这个双12,别人都在抢红包、逛淘宝、上京东,我选择再续我的“漫谈可视化”系列(好了,不装了,其实是郎中羞涩。。。)
上篇《漫谈可视化Prefuse(三)---Prefuse API数据结构阅读有感》主要介绍了可视化工具Prefuse API中主要解读的是prefuse.data包中的主要接口,并利用《漫谈可视化Prefuse(一)---从SQL Server数据库读取数据》中例子,将参数配置模块剥离出来,实现界面传值,绘制图形。
本篇决定不再贴API,实在没啥意思,还占篇幅(但是不容置疑的是API确实很重要,想了解API点这里)。那今天我们主要讲讲Prefuse比较常用的包以及如何使用这些包做出自己想要的展示效果:
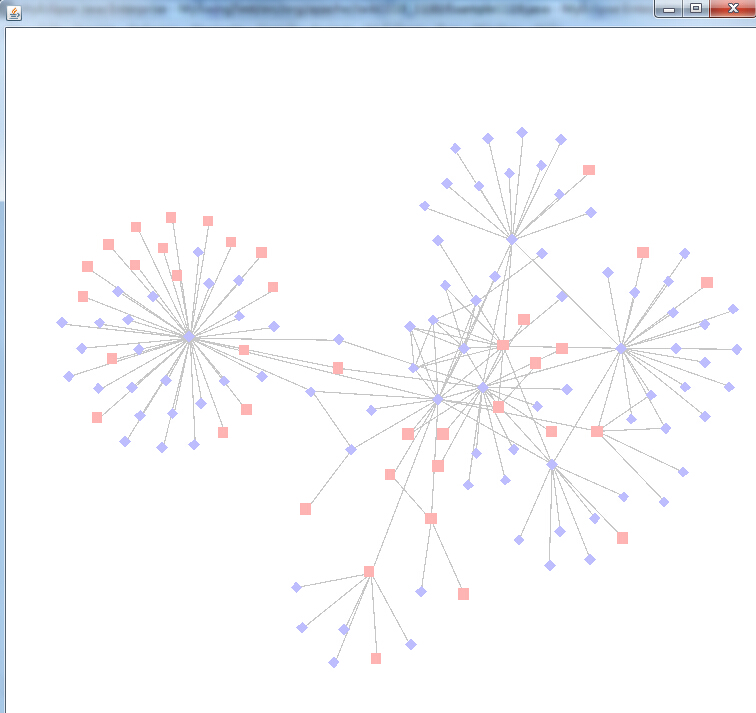
Demo1.解决图形元素形状单一化问题——DataShapeAction的使用
Prefuse对于节点的形状默认是使用Constants.SHAPE_RECTANGLE,这里使用DataShapeAction类完成一个图形中根据性别不同展示不同的节点形状,具体代码如下:
1 public class Demo1 { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 */ 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 8 Graph graph = null; 9 try { 10 graph = new GraphMLReader().readGraph("socialnet.xml"); 11 } catch (Exception e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 System.out.println("Error loading"); 14 System.exit(1); 15 } 16 17 Visualization vis = new Visualization(); 18 vis.add("graph", graph); 19 vis.setRendererFactory(new DefaultRendererFactory()); 20 21 int[] palette = new int[]{ColorLib.rgb(255, 180, 180),ColorLib.rgb(190, 190, 255)}; 22 DataColorAction fill = new DataColorAction("graph.nodes" , "gender" , Constants.NOMINAL, VisualItem.FILLCOLOR,palette); 23 ColorAction text = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.TEXTCOLOR, ColorLib.gray(0)); 24 ColorAction edges = new ColorAction("graph.edges", VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.gray(200)); 25 26 int[] shapes = new int[]{ Constants.SHAPE_RECTANGLE, Constants.SHAPE_DIAMOND}; 27 DataShapeAction shape = new DataShapeAction("graph.nodes", "gender", shapes); 28 29 ActionList color = new ActionList(); 30 color.add(fill); 31 color.add(text); 32 color.add(edges); 33 color.add(shape); 34 35 ActionList layout = new ActionList(Activity.INFINITY); 36 layout.add(new ForceDirectedLayout("graph")); 37 layout.add(new RepaintAction()); 38 39 vis.putAction("color", color); 40 vis.putAction("layout", layout); 41 42 Display display = new Display(vis); 43 display.setSize(750, 700); 44 display.pan(250, 