原文链接:https://russxia.com/2019/09/13/SpirngMVC%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E5%BC%82%E5%B8%B8%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86%E6%B5%81%E7%A8%8B/
SpringMVC中的异常处理流程
本文搭建的项目基于spring-boot版本 1.5.2.RELEASE ,spring版本是 4.3.7.RELEASE 。源码分析也是基于 4.3.7.RELEASE 的spring版本。
Spring Boot项目可以通过 server.error.whitelabel.enabled 参数设置关闭Spring Boot默认提供的统一错误信息处理。
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false
demo项目地址: https://github.com/RussXia/spring-boot-demo
SpringMVC中常见的几种异常处理
没有使用统一处理异常时,发生异常且没有捕获,会将异常的堆栈信息直接返回到前端页面。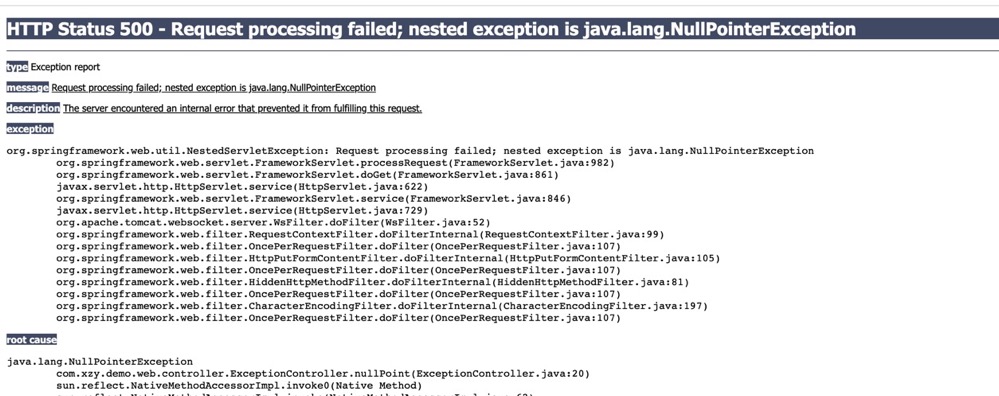
SpringMVC中,如果异常不被处理直接抛出,会将整个异常堆栈信息返回到前端,这样一来容易暴露服务的一些相对比较敏感的信息,二来对于json/xml这样的接口而言,完全无法解析。但是如果每个接口每个方法都去做try...catch,代码大量冗余,可读性维护性也都变差了。
所以我们就可以统一处理这样异常的方法,将异常处理独立出来,和业务代码解耦合。SpringMVC中提供了三种不同的异常统一处理的方法。
使用@ExceptionHandler处理异常
因为 @ExceptionHandler 注解只能作用于方法上,所以如果单纯只是使用 @ExceptionHandler 注解,要么每个controller都写一套这样的 @ExceptionHandler 标准的异常处理方法;要么封装一个统一的基类baseController,这个baseController里面进行异常的处理( @ExceptionHandler 注解的方法),然后其他controller继承自这个baseController。
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/exception")
public class ExceptionController {
@RequestMapping("/null")
public String nullPointer() {
log.info("start NullPointerException");
Object object = null;
return object.toString();
}
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
@ResponseBody
public String handlerNullPointer(NullPointerException ex) {
log.error("error happened:", ex);
return this.getClass().getSimpleName() + ":" + ex.getMessage();
}
}
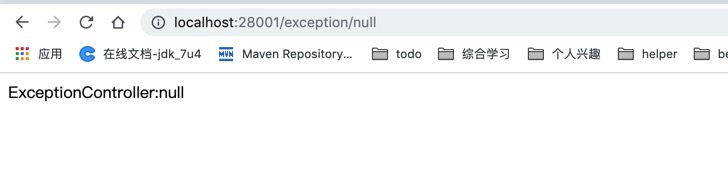
@ControllerAdvice和@ExceptionHandler相结合处理异常
前面我们提到 @ExceptionHandler 只能标准在方法上,异常处理会和我们的controller比较耦合,所以Spring后面提供了 @ControllerAdvice 注解。
同时使用 @ControllerAdvice 和 @ExceptionHandler ,可以像”切面”一样的,不侵入原有的controller,也能提供统一的异常处理。
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandlerAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler({NullPointerException.class, ArithmeticException.class})
@ResponseStatus(value= HttpStatus.NETWORK_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED, reason="hello123")
@ResponseBody
public String handlerNullPointer(RuntimeException ex) {
log.error("error happened:", ex);
return this.getClass().getSimpleName() + ":" + ex.getMessage();
}
}
自定义实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口的形式处理异常
自己实现 HandlerExceptionResolver 接口即可实现自定义的异常处理解析器。如果是你不想处理的异常,返回的ModelAndView返回为null即可。DispatcherServelt会继续遍历其他注册的 HandlerExceptionResolver 处理该异常。
在本例中,我们自定义的异常处理解析器 CustomHandlerExceptionResolver 会处理 NullPointerException ,并将http状态码修改为500,message补充为 'null_pointer_exception occurred just now!'。其他类型的异常我们并不处理。
如果自定义的异常处理解析器没有生效,有可能是 HandlerExceptionResolver 加载的顺序问题,可以通过 @Order(value = xx) 来指定加载的顺序。
@Slf4j
@Order(value = -1)
@Component
public class CustomHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof NullPointerException
|| (ex.getCause() != null && ex.getCause() instanceof NullPointerException)) {
try {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), "null_pointer_exception occurred just now!");
return new ModelAndView();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("some error occurred!", e);
}
}
return null;
}
}
SpringMVC中处理异常的大概流程分析。
DispatcherServlet#doDispatch 会对转发请求的结果进行处理,请求结果无外乎两种。一种是正常处理,拿到了返回值;另一种是处理失败,抛出了异常。
正常处理的情况下,exception为null,返回结果在ModelAndView中,正常的渲染视图,返回结果即可。异常情况下,会调用 processHandlerException 方法,对异常进行处理。
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
//检查注册的HandlerExceptionResolvers,HandlerExceptionResolver接口提供异常处理方法`resolveException`,并返回一个ModelAndView。
// Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers...
ModelAndView exMv = null;
for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
//遍历注册的异常处理解析器,处理解析异常
//如果异常处理成功,返回的ModelAndView不为null,结束遍历
exMv = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
//如果ModelAndView不为null,说明有HandlerExceptionResolver成功处理异常
if (exMv != null) {
if (exMv.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
return null;
}
