一、内容概要
1、Python 介绍
2、Python 版本
3、编写Hello World
4、编码
5、输入输出
6、变量
7、数据类型
8、条件语句
9、循环语句
10、常用数据类型
二、内容详细
1、Python 介绍
Python, 是一种面向对象的解释型计算机程序设计语言,由荷兰人Guido van Rossum于1989年发明,第一个公开发行版发行于1991年。
最新的TIOBE排行榜,Python赶超PHP占据第五!!!
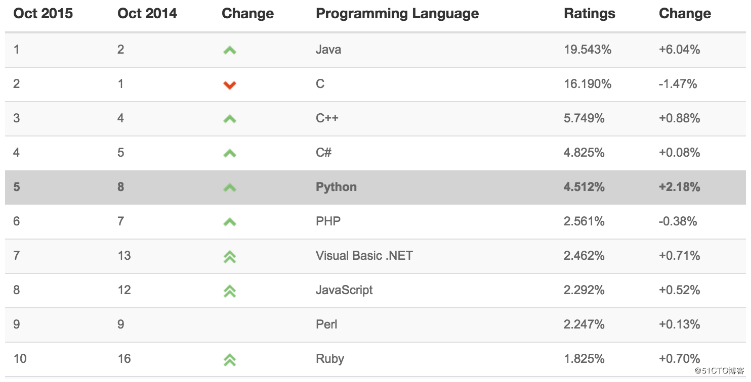
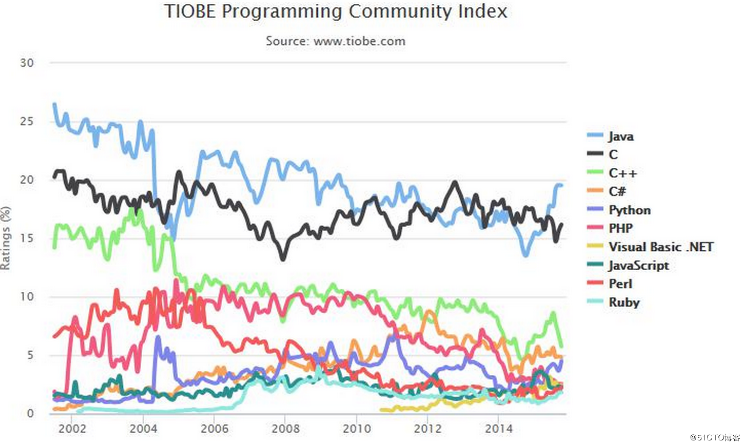
由上图可见,Python整体呈上升趋势,反映出Python应用越来越广泛并且也逐渐得到业内的认可!!!
Python可以应用于众多领域,如:数据分析、组件集成、网络服务、图像处理、数值计算和科学计算等众多领域。目前业内几乎所有大中型互联网企业 都在使用Python,如:Youtube、Dropbox、BT、Quora(中国知乎)、豆瓣、知乎、Google、Yahoo!、 Facebook、NASA、百度、腾讯、汽车之家、美团等。互联网公司广泛使用Python来做的事一般有:自动化运维、自动化测试、大数据分析、爬虫、Web 等。
1.1、为什么是Python而不是其他语言?
C 和 Python、Java、C#等
C语言: 代码编译得到 机器码 ,机器码在处理器上直接执行,每一条指令控制CPU工作
其他语言: 代码编译得到 字节码 ,虚拟机执行字节码并转换成机器码再后在处理器上执行
Python 和 C Python这门语言是由C开发而来
对于使用:Python的类库齐全并且使用简洁,如果要实现同样的功能,Python 10行代码可以解决,C可能就需要100行甚至更多.
对于速度:Python的运行速度相较与C,绝逼是慢了
Python 和 Java、C#等
对于使用:Linux原装Python,其他语言没有;以上几门语言都有非常丰富的类库支持
对于速度:Python在速度上可能稍显逊色
所以,Python和其他语言没有什么本质区别,其他区别在于:擅长某领域、人才丰富、先入为主。
1.2、Python的种类
Cpython
Python的官方版本,使用C语言实现,使用最为广泛,CPython实现会将源文件(py文件)转换成字节码文件(pyc文件),然后运行在Python虚拟机上。
Jyhton
Python的Java实现,Jython会将Python代码动态编译成Java字节码,然后在JVM上运行。
IronPython
Python的C#实现,IronPython将Python代码编译成C#字节码,然后在CLR上运行。(与Jython类似)
PyPy(特殊)
Python实现的Python,将Python的字节码字节码再编译成机器码。
RubyPython、Brython ...