250); 45 display.addControlListener(new DragControl()); 46 display.addControlListener(new PanControl()); 47 display.addControlListener(new ZoomControl()); 48 display.addControlListener(new WheelZoomControl()); 49 display.addControlListener(new FocusControl(1)); 50 display.addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl()); 51 52 JFrame jf = new JFrame(); 53 jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 54 jf.add(display); 55 jf.pack(); 56 jf.setVisible(true); 57 58 vis.run("color"); 59 vis.run("layout"); 60 61 } 62 63 }
DataShapeAction中的第一个参数为指定数据范围,这里指定针对“graph.nodes”点集;第二个参数为属性域,这里针对性别不同赋予不同的形状;第三个参数是形状数组,这里定义了Constants.SHAPE_RECTANGLE, Constants.SHAPE_DIAMOND,除此之外还有Constants.SHAPE_CROSS、Constants.SHAPE_ELLIPSE、Constants.SHAPE_STAR等。同理prefuse.action.assignment包下的DataColorAction用法与DataShapeAction类似。图形展示效果如下:
Demo2:打破输入输出流的垄断亲自绘制图形——Graph的使用
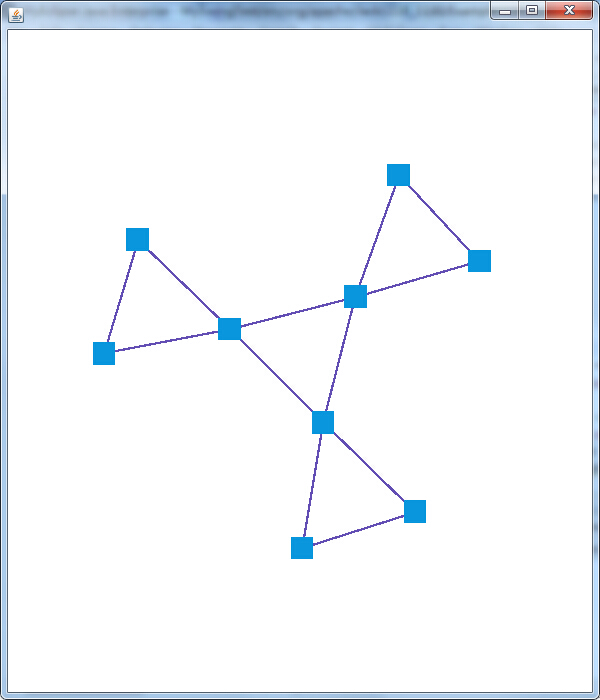
之前几篇介绍的例子主要依赖于prefuse.io中的读入写出操作类进行数据的导入,这里我们决定甩开膀子,自己丰衣足食,打造自己的图形,这里主要使用Graph类的添加节点以及添加边的方法,构建一个互连的三个三角形的形状。具体代码如下:
1 public class Demo2{ 2 3 public static void main(String[] argv) { 4 Visualization vis = new Visualization(); 5 Graph g = new Graph(); 6 for(int i = 0; i<3; i++){ 7 Node n1 = g.addNode(); 8 Node n2 = g.addNode(); 9 Node n3 = g.addNode(); 10 g.addEdge(n1, n2); 11 g.addEdge(n2, n3); 12 g.addEdge(n3, n1); 13 } 14 g.addEdge(0, 3); 15 g.addEdge(3, 6); 16 g.addEdge(6, 0); 17 18 vis.add("graph", g); 19 ShapeRenderer renderer = new ShapeRenderer(10); 20 vis.setRendererFactory(new DefaultRendererFactory(renderer)); 21 22 ColorAction nodeFill = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(10, 150, 220)); 23 ColorAction edgesStroke = new ColorAction("graph.edges", VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(100, 80, 180)); 24 ColorAction nodeHighlight = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.HIGHLIGHT, ColorLib.rgb(10, 150, 220)); 25 26 ActionList color = new ActionList(); 27 color.add(nodeFill); 28 color.add(edgesStroke); 29 30 ActionList