pay is X. You can use this formula to calculate X:
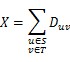
After that, all the edges from S to T are destroyed. In order to deliver huge number of supplies from S to T, his enemy will change all the remained directed edges (u, v) that u belongs to set T and v belongs to set S into undirected edges. (Surely, those edges exist because the original graph is strongly-connected)
To change an edge, they must remove the original directed edge at first, whose cost is D, then they have to build a new undirected edge, whose cost is B. The total cost they will pay is Y. You can use this formula to calculate Y:
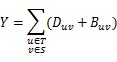
At last, if Y>=X, Tom will achieve his goal. But Tom is so lazy that he is unwilling to take a cup of time to choose a set S to make Y>=X, he hope to choose set S randomly! So he asks you if there is a set S, such that Y<X. If such set exists, he will feel unhappy, because he must choose set S carefully, otherwise he will become very happy.
Let’s represent his enemy’s transportation system as a simple directed graph G with n nodes and m edges. Each node is a city and each directed edge is a directed road. Each edge from node u to node v is associated with two values D and B, D is the cost to destroy/remove such edge, B is the cost to build an undirected edge between u and v.
His enemy can deliver supplies from city u to city v if and only if there is a directed path from u to v. At first they can deliver supplies from any city to any other cities. So the graph is a strongly-connected graph.
He will choose a non-empty proper subset of cities, let’s denote this set as S. Let’s denote the complement set of S as T. He will command his soldiers to destroy all the edges (u, v) that u belongs to set S and v belongs to set T.
To destroy an edge, he must pay the related cost D. The total cost he will pay is X. You can use this formula to calculate X:
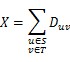
After that, all the edges from S to T are destroyed. In order to deliver huge number of supplies from S to T, his enemy will change all the remained directed edges (u, v) that u belongs to set T and v belongs to set S into undirected edges. (Surely, those edges exist because the original graph is strongly-connected)
To change an edge, they must remove the original directed edge at first, whose cost is D, then they have to build a new undirected edge, whose cost is B. The total cost they will pay is Y. You can use this formula to calculate Y:
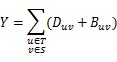
At last, if Y>=X, Tom will achieve his goal. But Tom is so lazy that he is unwilling to take a cup of time to choose a set S to make Y>=X, he hope to choose set S randomly! So he asks you if there is a set S, such that Y<X. If such set exists, he will feel unhappy, because he must choose set S carefully, otherwise he will become very happy.
Input
There are multiply test cases.
The first line contains an integer T(T<=200), indicates the number of cases.
For each test case, the first line has two numbers n and m.
Next m lines describe each edge. Each line has four numbers u, v, D, B.
(2=<n<=200, 2=<m<=5000, 1=<u, v<=n, 0=<D, B<=100000)
The meaning of all characters are described above. It is guaranteed that the input graph is strongly-connected.
The first line contains an integer T(T<=200), indicates the number of cases.
For each test case, the first line has two numbers n and m.
Next m lines describe each edge. Each line has four numbers u, v, D, B.
(2=<n<=200, 2=<m<=5000, 1=<u, v<=n, 0=<D, B<=100000)
The meaning of all characters are described above. It is guaranteed that the input graph is strongly-connected.
Output
For each case, output "Case #X: " first, X is the case number starting from 1.If such set doesn’t exist, print “happy”, else print “unhappy”.
Sample Input
2 3 3 1 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 2 2 3 3 1 2 10 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 2 2
Sample Output
Case #1: happy Case #2: unhappyHintIn first sample, for any set S, X=2, Y=4. In second sample. S= {1}, T= {2, 3}, X=10, Y=4.
Author
UESTC
Source
官方题解:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6bddecdc0102uzka.html
寻找是否存在能单独作为S集合的点!
代码例如以下:
//#pragma warning (disable:4786)
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
typedef long long LL;
#define N 1017
LL X[N], Y[N];
void init()
{
memset(X, 0, sizeof(X));
memset(Y, 0, sizeof(Y));
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
int u, v, D, B;
int t;
int cas = 0;
int flag = 0;
int i;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
init();
flag = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &n,&m);
for(i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &u, &v, &D, &B);
X[u]+=D;
Y[v]+=(D+B);
}
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(Y[i] < X[i])
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
printf("Case #%d: unhappy
",++cas);
else
printf("Case #%d: happy
",++cas);
}
return 0;
}
贴一发官方题解:

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define maxn 209
#define maxm 20000
#define INF 1e9
using namespace std;
struct Edge
{
int v,cap,next;
}edge[maxm];
int n,tot,src,des;
int head[maxn],h[maxn],gap[maxn],B[maxn];
void addedge(int u,int v,int cap)
{
edge[tot].v=v;
edge[tot].cap=cap;
edge[tot].next=head[u];
head[u]=tot++;
edge[tot].v=u;
edge[tot].cap=0;
edge[tot].next=head[v];
head[v]=tot++;
}
int dfs(int u,int cap)
{
if(u==des)return cap;
int minh=n-1;
int lv=cap,d;
for(int e=head[u];e!=-1;e=edge[e].next)
{
int v=edge[e].v;
if(edge[e].cap>0)
{
if(h[v]+1==h[u])
{
d=min(lv,edge[e].cap);
d=dfs(v,d);
edge[e].cap-=d;
edge[e^1].cap+=d;
lv-=d;
if(h[src]>=n)return cap-lv;
if(lv==0)
break;
}
minh=min(minh,h[v]);
}
}
if(lv==cap)
{
--gap[h[u]];
if(gap[h[u]]==0)
h[src]=n;
h[u]=minh+1;
++gap[h[u]];
}
return cap-lv;
}
int sap()
{
int flow=0;
memset(gap,0,sizeof(gap));
memset(h,0,sizeof(h));
gap[0]=n;
while(h[src]<n)flow+=dfs(src,INF);
return flow;
}
int main()
{
int N,M;
int cot=1;
int CAS;
scanf("%d", &CAS);
while(CAS--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&N,&M);
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(B,0,sizeof(B));
tot=0;src=0;des=N+1;n=des+1;
for(int i=1;i<=M;i++)
{
int u,v,b,l;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&u,&v,&b,&l);
addedge(u,v,l);
B[v]+=b;B[u]-=b;
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
if(B[i]>0)
{
addedge(src,i,B[i]);
sum+=B[i];
}
else if(B[i]<0)
{
addedge(i,des,-B[i]);
}
}
int flow=sap();
if(flow==sum)
{
printf("Case #%d: happy
",cot++);
}
else
{
printf("Case #%d: unhappy
",cot++);
}
}
return 0;
}