// We might still need view name translation for a plain error model...
if (!exMv.hasView()) {
exMv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Handler execution resulted in exception - forwarding to resolved error view: " + exMv, ex);
}
WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName());
return exMv;
}
//如果所有HandlerExceptionResolvers都无法处理的话,抛出到页面(这就是为什么不设置统一处理,会有堆栈信息返回到页面的原因)
throw ex;
}
在 DispatcherServlet 初始化的时候,会注册一批 HandlerExceptionResolver 到 DispatcherServlet 中,如: HandlerExceptionResolverComposite 和 DefaultErrorAttributes 等。
private void initHandlerExceptionResolvers(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) {
//查找所有注册到Spring容器中的`HandlerExceptionResolver`
// Find all HandlerExceptionResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerExceptionResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils
.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = new ArrayList<HandlerExceptionResolver>(matchingBeans.values());
//按配置的Order排序,多个`HandlerExceptionResolver`有先后顺序关系
// We keep HandlerExceptionResolvers in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerExceptionResolvers);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerExceptionResolver her =
context.getBean(HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerExceptionResolver.class);
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = Collections.singletonList(her);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, no HandlerExceptionResolver is fine too.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least some HandlerExceptionResolvers, by registering
// default HandlerExceptionResolvers if no other resolvers are found.
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers == null) {
//获取默认的异常处理策略
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerExceptionResolvers found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
下图是SpringMVC中如果配置了 <mvc:annotation-driven/> 就会引入的 HandlerExceptionResolverComposite 其持有的三个异常处理解析器: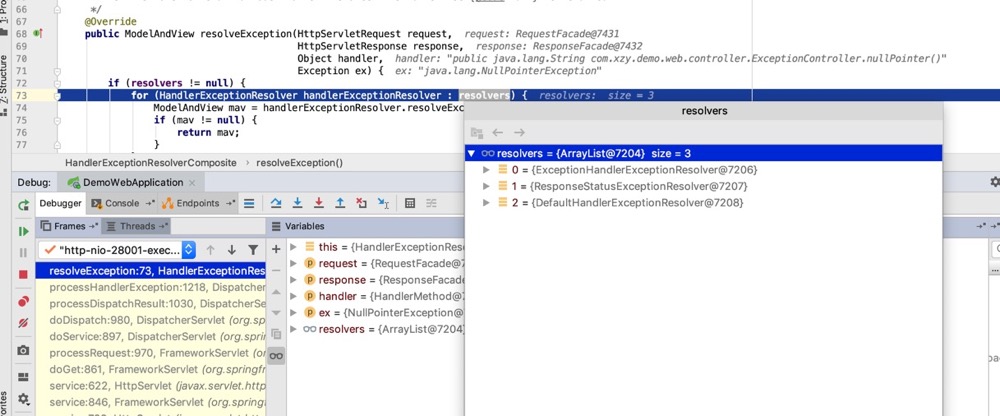
其中 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 类主要用来处理 @ExceptionHandler 注解, @ExceptionHandler 和 @ControllerAdvice 组合使用时,也是用 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 来处理。 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 也会处理 @ResponseStatus ,改变返回的http状态。
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 负责处理类似于NoSuchRequestHandlingMethodException,HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException,HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException,HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException…等等异常。是HandlerExceptionResolver接口的默认实现,负责处理标准的spring异常,并将其转变为对应的http状态码。
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver主要用来处理使用了@ResponseStatus注解的异常,根据@ResponseStatus注解的内容返回相应的http状态码。
因为一般第一个HandlerExceptionResolver解析了异常,就直接return了,所以我们重点分析下ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver。
在分析ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver之前,我们先来看看ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver。
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver源码分析
@ExceptionHandler注解作用于方法上,而ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver会扫描@ExceptionHandler所标注的方法,在调用ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver构造函数的时候,会扫描@ExceptionHandler所修饰的方法,并将其放到<Class<? extends Throwable>, Method>这样的一个map中。可以调用ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver#resolveMethod方法,根据传入的exception获取标注@ExceptionHandler的方法。
//ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver的构造函数
public ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(Class<?> handlerType) {
//找出传入的class及其父类中,所有标准了`@ExceptionHandler`注解的方法
for (Method method : MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS)) {
//@ExceptionHandler的value可以对应多个异常,遍历其标注的所有异常
for (Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType : detectExceptionMappings(method)) {
//以异常类型为key,方法为value,保存到map中缓存
addExceptionMapping(exceptionType, method);
}
}
}
//HandlerExceptionResolver会调用resolveMethod获取需要执行的method