layout = new ActionList(Activity.INFINITY); 31 layout.add(color); 32 layout.add(new ForceDirectedLayout("graph")); 33 layout.add(new RepaintAction()); 34 35 Display display = new Display(vis); 36 display.setSize(400, 500); 37 display.pan(250, 250); 38 display.addControlListener(new DragControl()); 39 display.addControlListener(new PanControl()); 40 display.addControlListener(new ZoomControl()); 41 display.addControlListener(new WheelZoomControl()); 42 display.addControlListener(new FocusControl(1)); 43 display.addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl()); 44 45 vis.putAction("color", color); 46 vis.putAction("layout", layout); 47 48 49 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); 50 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 51 frame.pack(); 52 frame.setSize(600, 700); 53 frame.add(display); 54 frame.setVisible(true); 55 56 vis.run("color"); 57 vis.run("layout"); 58 } 59 60 }
从代码可以看出,对于创建节点、添加边,Graph处理的游刃有余,只有你想不到的图形,没有创建不了的Graph。当然只是简单创建了node和edge只是有了骨架,还需要血肉的填充,所以可以看到有很多的Action纷纷来助阵,最终的众志成城之作如下:
Demo3:谁说点点之间只能“直肠子”——EdgeRenderer的使用
看不惯点与点之间的“直肠子”?可以,Prefuse了解你,知道你喜新厌旧,这不使用EdgeRenderer就可以实现曲线连接,具体代码与Demo1相近,只是多了一下几行代码:
1 DefaultRendererFactory rf = new DefaultRendererFactory(label); 2 EdgeRenderer edgeRenderer = new EdgeRenderer(Constants.EDGE_TYPE_CURVE); 3 rf.add(new InGroupPredicate("graph.edges"), edgeRenderer);
这里采用EdgeRenderer边渲染器,将边渲染为曲线,并统一应用到组“graph.edges”中的元素上,除了Constants.EDGE_TYPE_CURVE,还有Constants.EDGE_ARROW_FORWARD、Constants.EDGE_ARROW_NONE等。话不多说,看效果:
Demo4:Prefuse没节操?不知道筛选?No!——Predicate的使用
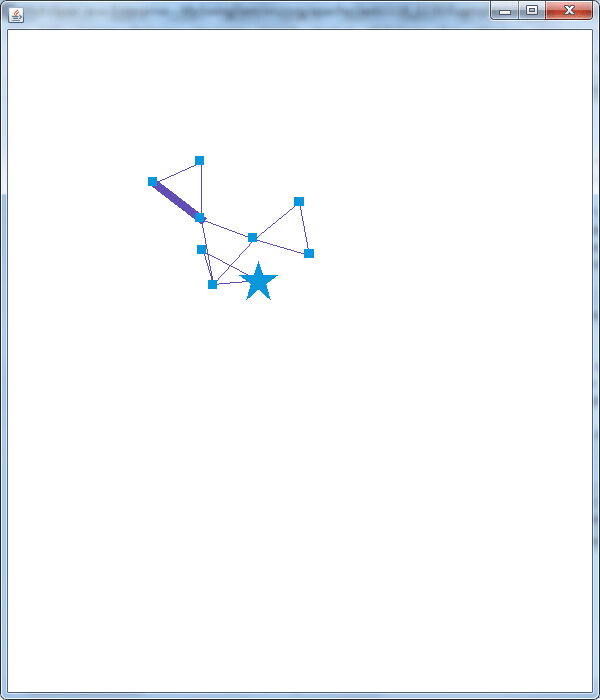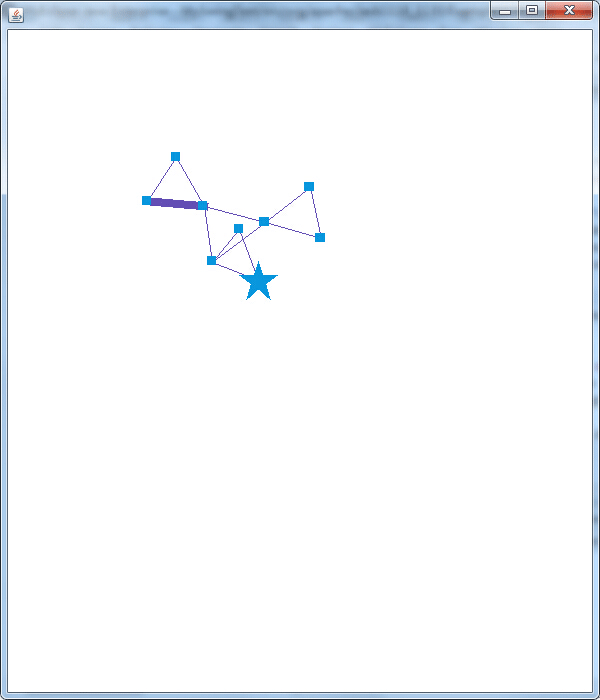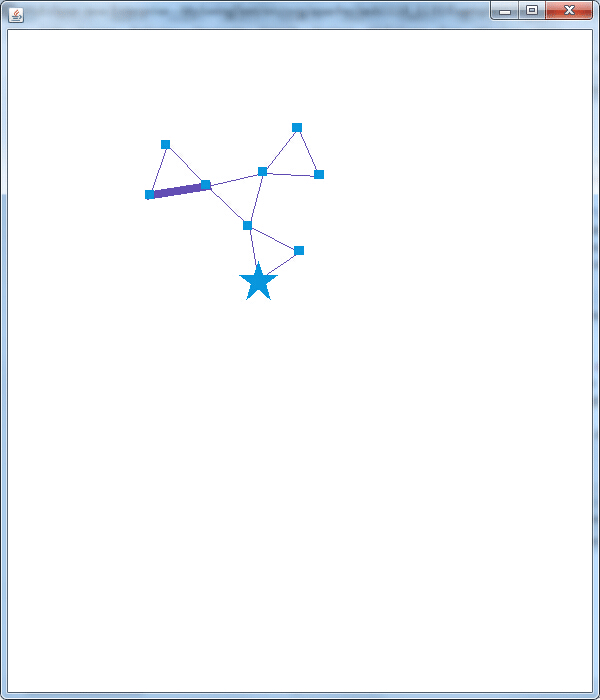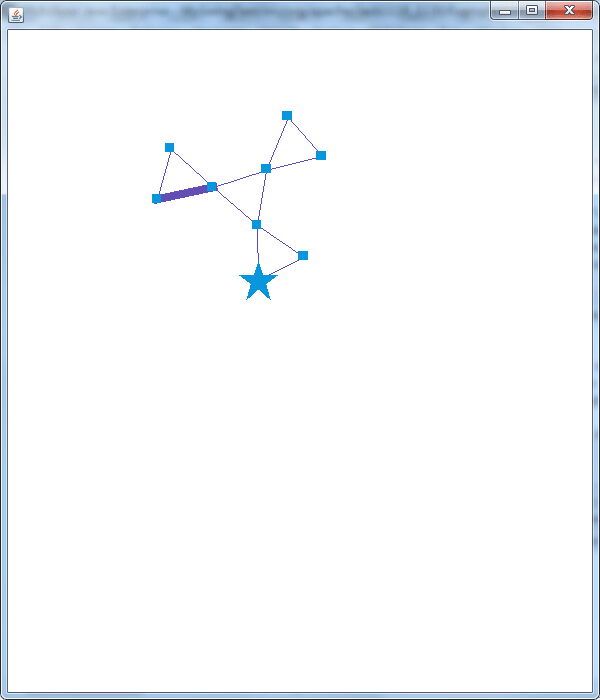
Prefuse自带过滤器,可以完成十分强大的过滤操作,视个别情况个别对待。拿Demo2中的图形来说,处在中间的节点可以不收节点控制(无法拖拽,不能交互),人家兄弟姐妹多,就拿那些势力若的边缘小弟拖过来拽过去^_^。具体代码如下:
