目录
python操作mysql
mysql
'''
mysql> select * from user_info;
+----+------+----------+
| id | name | password |
+----+------+----------+
| 1 | bigb | 123456 |
+----+------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
'''
import pymysql
user_name = input('请输入用户名: ').strip()
password = input('请输入密码: ').strip()
# 连接数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
user='root',
password='123',
database='db3',
charset='utf8'
)
# 游标
cursor = conn.cursor() # 默认以元祖返回
# cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 以字典返回
# 拼接sql语句
sql = "select * from user_info where name = '%s' and password = '%s'" % (user_name, password)
print(sql)
# 执行sql语句
res = cursor.execute(sql) # 返回执行sql语句影响成功的记录条数
print(res)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
if res:
print('登录成功!')
else:
print('登录失败!')
'''
请输入用户名: bigb
请输入密码: 123456
select * from user_info where name = 'bigb' and password = '123456'
1
登录成功!
'''
sql注入问题
问题描述
- 对于上面的登录脚本, 如果我们在输入用户名时, 在用户名在后面加上
' #, 这样即使密码错误也能登录成功 (绕过密码)
请输入用户名: bigb' #
请输入密码: 234235
select * from user_info where name = 'bigb' #' and password = '234235'
1
登录成功!
- 甚至用户名输错也能登录成功 (绕过用户名和密码)
请输入用户名: blake' or 1=1 #
请输入密码: 4647723
select * from user_info where name = 'blake' or 1=1 #' and password = '4647723'
1
登录成功!
- 上面描述的就是sql注入问题, 原因是我们可以通过输入特殊符号改变where后的筛选条件 (
#可以让后面的内容变成注释)
解决办法
- pymysql对sql针对注入问题进行了优化, 我们将sql语句的拼接工作交给
cursor.execute(sql, (user_name, password))即可
import pymysql
user_name = input('请输入用户名: ').strip()
password = input('请输入密码: ').strip()
# 连接数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
user='root',
password='123',
database='db3',
charset='utf8'
)
# 游标
cursor = conn.cursor() # 默认以元祖返回
# cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 以字典返回
# sql语句
sql = "select * from user_info where name = %s and password = %s"
print(sql)
# 拼接并执行sql语句
res = cursor.execute(sql, (user_name, password))
print(res)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
if res:
print('登录成功!')
else:
print('登录失败!')
增/删/改
- 在通过mysql进行增删改的时候, 要在最后加上
conn.commit()提交
'''
mysql> select * from user_info;
+----+-------+----------+
| id | name | password |
+----+-------+----------+
| 1 | bigb | 123456 |
| 3 | alpha | 111111 |
+----+-------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
'''
import pymysql
# 连接数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
user='root',
password='123',
database='db3',
charset='utf8'
)
# 游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 增加
sql = "insert into user_info (name, password) values ('%s', '%s')" % ('blake', '654321')
print(sql)
res = cursor.execute(sql)
print(res)
# 修改
sql = "update user_info set password='%s' where name='%s'" % ('222222', 'bigb')
print(sql)
res = cursor.execute(sql)
print(res)
# 删除
sql = "delete from user_info where name='%s' " % ('alpha')
print(sql)
res = cursor.execute(sql)
print(res)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
'''
mysql> select * from user_info;
+----+-------+----------+
| id | name | password |
+----+-------+----------+
| 1 | bigb | 222222 |
| 5 | blake | 654321 |
+----+-------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
'''
查询
cursor.fetchone()返回一条记录cursor.fetchmany(n)返回n条记录cursor.fetchall()返回所有记录- 注意
fetch会记录光标位置,fetchone()和fetchmany()会使光标向后移动相应条数,fetchall()直接将光标移动到末尾
'''
+----+---------+----------+
