- 使用alias和自定义的function的必要性和重要性就不说了 , 自己的通用做法是:
可以创建: ~/bin/my.alias 文件 作为自定义的 alias专门文件
创建: ~/libsh/my.func文件, 作为自己的 sh库函数文件:
然后在.bashrc文件中, 包含并执行这两个文件:
# 载入自定义命令文件
if [ -f ~/bin/my.alias ]; then
. ~/bin/my.alias
fi
# 载入自定义库~/lib中的函数/命令
if [ -f ~/libsh/my.func ]; then
. ~/libsh/my.func
fi
- 编辑~/libsh/my.func 的内容是:
# shell function library
function sidnf()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'sidnf: usage: sidnf PKG_TO_INSTALLED [...]'
return 1
fi
si='dnf install '$1
echo "sidnf: run su -c '"$si"' as root ..."
su -c "$si"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
- 编辑 ~/bin/my.alias的内容:
#自定义httpd的aliases
alias edh='su -c "vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf"'
alias rsh='su -c "systemctl restart httpd.service"'
alias stah='systemctl status httpd'
alias sth='su -c "systemctl stop httpd.service"'
# 自定义mariadb的aliases
alias rsm='su -c "systemctl restart mariadb.service"'
alias stam='systemctl status mariadb'
alias stm='su -c "systemctl stop mariadb.service"'
alias senf0='su -c "setenforce 0"'
alias senf1='su -c "setenforce 1"'
alias fwon='su -c "systemctl start firewalld"'
alias fwoff='su -c "systemctl stop firewalld"'
alias fwsta='systemctl status firewalld'
# 定义vi的alias
alias vi='vim'
重要的是, 可以把这里的这些别名加以记忆, 就作为自己的 固定的 别名和使用习惯了!! 如果记不住了, 可以使用 alias命令查看 一下即可.
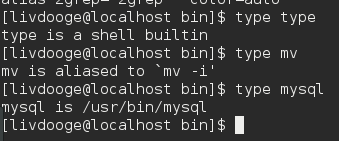
- type type 是显示 type 的类型. 可以看到 type 是 shell 的 builtin 内建 命令 , 输出结果的样子像: command is ....
对于shell:
如果是 另外 在机器上的 其他目录, 如 /usr/bin, /usr/sbin目录中, 真的有这样的命令文件 存在, 那么这种命令就是 shell的 "外部命令" , 显示: 比如: mysql is /usr/bin/mysql
如果在另外的机器目录上, 没有这样的命令文件存在, 那么就是shell的 "内建"命令, 显示: 比如: cd is a shell builtin.
如果是 "外表命令的别名" 则显示: mv is aliased to 'mv -i'
更全面的内容:
家目录下的 文件夹 libsh/下的文件 my.func
# shell function library
function sidnf()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'sidnf: usage: sidnf PKG_TO_INSTALLED [...]'
return 1
fi
si='dnf install '$*
echo "sidnf: Run su -c '"$si"' as root"
su -c "$si"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
function srdnf()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'srdnf: usage: srdnf PKG_TO_REMOVED [...]'
return 1
fi
sr='dnf remove '$*
echo "srdnf: Run su -c '"$sr"' as root"
su -c "$sr"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
function svi()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'svi: usage: svi file_to_edit_as_root'
return 1
fi
svi='vim '$1
echo "svi: Run su -c '"$svi"' as root ..."
su -c "$svi"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
function smv()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'usage: smv file_to_mv'
return 1
fi
smv='mv '$1' '$2
echo "smv: Run su -c '"$smv"' as root ..."
su -c "$smv"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
function scp()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'usage: scp file_to_cp'
return 1
fi
scp='cp '$1' '$2
echo "scp: Run su -c '"$scp"' as root ..."
su -c "$scp"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
function srm()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
echo 'usage: srm file_to_rm'
return 1
fi
srm='rm '$1
echo "Run su -c '"$srm"' as root"
su -c "$srm"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
function sls()
{
if [ $# -eq 0 ] ; then
su -c 'ls'
return 0
fi
sls='ls '$*
echo "Run su -c '"$sls"' as root"
su -c "$sls"
read -t1 -s svar
## exit
}
## 家目录下的 bin文件夹下的 my.alias
# 这里用 h代表 httpd服务; 用m代表mariadb.service服务
# 包括startx启动, 重载配置文件: reloadx , 停止stx, 状态stax, 重启: rsx
#
#自定义httpd的aliases
alias starth='su -c "systemctl start httpd"' # 其实这个可以不用 , 因为通常设置了 开机启动服务的
alias reloadh='su -c "systemctl reload httpd"'
alias edh='su -c "vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf"'
alias rsh='su -c "systemctl restart httpd.service"'
alias stah='systemctl status httpd'
alias sth='su -c "systemctl stop httpd.service"'
alias lsd='ls --group-directories-first'
alias lld='ll --group-directories-first'
alias lz='ll -Z --group-directories-first'
# 自定义mariadb的aliases
alias startm='su -c "systemctl start mariadb.service"' # 其实这个可以不用 , 因为通常设置了 开机启动服务的
# alias reloadm='su -c "systemctl reload mariadb"' # 提示对于 mariadb 这个命令reload 不适用.
alias rsm='su -c "systemctl restart mariadb.service"'
alias stam='systemctl status mariadb'
alias stm='su -c "systemctl stop mariadb.service"'
alias senf0='su -c "setenforce 0"'
alias senf1='su -c "setenforce 1"'
alias fwon='su -c "systemctl start firewalld"'
alias fwoff='su -c "systemctl stop firewalld"'
alias fwsta='systemctl status firewalld'
# 定义vi的alias
alias vi='vim'