2、python解释器版本
→Python2.7
→Python3.6
2.1、python安装
windows:
2.1.1、下载安装包
https://www.python.org/downloads/
2.1.2、安装
默认安装路径:C:python36
2.1.3、配置环境变量
【右键计算机】--》【属性】--》【高级系统设置】--》【高级】--》【环境变量】--》【在第二个内容框中找到 变量名为Path 的一行,双击】 --> 【Python安装目录追加到变值值中,用 ; 分割】
如:原来的值;C:python36,切记前面有分号
环境变量:
Python配置:
;C:Python36;
终端:python
pip配置:
;C:Python36Scripts
终端:pip3 install xxxx
;C:Python36;C:Python36Scripts;
linux:
无需安装,原装Python环境
3. 编写程序
创建任意文件.py
print('hello world')
4. 编码
ascii:用1个字节=8位来表示计算机能表达的所有东西。
ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国标准信息交换代码)是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言,其最多只能用 8 位来表示(一个字节),即:28 = 256,所以,ASCII码最多只能表示 256 个符号。
00000000 -> A
00000001 -> B
00000010 -> C
00000011
00000100
unicode: 万国码,用4个字节=32位来做对应关系
Unicode(统一码、万国码、单一码)是一种在计算机上使用的字符编码。Unicode 是为了解决传统的字符编码方案的局限而产生的,它为每种语言中的每个字符设定了统一并且唯一的二进制编码,规定虽有的字符和符号最少由 16 位来表示(2个字节),即:2 16 = 65536,
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 -> A
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 -> B
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000010 -> C
00000000 10000000 00010000 00011010 -> 紫
utf-8: 对万国码进行压缩,至少使用1个字节表示
UTF-8,是对Unicode编码的压缩和优化,他不再使用最少使用2个字节,而是将所有的字符和符号进行分类:ascii码中的内容用1个字节保存、欧洲的字符用2个字节保存,东亚的字符用3个字节保存...
00000000
00000001
00000010
10000000 00010000 00011010
PS: 中文3个字节=24位
gbk:对亚洲国家的文字做的对应关系
PS: 中文2个字节=16位
注意:
py2: 解释器默认编码ascii
#解释器默认编码utf-8
print('王紫薇')
py3:解释器默认编码utf-8
print('要睡觉')
py2/py3:#-- coding:gbk --
print('要睡觉')
4.1. IDE
→pycharm
→vim
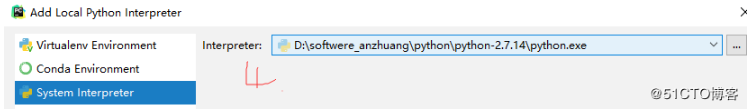
使用:
- 启动Pycharm:选择已存在的解释器
- 运行
- 配置
- 文字大小
- 模板

5. 输入输出
输出:
print("你是风儿我是沙")
输入:
user = input("请输入用户名:")
密码加密:
import getpass
pwd = getpass.getpass("请输入密码:") #需要在终端进行密码验证(密文)

6.变量
变量的作用:昵称,其代指内存里某个地址中保存的内容
变量定义的规则:
- 变量名只能是 字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
- 变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
以下关键字不能声明为变量名
['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
建议:见名知意; user_pwd = "xxx"
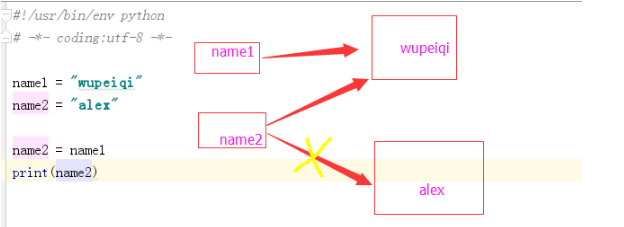
6.1、示例
7. 数据类型
age = 18 # 整数类型
name = "alex" # 字符串类型
xx = "18"
xx = '18'
xx = '''18'''
xx = """18"""
xx = "123'
8. 条件语句
格式一:
if 条件:
成功之后走这里
格式二:
if 条件:
成功之后走这里
else:
失败之后走这里
格式三:
if 条件:
成功之后走这里
elif 条件:
成功之后走这里
elif 条件:
成功之后走这里
else:
上述都失败
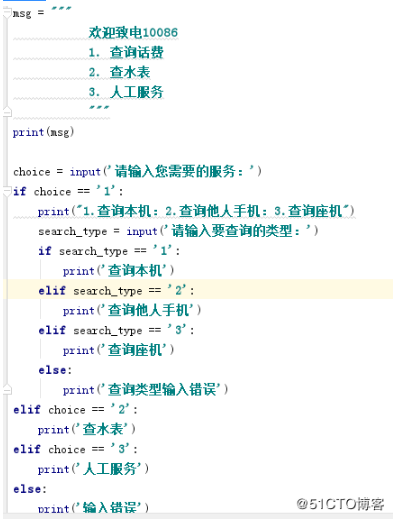
示例:
9. 循环语句
while 条件: 条件成立执行 while True: print('钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓') while 1==1 and 2==2: print('钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓')
timer = 0 while timer < 3: print('钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓') timer = timer + 1 print('完成') 示例: 练习1: 页面上输出 1 - 10 count = 1 while count < 11: print(count) count = count + 1 break,强制终止当前所在循环 while True: print('钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓') break 练习2: 页面上输出 1 - 10 (使用break) count = 1 while True: print(count) count = count + 1 if count == 11: break count = 1 while True: print(count) if count == 10: break count = count + 1 continue,跳出本次循环,继续下一次循环 练习题3:页面上输出 1 - 10,排除7 count = 1 while count < 11: if count == 7: count = count + 1 continue print(count) count = count + 1 第二种: count = 1 while count < 11: if count == 7: pass else: print(count) count = count + 1
10.常用数据类型
整数:
age = 18
