1053 Path of Equal Weight (30分)
Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
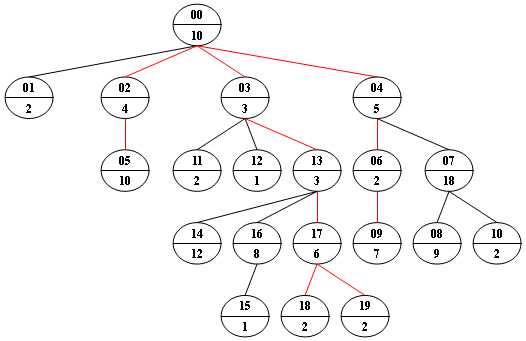
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let's consider the tree showed in the following figure: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in the figure.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0, the number of nodes in a tree, M (<), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence { is said to be greater than sequence { if there exists 1 such that Ai=Bi for ,, and Ak+1>Bk+1.
Sample Input:
20 9 24
10 2 4 3 5 10 2 18 9 7 2 2 1 3 12 1 8 6 2 2
00 4 01 02 03 04
02 1 05
04 2 06 07
03 3 11 12 13
06 1 09
07 2 08 10
16 1 15
13 3 14 16 17
17 2 18 19
Sample Output:
10 5 2 7
10 4 10
10 3 3 6 2
10 3 3 6 2
行吧,又是一道想杀死自己的题目。
这题,一上来愣头青写了一发,结果第一个样例死活wrong。吐了。
原因呢?是因为没有认真审题(其实就是菜),题目要求路径起点必须是root,重点必须是leaf node.....
行吧,我知道自己菜了。微笑脸.jpg
顺便强烈推荐一下这题我的写法,我存图用的是链式前向星,这个数据结构是真的好用,干啥都好,有需要的兄弟可以
传送门走一波/xyx
哦,对了,还记录一个小插曲。
如下
我那未编辑完且未发送的自信和躁动...还专门找了个算法笔记的pdf去看了看,结果人家一上来就告诉我我错哪了....
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <vector> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int maxn = 100 + 5; 8 9 int weight[maxn]; 10 11 int n, m, s; 12 13 struct Edge { 14 int to, next; 15 } edges[maxn * maxn]; 16 17 int head[maxn], cnt; 18 19 void init() { 20 memset(head, -1, sizeof head); 21 cnt = 2; 22 } 23 24 void addedge(int u, int v) { 25 edges[cnt].to = v; edges[cnt].next= head[u]; 26 head[u] = cnt ++; 27 } 28 29 vector <int> path; 30 vector <int> ans[maxn]; 31 32 int tot, tot_path; 33 34 35 void dfs(int u) { 36 if(tot == s && !~head[u]) { 37 ans[tot_path ++] = path; 38 return; 39 } else if(tot > s) { 40 return; 41 } 42 for(int k = head[u]; ~k; k = edges[k].next) { 43 int v = edges[k].to; 44 tot += weight[v]; 45 path.push_back(weight[v]); 46 dfs(v); 47 tot -= weight[v]; 48 path.pop_back(); 49 } 50 } 51 52 bool cmp(vector <int> a, vector <int> b) { 53 for(int i = 0; i < min(a.size(), b.size()); i ++) { 54 if(a[i] != b[i]) return a[i] > b[i]; 55 } 56 return a.size() > b.size(); 57 } 58 59 int main() { 60 init(); 61 scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &s); 62 for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { 63 scanf("%d", &weight[i]); 64 } 65 int u, v, num; 66 while(m --) { 67 scanf("%d %d", &u, &num); 68 while(num --) { 69 scanf("%d", &v); 70 addedge(u, v); 71 } 72 } 73 for(int i = 0; i < 1; i ++) { 74 path.clear(); 75 tot = weight[i]; 76 path.push_back(weight[i]); 77 dfs(i); 78 } 79 sort(ans, ans + tot_path, cmp); 80 for(int i = 0; i < tot_path; i ++) { 81 for(int j = 0; j < ans[i].size(); j ++) { 82 if(j) printf(" "); 83 printf("%d", ans[i][j]); 84 } 85 printf(" "); 86 } 87 return 0; 88 }