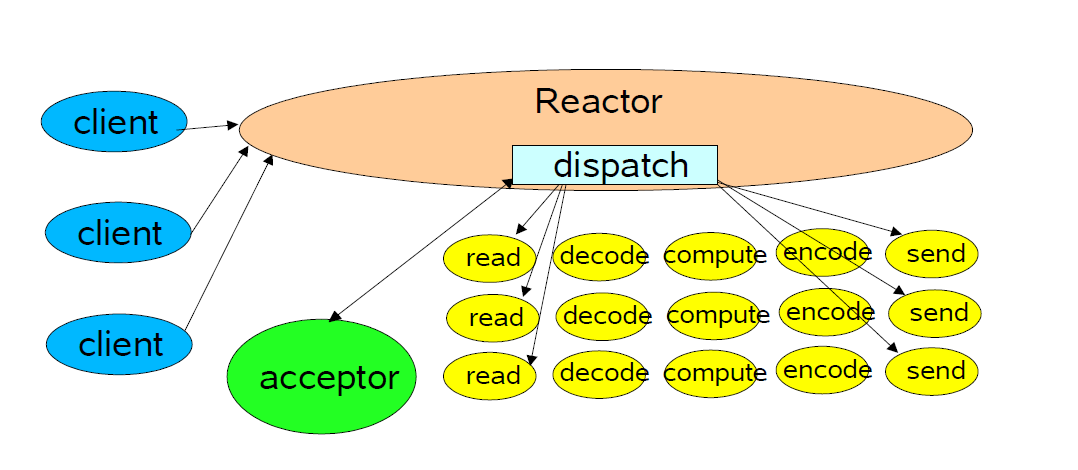
reactor模式称之为响应器模式,常用于nio的网络通信框架,其服务架构图如下
不同于传统IO的串行调度方式,NIO把整个服务请求分为五个阶段
read:接收到请求,读取数据
decode:解码数据
compute:业务逻辑处理
encode:返回数据编码
send:发送数据
其中,以read和send阶段IO最为频繁
代码实现
1 // Reactor線程 2 package server; 3 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.net.InetSocketAddress; 6 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; 7 import java.nio.channels.Selector; 8 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; 9 import java.util.Iterator; 10 import java.util.Set; 11 12 public class TCPReactor implements Runnable { 13 14 private final ServerSocketChannel ssc; 15 private final Selector selector; 16 17 public TCPReactor(int port) throws IOException { 18 selector = Selector.open(); 19 ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open(); 20 InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(port); 21 ssc.socket().bind(addr); // 在ServerSocketChannel綁定監聽端口 22 ssc.configureBlocking(false); // 設置ServerSocketChannel為非阻塞 23 SelectionKey sk = ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); // ServerSocketChannel向selector註冊一個OP_ACCEPT事件,然後返回該通道的key 24 sk.attach(new Acceptor(selector, ssc)); // 給定key一個附加的Acceptor對象 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 while (!Thread.interrupted()) { // 在線程被中斷前持續運行 30 System.out.println("Waiting for new event on port: " + ssc.socket().getLocalPort() + "..."); 31 try { 32 if (selector.select() == 0) // 若沒有事件就緒則不往下執行 33 continue; 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); // 取得所有已就緒事件的key集合 39 Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator(); 40 while (it.hasNext()) { 41 dispatch((SelectionKey) (it.next())); // 根據事件的key進行調度 42 it.remove(); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 47 /* 48 * name: dispatch(SelectionKey key) 49 * description: 調度方法,根據事件綁定的對象開新線程 50 */ 51 private void dispatch(SelectionKey key) { 52 Runnable r = (Runnable) (key.attachment()); // 根據事件之key綁定的對象開新線程 53 if (r != null) 54 r.run(); 55 } 56 57 }
1 // 接受連線請求線程 2 package server; 3 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; 6 import java.nio.channels.Selector; 7 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; 8 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; 9 10 public class Acceptor implements Runnable { 11 12 private final ServerSocketChannel ssc; 13 private final Selector selector; 14 15 public Acceptor(Selector selector, ServerSocketChannel ssc) { 16 this.ssc=ssc; 17 this.selector=selector; 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public void run() { 22 try { 23 SocketChannel sc= ssc.accept(); // 接受client連線請求 24 System.out.println(sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress().toString() + " is connected."); 25 26 if(sc!=null) { 27 sc.configureBlocking(false); // 設置為非阻塞 28 SelectionKey sk = sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); // SocketChannel向selector註冊一個OP_READ事件,然後返回該通道的key 29 selector.wakeup(); // 使一個阻塞住的selector操作立即返回 30 sk.attach(new TCPHandler(sk, sc)); // 給定key一個附加的TCPHandler對象 31 } 32 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 40 }
1 // Handler線程 2 package server; 3 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 6 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; 7 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; 8 import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; 9 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 10 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 11 12 public class TCPHandler implements Runnable { 13 14 private final SelectionKey sk; 15 private final SocketChannel sc; 16 17 int state; 18 19 public TCPHandler(SelectionKey sk, SocketChannel sc) { 20 this.sk = sk; 21 this.sc = sc; 22 state = 0; // 初始狀態設定為READING 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public void run() { 27 try { 28 if (state == 0) 29 read(); // 讀取網絡數據 30 else 31 send(); // 發送網絡數據 32 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 System.out.println("[Warning!] A client has been closed."); 35 closeChannel(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 private void closeChannel() { 40 try { 41 sk.cancel(); 42 sc.close(); 43 } catch (IOException e1) { 44 e1.