字符串:
name = "紫薇"
n1 = name[0] #获取紫
n2 = name[1] #获取薇
列表:
user_list = ["紫薇","尔康","18","海量","小鸡"]
n3 = user_list[0] #紫薇
n4 = user_list[1] # "尔康"
user_list = ["紫薇","尔康","18","海量","小鸡"]
for xxx in user_list:
print(xxx)
if xxx == '18':
break
字典:
user_info = {"name":"紫薇","age":18}
n5 = user_info["name"] #获取紫薇
n6 = user_info["age"] #获取18

user_info['count'] = 666 #{"name":"紫薇","age":18,"count":666} 数据类型嵌套: n7 = ["alex","eric",[11,22,33]] n7[1] # 获取 eric n7[2][1] #获取 11 n8 = [ "alex", {'name':'日天','age':18}, [11,22,33] ] n8[1]["age"] = 19 #修改键值对 问题1: 循环用户列表,打印用户姓名和密码 user_list = [ {'username':'alex', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, {'username':'eric', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, {'username':'tony', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, {'username':'oldboy', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, ] for item in user_list: print(item['username'],item['password'],item['count']) 问题2: 将每个用户的count改成1 user_list = [ {'username':'alex', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, {'username':'eric', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, {'username':'tony', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, {'username':'oldboy', 'password':'123', 'count':0 }, ] for item in user_list: if item['username'] == 'alex' and item['password'] == '123': item['count'] = 1 print(item) 问题3: 用户输入用户名和密码,在user_list中进行校验 user_list = [ {'username':'alex', 'password':'123' }, {'username':'eric', 'password':'123'}, {'username':'tony', 'password':'123'}, {'username':'oldboy', 'password':'123'}, ] user = input("请输入用户名:") pwd = input("请输入密码:") flag = False for item in user_list: if item['username'] == user and item['password'] == pwd: flag = True break else: pass if flag: print("登录成功") else: print("登录失败")
11、课后练习题
11.1 求1-100所有数的和
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- value = 0 i = 1 while i < 101: value = value + i i = i + 1 print(value)
11.2 求1-100内的所有奇数
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- i = 1 while i < 101: if i % 2 == 1: print(i) i = i + 1
11.3 求1-100内所有偶数
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- i = 1 while i < 101: if i % 2 == 0: print(i) i = i + 1
11.4 求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- i = 1 n = 2 while n < 100: i = i - n n = n + 1 i = i + n n = n + 1 print(i) 第二种 i =1 sum = 0 while True : if i % 2 ==0 : i = -i sum = sum + i i = abs(i) + 1 if i == 100 : break print(sum)
11.5 用户登录(3次机会)

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # 用户登录三次失败并直接退出 # i = 0 # while i < 3: # username = input('请输入用户名:') # password = input('请输入密码:') # if username == 'oldboy' and password == 'boss': # print('登录成功') # break # else: # print('用户名或密码失败') # i = i + 1 #用户登录三次失败并退出 user_list = [ {'username':'alex', 'password':'123' }, {'username':'eric', 'password':'123'}, {'username':'tony', 'password':'123'}, {'username':'oldboy', 'password':'123'} ] i = 1 while True: user = input("请输入用户名:") passwd = input("请输入密码:") flag = False for item in user_list: if item['username'] == user and item['password'] == passwd: print("登录成功") flag = True break if flag: break else: print("用户名或密码有误") if i < 3: pass else: print("登录失败") break i += 1
