一、可以生成文档
/** * @author meng * @version 1.2 */ public class Student { /** * * @param a 参数1 * @param b 参数2 * @return 两数之和 */ public int add(int a, int b){ return a+b; } }
生成文档
javadoc Student.java
生成一堆html文件,打开index.html
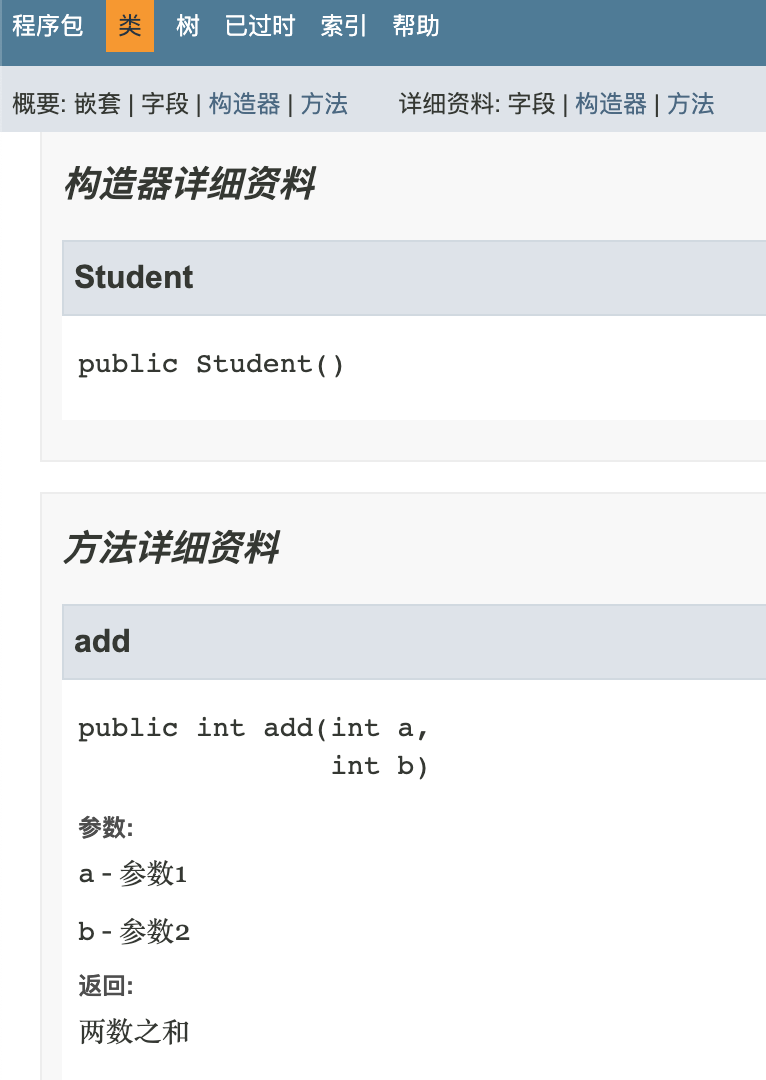
二、编译检查
例如
如果父类里没有改方法名,则报错
@Override public String toString1(){ return name+age; }
三、代码分析
1. 基本注解
(1)@override
(2)@Deprecated
标注已过时
@Deprecated public int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
(3)@SuppressWarning
关闭警告
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Student {
}
2.注解的本质
Student.java文件
public @interface Student { }
使用javac编译
javac Stuent.java
反编译
javap Student.class
命令行得到代码
public interface Student extends java.lang.annotation.Annotation { }
本质是继承了Annotation接口
3.注解的属性
//可以返回的类型 public @interface Student { //基本数据类型 int a(); //String类型 String b(); //枚举类型 //注解类型 //以及以上四种类型的数组。 //剩下其他的返回类型都不可以 }
4.元注解
(1)@Target
控制注释能修饰的位置(类、变量、方法等)
例如
ElementType.TYPE表示只能作用于类
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface Student { }
(2)@Retention
注解被保留到哪一个阶段
例如
被保留到runtime 运行时阶段
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Student { }
(3)@Documented
注解能够被保留到文档
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Student { }
(4)@Inherited
如果父类添加了Inherited,则子类会自动继承父类的注解
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited public @interface Student { }
5.自定义注解的使用
编写注解类
import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface ZhuJie { String m(); }
使用注解
@ZhuJie(m="hello1") public class Student { }
框架等方式解析注解
public class Test { public Test() { } public static void main(String[] args) { //反射Student类 Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class; //获取类中的指定注解 ZhuJie zj = studentClass.getAnnotation(ZhuJie.class); //调用注释里的方法,获取到hello var a= zj.m(); System.out.println(a); } }