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 } 47 48 private synchronized void read() throws IOException { 49 // non-blocking下不可用Readers,因為Readers不支援non-blocking 50 byte[] arr = new byte[1024]; 51 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(arr); 52 53 int numBytes = sc.read(buf); // 讀取字符串 54 if(numBytes == -1) 55 { 56 System.out.println("[Warning!] A client has been closed."); 57 closeChannel(); 58 return; 59 } 60 String str = new String(arr); // 將讀取到的byte內容轉為字符串型態 61 if ((str != null) && !str.equals(" ")) { 62 process(str); // 邏輯處理 63 System.out.println(sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress().toString() 64 + " > " + str); 65 state = 1; // 改變狀態 66 sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); // 通過key改變通道註冊的事件 67 sk.selector().wakeup(); // 使一個阻塞住的selector操作立即返回 68 } 69 } 70 71 private void send() throws IOException { 72 // get message from message queue 73 74 String str = "Your message has sent to " 75 + sc.socket().getLocalSocketAddress().toString() + " "; 76 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes()); // wrap自動把buf的position設為0,所以不需要再flip() 77 78 while (buf.hasRemaining()) { 79 sc.write(buf); // 回傳給client回應字符串,發送buf的position位置 到limit位置為止之間的內容 80 } 81 82 state = 0; // 改變狀態 83 sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ); // 通過key改變通道註冊的事件 84 sk.selector().wakeup(); // 使一個阻塞住的selector操作立即返回 85 } 86 87 void process(String str) { 88 // do process(decode, logically process, encode).. 89 // .. 90 } 91 }
1 package server; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 public class Main { 6 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 try { 11 TCPReactor reactor = new TCPReactor(1333); 12 reactor.run(); 13 } catch (IOException e) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 }
客户端代码
1 package main.pkg; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 6 import java.io.PrintWriter; 7 import java.net.Socket; 8 import java.net.UnknownHostException; 9 10 public class Client { 11 12 /** 13 * @param args 14 */ 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 String hostname=args[0]; 18 int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); 19 //String hostname="127.0.0.1"; 20 //int port=1333; 21 22 System.out.println("Connecting to "+ hostname +":"+port); 23 try { 24 Socket client = new Socket(hostname, port); // 連接至目的地 25 System.out.println("Connected to "+ hostname); 26 27 PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(client.getOutputStream()); 28 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream())); 29 BufferedReader stdIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 30 String input; 31 32 while((input=stdIn.readLine()) != null) { // 讀取輸入 33 out.println(input); // 發送輸入的字符串 34 out.flush(); // 強制將緩衝區內的數據輸出 35 if(input.equals("exit")) 36 { 37 break; 38 } 39 System.out.println("server: "+in.readLine()); 40 } 41 client.close(); 42 System.out.println("client stop."); 43 } catch (UnknownHostException e) { 44 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 45 System.err.println("Don't know about host: " + hostname); 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 48 System.err.println("Couldn't get I/O for the socket connection"); 49 } 50 51 } 52 53 }
代码解读:
1.创建TCPReactor 类的实例,启动端口监听
2.Acceptor 类只用于处理接受请求的时候,后续的读写跟其无任何关系
3.TCPReactor.run( )一直在进行,后续selectionkey有变动,会监听到,一直执行dispatch方法
最后提醒一点,从性能来说,单线程的reactor没过多的提升,因为IO和CPU的速度还是严重不匹配
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/yehjordan/article/details/51012833