react-router-dom
react-router-dom文档地址: https://reacttraining.com/react-router/
安装
npm i -S react-router-dom
react-router提供多个包可以单独使用
| package | description |
|---|---|
| react-router | 路由核心功能 |
| react-router-dom | 基于react-router提供在浏览器运行环境下功能 |
| react-router-native | for React Native |
| react-router-config | static route congif helpers |
API 路由和底层接口 (React router中最重要的模块,主要职责是当location匹配路由时,会将UI render出来)
- 1、
component: 当传递component渲染UI时,router将会用React.createElement来将组件封装成一个新的React element, 当传递一个inline func, react每次render都会unmount, mount一个新的组件,会消耗性能,此时可以使用render/children prop - 2、
render: func, inline func不会有上述性能问题,参数同route props相同。 - 3、
children: func, 有时,无论location是否匹配路由,你都想render某个UI,此时可以使用children prop ,等同于render。 函数参数同route props component, render优先级高于children,所以不要一次使用一种以上的渲染方式。 - 4、
path: string | string[], 一个url字符串,或者一组url 字符串,会进行正则匹配。 - 5、
exact: bool, 为true, 要精准匹配,path同location.pathname完全一致。
使用redirect将跳转到一个新的路由,新的location将会覆盖history stack中的当前location。
- 1、
to: string, url地址 。 - 2、
to: object, location object, 属性有:pathname: 跳转路径,search: 查询参数, hash: url中的hash, eg. #a-hash, state:存储到location中的额外状态数据. location中的state可以在redirect跳转组件的this.props.location.state访问。 - 3、
push: 为true表示redirect path将往history stack中推一条新数据而不是替换他。 - 4、
from: redirect from url, 会进行正则匹配。只能用在中。 - 5、
exact: bool, 精准匹配。
进入页面路由的链接
- 1、
to: string, 路由链接, 由location的path, search, hash属性拼接而成。 - 2、
to : object{ pathname: 跳转路径,search: 查询参数, hash: url中的hash, eg. #a-hash, state:存储到location中的额外状态数据}。 - 3、
replace: 布尔值- 为true时,将会替换history stack中的当前路径innerRef: function允许访问Link的底层组件<a></a>,eg. <Link to='/' innerRef={(node)=>{this.refNode=node}} />。
路由组件
react-router包含三种类型的组件:路由组件、路由匹配组件 、导航组件。在你使用这些组件的时候,都必须先从react-router-dom引入。
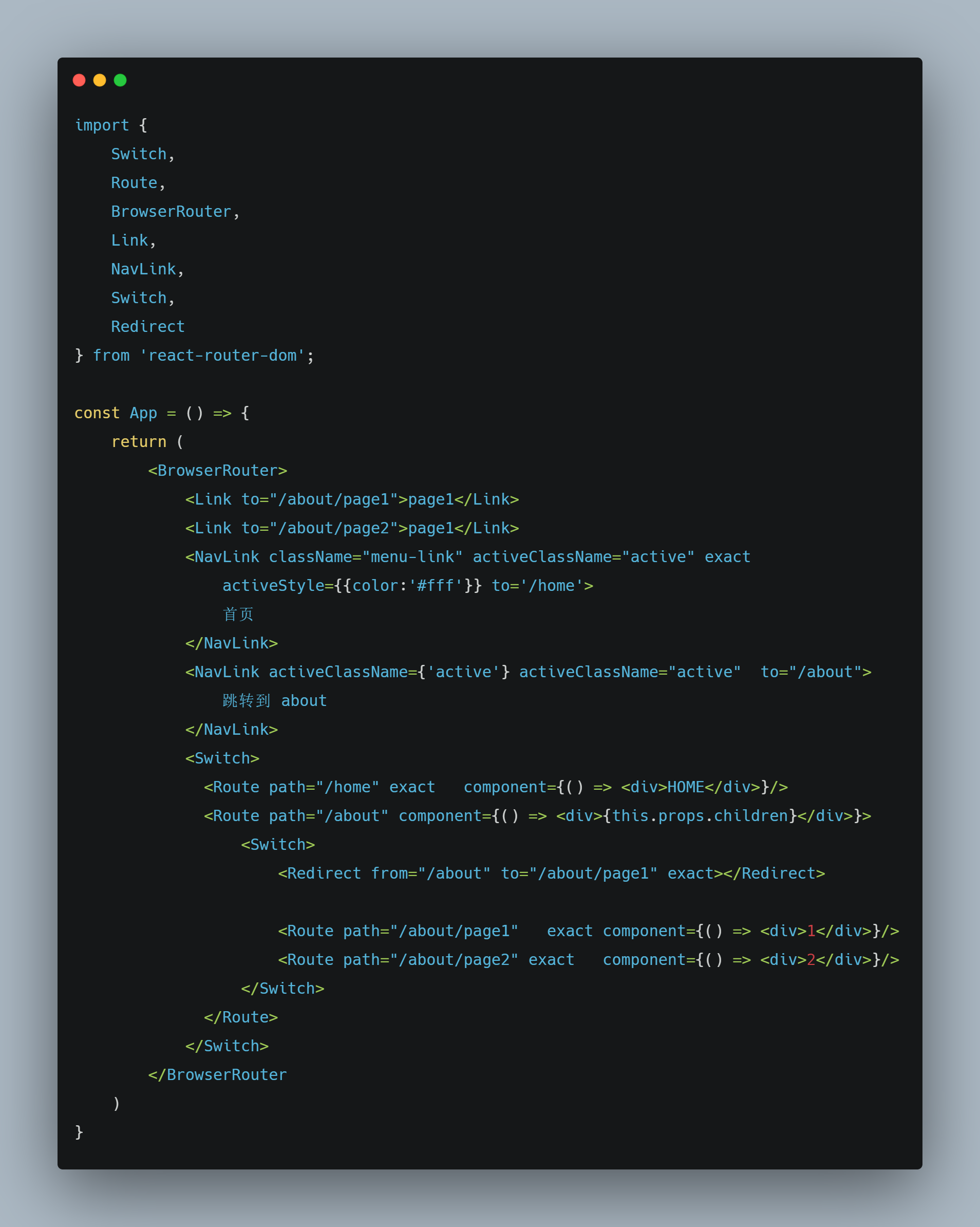
路由组件
react-router提供了两种路由组件:
BrowserRouter其中BrowserRouter是基于HTML5 history API (pushState,replaceState,popstate)事件
HashRouter当然与之对应的还有HashRouter是基于window.location.hash。
路由匹配组件
路由匹配组件有两种:Route和Switch,Switch把多个路由组合在一起。
对于一个<Route>组件,可以设置三种属性:component、render、children来渲染出对应的内容。
当组件已存在时,一般使用component属性当需要传递参数变量给组件时,需要使用render属性
导航组件
有三种常用的导航组件,分别是:<Link>、<NavLink>、<Redirect>。<NavLink>是一种特殊的Link组件,匹配路径时,渲染的a标签带有active。
基本使用
import React from 'react';
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Switch,
Route,
Link
} from "react-router-dom";
const App = () => {
return (
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/about">About</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/person">Person</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
)
}
当然此处路由也可以有其他写法,比如
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home}></Route>
<Route path="/about" component={About}></Route>
<Route path="/person/:id" component={Person}></Route>
<Route component={NotFind}></Route>
</Switch>
其中的exact表示的是精确匹配,比如上面
<Route exact path="/" component={Home}></Route>
如果没有写精确匹配的化,那么后面的所有路径都可以匹配到首页,解决方式就是增加exact或者将此路由放置最后面。
Route动态传参
1、第一种方式通过动态路由
在一个路由匹配组件上设置参数,比如说上面的Person组件
<Route path="/person/:id" component={Person}></Route>
设置是以:开始然后紧跟key值,然后我们在Person组件中就可以通过获取props获取这个参数值
import React from 'react';
export default class Person extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log(this.props.match.params.id)
}
render() {
const id = this.props.match.params.id
return (
<div>
<h2>个人中心页面</h2>
<p>个人id是:{id}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
2、第二种方式:通过query 前提:必须由其他页面跳过来,参数才会被传递过来
function My(props) {
console.log(props.match.params); // 通过动态路由
console.log(props.location.query); // 通过query
console.log(props.location.state); // 通过state
return (
<div>
</div>
)
}
<Link to={{ path : '/my' , query : { id : 1 }}}>我的</Link>
<Switch>
<Route path="/my" component={My}></Route>
</Switch>
this.props.history.push({ path : '/my' ,query : {id: 1} })
3、第三种方式: 通过state
<Link to={{pathname: '/my' , state:{ id : 1 }}}>我的</Link>
<Switch>
<Route path="/my" component={My}></Route>
</Switch>
this.props.history.push({ pathname: '/my' ,state: {id: 1} })
以上为传统class组件的写法,现在可以使用hooks,可以使用useParams,代码如下:
import React from 'react';
import { useParams } from 'react-router-dom'
const Person = () => {
const { id } = useParams();
return (
<div>
<h2>个人中心页面</h2>
<p>个人id是:{id}</p>
</div>
)
}
嵌套路由
在About页面有一个嵌套路由代码示例:
import React from 'react';
import { Link, Switch, Route } from 'react-router-dom'
import Tshirt from './product/Tshirt';
import Jeans from './product/Jeans'
export default class About extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
console.log(this.props.match)
}
render() {
const match = this.props.match;
return (
<>
<nav>
<Link to={`${match.url}/tshirt`}>Tshirt</Link>|
<Link to={`${match.url}/jeans`}>Jeans</Link>
</nav>
<Switch>
<Route path={`${match.path}/tshirt`} component={Tshirt}></Route>
<Route path={`${match.path}/jeans`} exact component={Jeans}></Route>
</Switch>
</>
)
}
}
此处如果换成Function的话可以直接使用另一个钩子函数useRouteMatch,获取当前匹配的路径和路由
import { useRouteMatch } from 'react-router-dom'
const About = () => {
const { path, url } = useRouteMatch();
...省略
}
路由重定向
Redirect路由重定向,使路由重定向到某个页面,比如我们经常会做的没有登录重定向到登录页面
<Route exact path="/">
{loggedIn ? <Redirect to="/dashboard" /> : <PublicHomePage />}
</Route>
滚动还原
大部分情况下,我们需要的是每次导航到某个新页面的的时候,滚动条都是在顶部,这种比较好实现
hooks版本
import { useEffect } from "react";import { useLocation } from "react-router-dom";
export default function ScrollToTop() {
const { pathname } = useLocation();
useEffect(() => {
window.scrollTo(0, 0);
}, [pathname]);
