Spring 还支持基于 JSR-250 的注解,其中包括 @PostConstruct,@PreDestroy 和 @Resource 注解。虽然这些注解不是真正需要的,因为你已经有其他替代品,但让我们简要了解一下。
@PostConstruct 和@PreDestroy 注解:
- 要定义一个 bean 的设置和拆卸,我们只需使用 init-method 或 destroy-method 参数声明 bean。init-method 属性指定一个在实例化后立即在 bean 上调用的方法。类似地,destroy-method 指定在 bean 从容器中删除之前调用的方法。
- 在这里你可以使用 @PostConstruct 注解作为初始化回调和 @PreDestroy 注解的替代,作为销毁回调的替代。下面通过一个例子来说明一下。
创建包 com.shiyanlou.demo.helloworld,然后创建 HelloWorld.java,代码如下:
package com.shiyanlou.demo.helloworld;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class HelloWorld {
private String messageString;
public void setMessage(String message){
this.messageString = message;
}
public void getMessage(){
System.out.println(this.messageString);
}
@PostConstruct
public void initPost(){
System.out.println("@ init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroyPre(){
System.out.println("@ destroy");
}
}
在 SpringBeans.xml 中增加如下代码:
<bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.shiyanlou.demo.helloworld.HelloWorld">
<property name = "Message" value = "Hello World!"/>
</bean>
修改 App.java 如下:
package com.shiyanlou.demo;
import com.shiyanlou.demo.helloworld.HelloWorld;
import com.shiyanlou.demo.entity.Dog;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
public class App {
// private static ApplicationContext context;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SpringBeans.xml");
// Dog dog = (Dog) context.getBean("dogBean");
// System.out.println(dog);
AbstractApplicationContext abstractApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SpringBeans.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)abstractApplicationContext.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.getMessage();
abstractApplicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
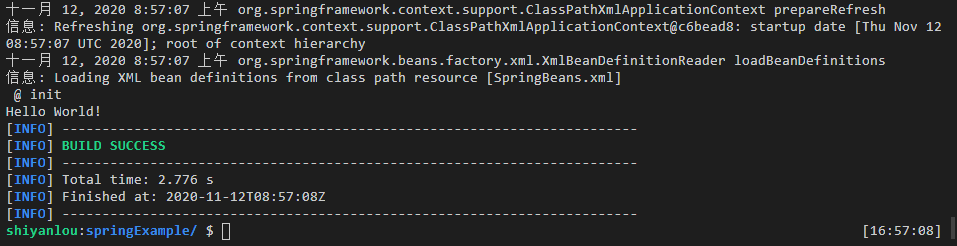
运行:
mvn compile
mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.shiyanlou.demo.App"
实验结果如下:
@Resource 注解:
- 你可以对字段或 setter 方法使用 @Resource 注解,它与 Java EE 5 中的工作方式相同。@Resource 注解采用 “name” 属性,将被解释为要注入的 bean 名称。
- 如果没有明确指定 “name”,则默认名称是从字段名称或 setter 方法派生的。在一个字段的情况下,它需要字段名称,在 setter 方法的情况下,它将使用 bean 属性名称。
修改 HelloWorld.java:
package com.shiyanlou.demo.helloworld;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class HelloWorld {
private String messageString;
@Resource(name = "msg")
public void setMessage(String message){
this.messageString = message;
}
public void getMessage(){
System.out.println(this.messageString);
}
@PostConstruct
public void initPost(){
System.out.println("@ init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroyPre(){
System.out.println("@ destroy");
}
}
增加 SpringBeans.xml:
<bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.shiyanlou.demo.helloworld.HelloWorld">
<!--<property name = "Message" value = "Hello World!"/>-->
</bean>
<bean id = "msg" class = "java.lang.String">
<constructor-arg index = "0" value = "Hello World!"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
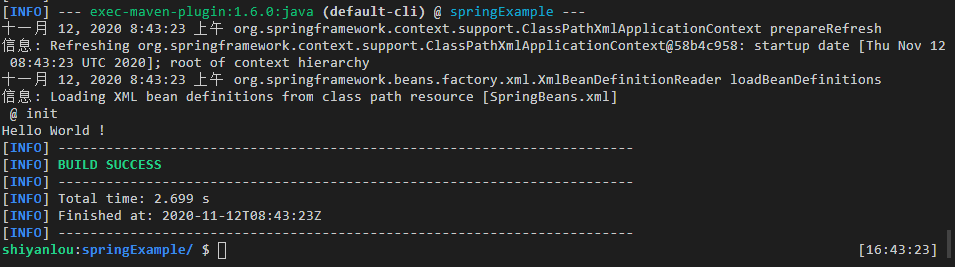
运行:
mvn compile
mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.shiyanlou.demo.App"
实验结果如下: