一、编译安装
首先到官网下载iozone的稳定版源码
http://www.iozone.org/
然后解压编译
tar -vxf iozone3_458.tar cd iozone3_458/src/current make linux-AMD64
最后生成了iozone的可执行文件;
二、使用说明
./iozone -h查看运行参数

[root@localhost iozone3_458]# ./iozone -h iozone: help mode Usage: iozone [-s filesize_kB] [-r record_size_kB] [-f [path]filename] [-h] [-i test] [-E] [-p] [-a] [-A] [-z] [-Z] [-m] [-M] [-t children] [-l min_number_procs] [-u max_number_procs] [-v] [-R] [-x] [-o] [-d microseconds] [-F path1 path2...] [-V pattern] [-j stride] [-T] [-C] [-B] [-D] [-G] [-I] [-H depth] [-k depth] [-U mount_point] [-S cache_size] [-O] [-L cacheline_size] [-K] [-g maxfilesize_kB] [-n minfilesize_kB] [-N] [-Q] [-P start_cpu] [-e] [-c] [-b Excel.xls] [-J milliseconds] [-X write_telemetry_filename] [-w] [-W] [-Y read_telemetry_filename] [-y minrecsize_kB] [-q maxrecsize_kB] [-+u] [-+m cluster_filename] [-+d] [-+x multiplier] [-+p # ] [-+r] [-+t] [-+X] [-+Z] [-+w percent dedupable] [-+y percent_interior_dedup] [-+C percent_dedup_within] -a Auto mode -A Auto2 mode -b Filename Create Excel worksheet file -B Use mmap() files -c Include close in the timing calculations -C Show bytes transferred by each child in throughput testing -d # Microsecond delay out of barrier -D Use msync(MS_ASYNC) on mmap files -e Include flush (fsync,fflush) in the timing calculations -E Run extension tests -f filename to use -F filenames for each process/thread in throughput test -g # Set maximum file size (in kBytes) for auto mode (or #m or #g) -G Use msync(MS_SYNC) on mmap files -h help -H # Use POSIX async I/O with # async operations -i # Test to run (0=write/rewrite, 1=read/re-read, 2=random-read/write 3=Read-backwards, 4=Re-write-record, 5=stride-read, 6=fwrite/re-fwrite 7=fread/Re-fread, 8=random_mix, 9=pwrite/Re-pwrite, 10=pread/Re-pread 11=pwritev/Re-pwritev, 12=preadv/Re-preadv) -I Use VxFS VX_DIRECT, O_DIRECT,or O_DIRECTIO for all file operations -j # Set stride of file accesses to (# * record size) -J # milliseconds of compute cycle before each I/O operation -k # Use POSIX async I/O (no bcopy) with # async operations -K Create jitter in the access pattern for readers -l # Lower limit on number of processes to run -L # Set processor cache line size to value (in bytes) -m Use multiple buffers -M Report uname -a output -n # Set minimum file size (in kBytes) for auto mode (or #m or #g) -N Report results in microseconds per operation -o Writes are synch (O_SYNC) -O Give results in ops/sec. -p Purge on -P # Bind processes/threads to processors, starting with this cpu -q # Set maximum record size (in kBytes) for auto mode (or #m or #g) -Q Create offset/latency files -r # record size in Kb or -r #k .. size in kB or -r #m .. size in MB or -r #g .. size in GB -R Generate Excel report -s # file size in Kb or -s #k .. size in kB or -s #m .. size in MB or -s #g .. size in GB -S # Set processor cache size to value (in kBytes) -t # Number of threads or processes to use in throughput test -T Use POSIX pthreads for throughput tests -u # Upper limit on number of processes to run -U Mount point to remount between tests -v version information -V # Verify data pattern write/read -w Do not unlink temporary file -W Lock file when reading or writing -x Turn off stone-walling -X filename Write telemetry file. Contains lines with (offset reclen compute_time) in ascii -y # Set minimum record size (in kBytes) for auto mode (or #m or #g) -Y filename Read telemetry file. Contains lines with (offset reclen compute_time) in ascii -z Used in conjunction with -a to test all possible record sizes -Z Enable mixing of mmap I/O and file I/O -+b #,# burst size (KB),sleep between burst (mili-second) -+E Use existing non-Iozone file for read-only testing -+F Truncate file before write in thread_mix_test -+J Include think time (-j #) in throughput calculation -+K Sony special. Manual control of test 8. -+m Cluster_filename Enable Cluster testing -+d File I/O diagnostic mode. (To troubleshoot a broken file I/O subsystem) -+u Enable CPU utilization output (Experimental) -+x # Multiplier to use for incrementing file and record sizes -+p # Percentage of mix to be reads -+r Enable O_RSYNC|O_SYNC for all testing. -+t Enable network performance test. Requires -+m -+n No retests selected. -+k Use constant aggregate data set size. -+q Delay in seconds between tests. -+l Enable record locking mode. -+L Enable record locking mode, with shared file. -+B Sequential mixed workload. -+D Enable O_DSYNC mode. -+A # Enable madvise. 0 = normal, 1=random, 2=sequential 3=dontneed, 4=willneed -+N Do not truncate existing files on sequential writes. -+S # Dedup-able data is limited to sharing within each numerically identified file set. -+W # Add this value to the child thread ID, so that additional files can be added while maintaining the proper dedupability with previously existing files that are within the same seed group (-+S). -+V Enable shared file. No locking. -+X Enable short circuit mode for filesystem testing ONLY ALL Results are NOT valid in this mode. -+Z Enable old data set compatibility mode. WARNING.. Published hacks may invalidate these results and generate bogus, high values for results. -+w ## Percent of dedup-able data in buffers. -+y ## Percent of dedup-able within & across files in buffers. -+C ## Percent of dedup-able within & not across files in buffers. -+H Hostname Hostname of the PIT server. -+P Service Service of the PIT server. -+z Enable latency histogram logging.
三、常用的参数说明:
-n -g 用于指定测试的filesize的范围,相对应的-s指定一个确定值;
-y -q 用于指定每次读写的blocksize范围,相对应的-r指定一个定值;
-l -u用于指定使用的用户数从多少到多少;
-a 如果你指定了范围类的参数,那么不加-a,最后的结果只有第一列有数据;
-i 指定测试那种类型的读写,1-12可供选择;
-I 跳过缓存直接读写磁盘;
-f 指定输入文件的具体位置,这个文件一定要在你要测的那个磁盘上;
-F 如果你用了 -l -u 的话,那么里面有多少个用户,就要用这个参数指定多少个文件,文件之间用空格分隔,如:-F tmp.1 tmp.2 tmp.3;
-w 测试之后不删除测试文件;
-R 产生Excel到标准输出
-b 指定输出到指定文件上. 比如 -Rb ttt.xls
-Rb filename.xls 将结果写到Excel表格中;
四、测试命令示例和结果说明
./iozone -a -i 0 -i 1 -i 2 -i 6 -i 7 -i 8 -n 64m -g 256m -y 256 -q 8192 -I -f /mnt/mfs/1m.tmp -w -Rb ./xls/mfs_i.xls
结果的片段如下:
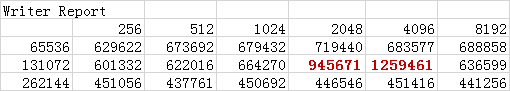
第一行,就是-i指定的那个参数,比如:表中使Writer Report,那么参数中就有 -i 2, 当然也有可能是-a自动加的;
第二行,各列值就是由"-y 256 -q 8192"指定的,单位是K,表示每次读写多大,当然在指定的时候也可以写M、G但是B是不起作用的;
第一列,各行就是由"-n 64m -g 256m"指定的,表示读写的文件依次从64m到256m,以2倍的形式增长;
中间的数据单位都是Kb/s表示读写速度;
另外可以看见标红色字体的部分,就是由于指定了"-I"参数,说明磁盘很希望你用每次读2048K的大小读取128M的文件。
五、所有参数具体意义说明
参考网址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20791108-id-483295.html
-a
用来使用全自动模式。生成包括所有测试操作的报告,使用的块 大小从4k到16M,文件大小从64k到512M。
-A
这种版本的自动模式提供更加全面的测试但是消耗更多时间。参数–a在文件不小于
32MB时将自动停止使用低于64K的块大小测试。这节省了许多时间。而参数–A
则告诉Iozone你不介意等待,即使在文件非常大时也希望进行小块 的测试。
注意: 不推荐在Iozone3.61版中使用这个参数。使用–az –i 0 –i 1替代。
-b filename
Iozone输出结果时将创建一个兼容Excel的二进制格式的文件。
-B
使用mmap()文件。这将使用mmap()接口来创建并访问所有测试用的临时文件。一
些应用程序倾向于将文件当作内存的一块来看待。这些应用程序对文件执行mmap()
调用,然后就可以以读写内存的方式访问那个块来完成文件I/O。
-c
计算时间时将close()包括进来。This is useful only if you suspect that close() is
broken in the operating system currently under test. 对于NFS版本3测试而言这将会
很有用,同时它也能帮助我们识别nfs3_commit 是否正常工作。
-C
显示吞吐量测试中每个客户传输的字节数。如果你的操作系统在文件I/O或进程管
理方面存在饥饿问题时这将派上用场。
-d #
穿过“壁垒”时微秒级的延迟。在吞吐量测试中所有线程或进程在执行测试前都必
须挂起在一道“壁垒”之前。通常来说,所有线程或进程在同一时间被释放。这个
参数允许在释放每个进程或线程之间有一定的延迟(微秒级)。Microsecond delay out of barrier. During the throughput tests all threads or processes are
forced to a barrier before beginning the test.
-D
对mmap文件使用msync(MS_ASYNC) 。这告诉操作系统在mmap空间的所有数据
需要被异步地写到磁盘上。
-e
计算时间时将flush (fsync,fflush) 包括进来。
-E
用来进行一些扩展的测试。只在一些平台上可用。使用pread 接口。
-f filename
用来指定测试时使用的临时文件的文件名。当使用unmount参数时这将很有用。测试时在每个测试之间进行unmount的话,测试使用的临时文件在一个可以被卸载的文件夹中是很有必要的。卸载当前工作目录是不可能的,因为Iozone进程运行于此。
-F filename filename filename …
指定吞吐量测试中每个临时文件的文件名。文件名的数量应该和指定的进程或线程
数相同。
-g #
设置自动模式可使用的最大文件大小(Kbytes)。
-G
对mmap文件使用msync(MS_SYNC)。这告诉操作系统在mmap空间的所有数据
需要被同步地写到磁盘上。
-h
显示帮助。
-H #
使用POSIX异步I/O接口中的#号异步操作。Iozone使用POSIX 异步I/O接口,并使
用bcopy 从异步缓存拷贝回应用程序缓存。一些版本的MSC NASTRAN就是这么进
行I/O操作的。应用程序使用这一技术以便异步I/O可以在一个库中实现,而不需要
更改程序内模。
-i #
用来指定运行哪个测试。 (0=write/rewrite, 1=read/re-read, 2=random-read/write
3=Read-backwards, 4=Re-write-record, 5=stride-read, 6=fwrite/re-fwrite, 7=fread/Re-fread,
8=random mix, 9=pwrite/Re-pwrite, 10=pread/Re-pread, 11=pwritev/Re-pwritev, 12=preadv/Re-preadv).
总是需要先进行0号测试以便后面的测试有文件可以测试。
也支持使用-i # -i # -i # 以便可以进行多个测试。
-I
对所有文件操作使用VxFS VX_DIRECT 。告诉VXFS 文件系统所有对文件的操作将跨
过缓存直接在磁盘上进行。
-j #
设置访问文件的跨度为 (# * 块 大小). Stride read测试将使用这个跨度来读块 。
-J # (毫秒级)
在每个I/O操作之前产生指定毫秒的计算延迟。看 -X 和-Y来获取控制计算延
迟的其他参数。
-k #
Use POSIX async I/O (no bcopy) with # async operations. Iozone will use POSIX async
I/O and will not perform any extra bcopys. The buffers used by Iozone will be handed to
the async I/O system call directly.
-K
在普通测试时生成一些随机访问。
-l #
用的时候要与-u搭配比如:"-l 1 -u 4"就表示测试的时候会从一个用户并发到4个用户并发,每个用户单开一个线程
-L #
Set processor cache line size to value (in bytes). Tells Iozone the processor cache line size.
This is used internally to help speed up the test.
-m
Tells Iozone to use multiple buffers internally. Some applications read into a single
buffer over and over. Others have an array of buffers. This option allows both types of
applications to be simulated. Iozone’s default behavior is to re-use internal buffers.