return null;
}
class版本
import React from "react";import { withRouter } from "react-router-dom";
class ScrollToTop extends React.Component {
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
if (
this.props.location.pathname !== prevProps.location.pathname
) {
window.scrollTo(0, 0);
}
}
render() {
return null;
}}
我们需要把ScrollToTop组件放在Router里面eg:
function App() {
return (
<Router>
<ScrollToTop />
<App />
</Router>
);}
而对于某些情况下比如一些tab我们希望切换回我们浏览过的tab页时我们希望滚动条滚动到我们之前浏览的位置,此处自行去实现。
路由守卫
有时候我们在某个表单页面填好了表单,然后点击跳转到另外一个页面。
这时候我们就需要提醒用户有未提交的表单。当然这一步其实也是在实际的业务代码中实现。
import React, { useState } from "react";
import {
Prompt
} from "react-router-dom";
const BlockingForm = ()=>{
let [isBlocking, setIsBlocking] = useState(false);
return (
<form
onSubmit={event => {
event.preventDefault();
event.target.reset();
setIsBlocking(false);
}}
>
<Prompt
when={isBlocking}
message={location =>
`你是否要跳转到 ${location.pathname}`
}
/>
<p>
Blocking?{" "}
{isBlocking ? "Yes, click a link or the back button" : "Nope"}
</p>
<p>
<input
size="50"
placeholder="输入值测试路由拦截"
onChange={event => {
setIsBlocking(event.target.value.length > 0);
}}
/>
</p>
<p>
<button>提交表单模拟接触拦截</button>
</p>
</form>
);
}
export default BlockingForm;
代码分割
有时候为了避免文件过大加快加载速度,我们需要将代码分割,将某些路由对应的组件只有在点击的时候再加载js,就是组件的懒加载。
我们使用webpack, @babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import,loadable-components实现代码分割。
1、首先在.babelrc文件中增加配置
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-react"],
"plugins": ["@babel/plugin-syntax-dynamic-import"]
}
2、 在我们需要懒加载的组件使用loadabel
import React from 'react';
import loadable from '@loadable/component';
const BlockForm = loadable(() => import('../pages/BlockForm/index'), {
fallback: <Loading />
})
其中BlockForm为懒加载得组件。
loadable参考文档地址 跳转
withRouter
您可以通过withRouter高阶组件访问history属性和匹配的Route,
withRouter will pass updated match, location, and history props to the wrapped component whenever it renders.
import React from "react";import PropTypes from "prop-types";import { withRouter } from "react-router";
// A simple component that shows the pathname of the current locationclass ShowTheLocation extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
match: PropTypes.object.isRequired,
location: PropTypes.object.isRequired,
history: PropTypes.object.isRequired
};
render() {
const { match, location, history } = this.props;
return <div>You are now at {location.pathname}</div>;
}}
// Create a new component that is "connected" (to borrow redux// terminology) to the router.const ShowTheLocationWithRouter = withRouter(ShowTheLocation);
其他hooks
之前使用了useParams和useRouteMatch两个hook,还有另外两个hook
useHistory和useLocation
useHistory 可以访问到history实例,我们可以通过这个实例访问某个路由
useLocation返回location对象