| id | name | password |
+----+---------+----------+
| 1 | bigb | 111111 |
| 2 | blake | 222222 |
| 3 | black | 333333 |
| 4 | alpha | 111111 |
| 5 | bravo | 222222 |
| 6 | charlie | 333333 |
| 7 | delta | 111111 |
| 8 | echo | 222222 |
| 9 | foxtrot | 333333 |
+----+---------+----------+
'''
import pymysql
# 连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
user='root',
password='123',
database='db3',
charset='utf8'
)
# 游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "select * from user_info"
# 执行sql语句
rows = cursor.execute(sql)
print(rows)
res1 = cursor.fetchone()
res2 = cursor.fetchone()
res3 = cursor.fetchone()
res4 = cursor.fetchmany(3)
res5 = cursor.fetchall()
print(res1)
print(res2)
print(res3)
print(res4)
print(res5)
'''
9
(1, 'bigb', '111111')
(2, 'blake', '222222')
(3, 'black', '333333')
((4, 'alpha', '111111'), (5, 'bravo', '222222'), (6, 'charlie', '333333'))
((7, 'delta', '111111'), (8, 'echo', '222222'), (9, 'foxtrot', '333333'))
'''
索引
基本概念
- 索引相当于字典的音序表, 如果查某个字, 可以根据音序表快速定位这个字在字典中的位置, 如果不使用音序表则要一页一页查找
- 优点: 索引可以提升查询数据的速度
- 缺点: 增加索引会消耗很多内存资源
索引的原理
-
原理: 不断缩小搜索范围, 把随机事件变顺序事件
-
底层数据结构: B+树
mysql索引种类
普通索引
- index 加速查找
唯一索引
- primary key 主键唯一索引, 加速查找, 不为空, 不重复
- unique 普通唯一索引, 加速查找, 不重复
联合索引
- primary key (id, name) 联合主键索引
- unique (id, name) 联合唯一索引
- index (id, name) 联合普通索引
创建索引
- 在创建表时添加
creat table 表名 (
列名1 列类型 [列约束],
列名2 列类型 [列约束],
index/primary key/unique [索引名] (列名1)
);
mysql> create table user (
-> id int auto_increment,
-> name char(10) not null default '',
-> email char(20) not null default '',
-> primary key pk_id (id)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
- 在已创建的表上添加
alter table 表名 add index/unique index [索引名] (列名)
create index/unique index [索引名] on 表名(列名)
- 删除索引
alter table 表名 drop 索引名
drop index 索引名 on 表名
正确使用索引
索引未命中
- 进行四则运算
- 使用函数
- 条件不明确 :
> >= < <= != between...and... like
最左前缀
- 基于联合索引的情况下
- 假设我们创建index(clo1, clo2, clo3)这样的一个联合索引, 相当于 (clo1), (clo1, clo2), (clo1, clo2, clo3) 三非索引
索引覆盖
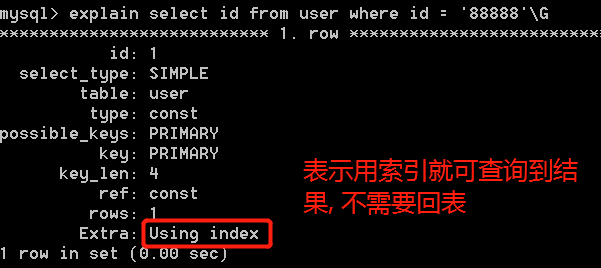
- 在查询的时候,利用到的索引已经完全包含需要查询数据,在这种情况下,查询结果直接就是索引的值,并不需要再利用索引回表查询了
- 如
select id from user where id = '88888'
explain
-
可以模拟优化器执行SQL查询语句,从而知道MySQL是如何处理你的SQL语句的
-
explain sql语句
慢查询日志
基本概念
-
MySQL提供的一种日志记录,它用来记录在MySQL中响应时间超过阀值的语句
-
show varibles like %slow%;查看当前日志状态 (是否开启, 日志文件保存位置)
mysql> show variables like '%slow%';
+---------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| log_slow_admin_statements | OFF |
| log_slow_slave_statements | OFF |
| slow_launch_time | 2 |
| slow_query_log | OFF |
| slow_query_log_file | D:MySQLmysql-5.6.46-winx64dataBlack-PC-slow.log |
+---------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
show varibles like %long%;查看慢查询设定的时间(10秒)
mysql> show variables like '%long%';
+--------------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| long_query_time | 10.000000 |
| performance_schema_events_stages_history_long_size | 10000 |
| performance_schema_events_statements_history_long_size | 10000 |
| performance_schema_events_waits_history_long_size | 10000 |
+--------------------------------------------------------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
配置
set global 变量名 = 值
mysql> set global slow_query_log = on;
mysql> set global slow_query_log_file = "D:/MySQL/myslow.log";
mysql> set global long_query_time = 1;