ApplicationContext的继承体系
applicationContext:接口类型,代表应用上下文,可以通过 实例获得 Spring 容器中的 Bean 对象。
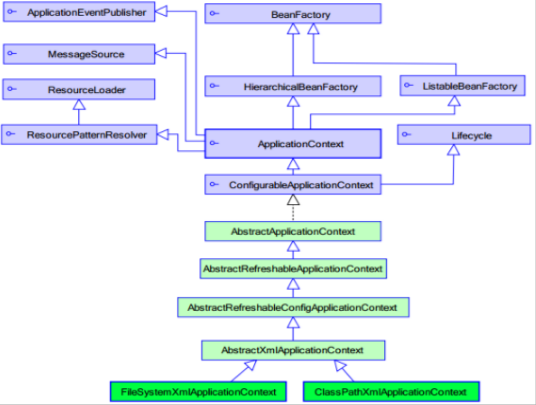
上图中 紫色是接口 。
ApplicationContext的实现类:
1)ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 它是从类的根路径下加载配置文件 推荐使用这种
2)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 它是从磁盘路径上加载配置文件,配置文件可以在磁盘的任意位置。
3)AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 当使用注解配置容器对象时,需要使用此类来创建 spring 容器。它用来读取注解。
意思就是说 我们可以从这3个实现类中 获取Bean对象。
详解:
其中第一个我们用过 就是直接通过本地的XMl中获取,,,例如:
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("store.xml");
其中 store.xml本项目中Spring自动寻找的根路径。
2.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
他是写入 绝对路径 ,例:
ApplicationContext app = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:\Users\Bi-Hu\IdeaProjects\Spring\src\main\resources\store.xml");
3.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
待写....
getBean()方法使用
我们看一下 getBean的源代码:
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException { assertBeanFactoryActive(); return getBeanFactory().getBean(name); } public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException { assertBeanFactoryActive(); return getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType); }
他有两个构造,
一个String类型的、一个Class<T> 类型的。
String类型那个 参数是配置文件Bean标签的id 我们getBean的时候要强转。 例:
HelloServiceImpl service = (HelloServiceImpl)app.getBean("Service");
Class<T> 那个参数是字节码文件名,然后他不需要强转,因为字节码文件就很好的说明了它是什么类型。 例:
HelloServiceImpl service = app.getBean(HelloServiceImpl.class);
所以这里 如果配置文件中 存在多个bean 推荐用id
如果存在单独一个 推荐用Class