1 public class Demo4{ 2 3 public static void main(String[] argv) { 4 Visualization vis = new Visualization(); 5 Graph g = new Graph(); 6 for(int i = 0; i<3; i++){ 7 Node n1 = g.addNode(); 8 Node n2 = g.addNode(); 9 Node n3 = g.addNode(); 10 g.addEdge(n1, n2); 11 g.addEdge(n2, n3); 12 g.addEdge(n3, n1); 13 } 14 g.addEdge(0, 3); 15 g.addEdge(3, 6); 16 g.addEdge(6, 0); 17 vis.add("graph", g); 18 19 ShapeRenderer renderer = new ShapeRenderer(10); 20 EdgeRenderer edgeRenderer = new EdgeRenderer(Constants.EDGE_TYPE_CURVE); 21 DefaultRendererFactory drf = new DefaultRendererFactory(); 22 drf.add(new InGroupPredicate("graph.edges"), edgeRenderer); 23 vis.setRendererFactory(drf); 24 25 ColorAction nodeFill = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(10, 150, 220)); 26 ColorAction edgesStroke = new ColorAction("graph.edges", VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(100, 80, 180)); 27 ColorAction nodeHighlight = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.HIGHLIGHT, ColorLib.rgb(10, 150, 220)); 28 29 ShapeAction shape = new ShapeAction("graph.nodes",Constants.SHAPE_CROSS); //设置节点形状 30 31 ActionList color = new ActionList(); 32 color.add(nodeFill); 33 color.add(edgesStroke); 34 color.add(shape); 35 36 ActionList layout = new ActionList(Activity.INFINITY); 37 layout.add(color); 38 layout.add(new ForceDirectedLayout("graph")); 39 layout.add(new RepaintAction()); 40 41 Point p = new Point(100,200); 42 p.move(300, 400); 43 44 45 Predicate pCount =(Predicate)ExpressionParser.parse("degree()>2"); 46 47 Display display = new Display(vis); 48 display.setSize(400, 500); 49 display.pan(250, 250); 50 display.animatePanAbs(230, 220, 2000); 51 display.addControlListener(new DragControl()); 52 display.addControlListener(new PanControl()); 53 display.addControlListener(new ZoomControl()); 54 display.addControlListener(new WheelZoomControl()); 55 display.addControlListener(new FocusControl(1)); 56 display.addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl()); 57 58 vis.removeGroup("graph"); 59 VisualGraph vg = vis.addGraph("graph", g); 60 Iterator nodes = vg.nodes(); 61 display.addControlListener(new ControlAdapter() { 62 public void