//然后通过反射的方式执行这个method
public Method resolveMethod(Exception exception) {
Method method = resolveMethodByExceptionType(exception.getClass());
if (method == null) {
Throwable cause = exception.getCause();
if (cause != null) {
method = resolveMethodByExceptionType(cause.getClass());
}
}
return method;
}
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver部分源码解析
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver这个类实现了InitializingBean接口,并且在afterPropertiesSet()方法中,扫描标记了@ControllerAdvice和@ExceptionHandler的注解,保存到map中缓存。
private void initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache() {
if (getApplicationContext() == null) {
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for exception mappings: " + getApplicationContext());
}
//查找所有标记了`@ControllerAdvice`注解的Bean
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(adviceBeans);
//遍历所有标记了`@ControllerAdvice`注解的Bean
for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) {
//构造异常解析器,上面我们分析过了
//构造`ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver`时会扫描这个Bean里面的所有`@ExceptionHandler`注解
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(adviceBean.getBeanType());
//如果存在exception-handler_method这样的映射关系
//将这个adviceBean和对应的解析器resolver保存到缓存从
if (resolver.hasExceptionMappings()) {
this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, resolver);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected @ExceptionHandler methods in " + adviceBean);
}
}
//如果这个exception_handler_method方法上,标准了`@ResponseBody`,将其添加到`responseBodyAdvice`,这个在返回值处理方式略有不同
if (ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(adviceBean.getBeanType())) {
this.responseBodyAdvice.add(adviceBean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected ResponseBodyAdvice implementation in " + adviceBean);
}
}
}
}
前面我们分析到,DispatcherServlet会调用HandlerExceptionResolver#resolveException方法处理解析异常。在ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver中,resolveException方法会调用ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver#doResolveHandlerMethodException方法,在doResolveHandlerMethodException方法中处理解析异常。
@Override
protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
//根据request请求对应的controller方法和抛出的异常来匹配对应的`@ExceptionHandler`方法
//分两种情况,一种是只使用了`@ExceptionHandler`,另一种是`@ExceptionHandler`和`@ControllerAdvice`组合使用
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception);
if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) {
return null;
}
//注入`HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite`和`HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite`
//方便处理HandlerMethod的请求参数和返回值
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
try {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking @ExceptionHandler method: " + exceptionHandlerMethod);
}
//执行异常处理方法,这里先尝试下获取异常原因,如果获取到用异常原因的那个throwable作参数
Throwable cause = exception.getCause();
if (cause != null) {
// Expose cause as provided argument as well
exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, exception, cause, handlerMethod);
}
else {
// Otherwise, just the given exception as-is
exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, exception, handlerMethod);
}
}
catch (Throwable invocationEx) {
// Any other than the original exception is unintended here,
// probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like).
if (invocationEx != exception && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failed to invoke @ExceptionHandler method: " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx);
}
// Continue with default processing of the original exception...
return null;
}
//渲染返回结果,返回结果在`ModelAndViewContainer`中
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return new ModelAndView();
}
else {
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
HttpStatus status = mavContainer.getStatus();
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, status);
mav.setViewName(mavContainer.getViewName());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.