概述
- 分布式面临的问题
- 复杂的分布式体系结构中的应用程序中有数十个依赖关系, 每个依赖关系在某些时候将不可避免地失败.
- 服务雪崩
- 多个微服务之间调用的时候, 假设微服务A调用微服务B和C, 微服务B和C又调用其他的微服务, 这就是所谓的"扇出". 如果扇出的链路上某个微服务的调用响应时间过长或不可用, 对微服务A的调用就会占用越来越多的系统资源, 进而引起系统崩溃, 即所谓的"雪崩效应"
- 对于高流量的应用来说, 单一的后端依赖可能会导致所有的服务器上的所有资源在几秒钟之内饱和. 甚至这些应用程序可能导致服务间的延迟增加, 备份队列, 线程和其他系统资源紧张, 导致整个系统的级联故障, 这些都表示需要对故障和延迟进行隔离和管理, 以便单个依赖关系的失败不会取消整个应用程序或系统.
- 通常当你发现一个模块下的某个实例失败后, 这时候这个模块依然还会接受流量, 然后这个有问题的模块还调用了其他模块, 这样就会发生级联故障(雪崩).
- Hystrix是什么
- Hystrix是一个用于处理分布式系统的延迟和容错开源库, 在分布式系统中, 许多依赖不可避免的会调用失败, 比如超时/异常等, Hystrix能保证在一个依赖出问题的情况下, 不会导致整体服务失败, 避免级联故障, 以提高分布式系统的弹性.
- "断路器"本身是一种开关装置, 当某个服务单元发生故障后, 通过断路器的故障监控, 像调用方返回一个符合预期的, 可处理的备选响应(Fallback), 而不是长时间的等待或抛出调用方无法处理的异常, 这样就保证了服务调用方的线程不会被长时间, 不必要的占用, 从而避免了雪崩.
- Hystrix能干什么
- 服务降级
- 服务熔断
- 接近实时的服务监控
- Hystrix停更进维
- 但Hystrix的设计理念还是非常优秀, 有必要学习!
Hystrix的重要概念
- 服务降级(fallback)
- 简单的说, 就是对方系统不可用了, 需要给出一个兜底的解决方案.
- 比如: 服务器忙, 请稍后再试, 不要让客户端等待, 要立即返回, 并给一个友好提示
- 触发降级的情况
- 程序运行异常
- 超时
- 服务熔断触发服务降级
- 线程池/信号量打满也会导致服务降级
- 服务熔断(break)
- 类比保险丝, 电流过大的时候, 直接跳闸, 避免失火.
- 当达到最大服务访问后, 会直接拒绝访问, 然后再触发服务降级
- 服务限流(flowlimit)
- 秒杀等高并发操作时, 严禁一窝蜂的过来拥挤, 要排好队, 一秒钟n个, 有序进行.
Hystrix案例
- 搭建测试Module: cloud-provider-hystrix-payment8001
- pom
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId> </dependency>
- yml
server: port: 8001 eureka: client: register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: true service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/ spring: application: name: cloud-provider-hystrix-payment - 主启动类
@EnableEurekaClient @SpringBootApplication public class PaymentHystrixMain8001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentHystrixMain8001.class, args); } }
- 业务类
- service
@Service public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService { @Override public String paymentInfo_OK(Integer id) { return "线程池: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_OK, id: " + id; } @Override public String paymentInfo_Timeout(Integer id) { int timeNumber = 3; try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(timeNumber); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "线程池: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_Timeout, id: " + id + ", 耗时: " + timeNumber; } }
- controller
@RestController @Slf4j public class PaymentController { @Resource private PaymentService paymentService; @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_OK(id); log.info("************result" + result); return result; } @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}") public String paymentInfo_Timeout(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_Timeout(id); log.info("************result" + result); return result; } }
- service
- 正常测试
- http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/ok/1
- http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/timeout/1
- 服务端高并发测试
- 上述例子在非高并发下勉强能满足, 但在高并发的情况下...
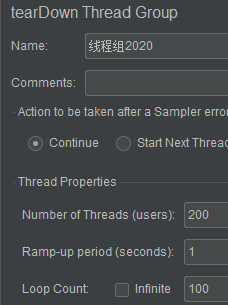
- 开启Jmeter, 模拟20000个并发去访问http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/timeout/1
- 这时我们发现这两个测试都会延迟卡顿, 这是为什么?
- 因为tomcat的线程池被打满了, 没有多余的线程来分解压力和处理了.
- 开启Jmeter, 模拟20000个并发去访问http://localhost:8001/payment/hystrix/timeout/1
- 上面的还只是服务提供者8001自己测试, 如果此时外部的消费者80也来访问, 那么消费者只能干等, 最终导致消费的80不满意, 服务器8001直接被拖死.
- 加入消费者80: cloud-consumer-feign-hystrix-order80
- pom
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency>
- yml
server: port: 80 eureka: client: register-with-eureka: false service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka - 主启动类
@SpringBootApplication @EnableFeignClients public class OrderHystrixMain80 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderHystrixMain80.class,args); } }
- 业务类
- service
@FeignClient(value="cloud-provider-hystrix-payment") public interface PaymentHystrixService { @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id); @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}") String paymentInfo_Timeout(@PathVariable("id") Integer id); }
- controller
@RestController @Slf4j public class OrderHystrixController { @Resource private PaymentHystrixService paymentHystrixService; @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_OK(id); return result; } @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/timeout/{id}") public String paymentInfo_Timeout(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { String result = paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_Timeout(id); return result; } }
- service
- 正常测试
- http://localhost/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/1
- 消费端高并发测试
- 2W个线程去压8001
- 这时消费者80微服务再去访问正常的OK微服务8001地址
- 发现要么转圈等待
- 要么消费端报超时错误
- 故障的现象和原因
- 8001同一层次的其他接口服务被困死, 因为tomcat线程里面的工作现场已被挤占完毕.
- 80此时调用8001, 客户端访问响应缓慢, 转圈圈.
- 也正因这些故障或不佳现象, 才有我们的降级/容错/限流技术的诞生.
- 如何解决?
- 当对方服务(8001)超时了, 调用者(80)不能一直卡死等待, 必须又服务降级.
- 当对方服务宕机了, 调用者不能一直卡死等待, 必须有服务降级.
- 若对方服务OK, 调用者自己出故障或有自我要求(如自己的等待时间小于服务提供者), 自己处理降级.