itemEntered(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) { 63 System.out.println("伦家已经是:" + item.getGroup()+"的人了"); 64 } 65 public void itemExited(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) { 66 System.out.println("哦,那杰哥再找找-_-"); 67 } 68 });//为组件添加监控并作相应的响应 69 70 vis.setInteractive("graph.nodes", pCount, false); 71 72 vis.putAction("color", color); 73 vis.putAction("layout", layout); 74 75 76 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); 77 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 78 frame.pack(); 79 frame.setSize(600, 700); 80 frame.add(display); 81 frame.setVisible(true); 82 83 vis.run("color"); 84 vis.run("layout"); 85 } 86 87 }
这里Predicate pCount =(Predicate)ExpressionParser.parse("degree()>2")表示过滤出节点度数大于2的,该过滤条件在vis.setInteractive("graph.nodes", pCount, false)中执行,即在组“graph.nodes”元素中节点度数大于2的不能交互(即鼠标拖拽无效)。
另外从代码中可以看出当鼠标经过和离开VisualItem(点或边)时会执行相应的操作,下图展现了部分结果:

Demo5:个性化定制,我有我个性——VisualItem的领悟
要知道,在数据中心Visualizaiton里,每一个node或是edge都可以看成一个VisualItem,每个VisualItem都可以有属于自己的造型、尺寸,这里我们还是用Demo2中的图形继续玩,直到玩坏为止。具体代码如下:
1 public class Demo5{ 2 public static Visualization vis = new Visualization(); 3 4 public static void main(String[] argv) { 5 6 Graph g = new Graph(); 7 for(int i = 0; i<3; i++){ 8 Node n1 = g.addNode(); 9 Node n2 = g.addNode(); 10 Node n3 = g.addNode(); 11 g.addEdge(n1, n2); 12 g.addEdge(n2, n3); 13 g.addEdge(n3, n1); 14 } 15 g.addEdge(0, 3); 16 g.addEdge(3, 6); 17 g.addEdge(6, 0); 18 19 vis.add("graph", g); 20 ShapeRenderer renderer = new ShapeRenderer(10); 21 vis.setRendererFactory(new DefaultRendererFactory(renderer)); 22 23 vis.removeGroup("graph"); 24 VisualGraph vg = vis.addGraph("graph", g); 25 VisualItem nodeI = (VisualItem)vg.getEdge(7).getSourceNode(); 26 nodeI.setShape(Constants.SHAPE_STAR); 27 nodeI.setSize(4); 28 nodeI.setFixed(true); 29 VisualItem edgeI = (VisualItem)vg.getEdge(5); 30 edgeI.setSize(8); 31 32 ColorAction nodeFill = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(10, 150, 220)); 33 ColorAction edgesStroke = new ColorAction("graph.edges", VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(100, 80, 180)); 34 ColorAction nodeHighlight = new ColorAction("graph.nodes", VisualItem.HIGHLIGHT, ColorLib.rgb(10, 150, 220)); 35 36 ActionList color = new ActionList(); 37 color.add(nodeFill); 38 color.add(edgesStroke); 39 40 ActionList layout = new ActionList(3000); 41 layout.add(color); 42 layout.add(new ForceDirectedLayout("graph")); 43 layout.add(new RepaintAction()); 44 45 Display display = new Display(vis); 46 display.setSize(400, 500); 47 display.pan(250, 250); 48 display.addControlListener(new DragControl()); 49 display.addControlListener(new PanControl()); 50 display.addControlListener(new ZoomControl()); 51 display.addControlListener(new WheelZoomControl()); 52 display.addControlListener(new FocusControl(1)); 53 display.addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl()); 54 display.addControlListener(new ControlAdapter(){ 55 public void itemEntered(VisualItem item, MouseEvent e) { 56 57 System.out.println("伦家已经是:" + item.getGroup()+"的人了"); 58 vis.run("color"); 59 vis.run("layout");//重绘三秒 60 } 61 }); 62 63 vis.putAction("color", color); 64 vis.putAction("layout", layout); 65 66 67 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); 68 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 69 frame.pack(); 70 frame.setSize(600, 700); 71 frame.add(display); 72 frame.setVisible(true); 73 74 vis.run("color"); 75 vis.run("layout"); 76 } 77 78 }
可以看出代码中nodeI.setShape(Constants.SHAPE_STAR);nodeI.setSize(4);nodeI.setFixed(true);是将节点的形状设为星形,大小放大为4并固定此节点;edgeI.setSize(8);将边的粗细设为8。这里还具有一个功能,就是代码跑起来显示图形运行三秒,当鼠标经过某点或边是,整个图形在运行三秒,为展示这种效果,首次使用ps做gif,想想也是醉了。。。
Prefuse就先玩到这吧,真材实料送上5个Demo,虽然抢不到红包,抢点Demo补补脑也不错哦,走到这里,似乎我已经拉近了与Prefuse的距离,下一步就是力求亲密接触,碰撞出可视化狂拽炫酷的展示效果。觉得有用,记得点赞哦。
本文链接:《漫谈可视化Prefuse(四)---被玩坏的Prefuse API》http://www.cnblogs.com/bigdataZJ/p/VisualizationSoloShow4.html
友情赞助
如果你觉得博主的文章对你那么一点小帮助,恰巧你又有想打赏博主的小冲动,那么事不宜迟,赶紧扫一扫,小额地赞助下,攒个奶粉钱,也是让博主有动力继续努力,写出更好的文章^^。
1. 支付宝 2. 微信