This option allows one to override the default and to use multiple internal buffers.
-M
Iozone will call uname() and will put the string in the output file.
-n #
为自动模式设置最小文件大小(Kbytes)。
-N
报告结果以毫秒每操作的方式显示。
-o
写操作是同步写到磁盘的。 (O_SYNC). Iozone 会以O_SYNC 标志打开文件。这强制所有写操作完全写入磁盘后才返回测试。
-O
报告结果以操作每秒的方式显示。
-p
This purges the processor cache before each file operation. Iozone will allocate another
internal buffer that is aligned to the same processor cache boundary and is of a size that
matches the processor cache. It will zero fill this alternate buffer before beginning each test.
This will purge the processor cache and allow one to see the memory subsystem without
the acceleration due to the processor cache.
-P #
Bind processes/threads to processors, starting with this cpu #. Only available on some
platforms. The first sub process or thread will begin on the specified processor. Future processes or threads will be placed on the next processor. Once the total number of cpus is exceeded then future processes or threads will be placed in a round robin fashion.
-q #
设置自动模式下使用的最大块大小(Kbytes) 。也可以通过-q #k ( Kbytes) 或 -q #m ( Mbytes) 或 -q #g ( Gbytes)。设置最小块大小见 –y 。
-Q
Create offset/latency files. Iozone will create latency versus offset data files that can be
imported with a graphics package and plotted. This is useful for finding if certain offsets
have very high latencies. Such as the point where UFS will allocate its first indirect block.
One can see from the data the impacts of the extent allocations for extent based filesystems
with this option.
-r #
指定测试块 大小,K字节。也可以通过-r #k (Kbytes) 或 -r #m (Mbytes) 或 -r #g (Gbytes).
-R
生成Excel报告. Iozone将生成一个兼容Excel的标准输出报告。这个文件可以使用
Microsoft Excel打开,可以创建一个文件系统性能的图表。注意:3D图表是面向列
的。画图时你需要选择这项因为Excel默认处理面向行的数据。
-s #
指定测试文件大小,K字节。也可以通过-s #k (Kbytes) 或 -s #m (Mbytes) 或 -s #g (Gbytes).
-S #
Set processor cache size to value (in Kbytes). This tells Iozone the size of the processor cache.
It is used internally for buffer alignment and for the purge functionality.
-t #
以吞吐量模式运行Iozone。这一选项允许用户指定测试时使用多少个线程或者进程。
-T
吞吐量测试时使用POSIX线程。仅在兼容POSIX线程的平台上可用。
-u #
Set the upper limit on number of processes to run. When running throughput tests this
option allows the user to specify the greatest number of processes or threads to start.
This option should be used in conjunction with the -l option.
-U mountpoint
在测试之间卸载并重新挂载挂载点。这保证了缓存cache不包含任何测试过的文件。
-v
显示Iozone的版本号。
-V #
Specify a pattern that is to be written to the temporary file and validated for accuracy in
each of the read tests.
-w
当临时文件使用完毕时不删除它们。把它们留在文件系统中。
-W
读或写时锁文件。
-x
关闭“stone-walling”. Stonewalling 是 Iozone内部使用的一种技术。它是在进行吞吐量测试时使用的。程序启动所有线程或进程然后将它们暂停在“壁垒”前。
一旦它们都做好准备工作,它们将被同时释放。当其中任何一个线程或进程完成工作,整个测试就终止了并计算到达这个点时所有I/O的吞吐量。这保证了整个测试进行时所有的进程和线程都是并行的。这个标志位允许取消 stonewalling并看看会发生什么。
-X filename
Use this file for write telemetry information. The file contains triplets of information:
Byte offset, size of transfer, compute delay in milliseconds. This option is useful if one has
taken a system call trace of the application that is of interest. This allows Iozone to replicate the I/O operations that this specific application generates and provide benchmark results for this file behavior. (if column 1 contains # then the line is a comment)
-y #
设置自动模式下使用的最小块大小(Kbytes) 。也可以通过-y #k ( Kbytes) 或 -y #m ( Mbytes) 或 -y #g ( Gbytes)。设置最大块大小见 –y 。
-Y filename
Use this file for read telemetry information. The file contains triplets of information:
Byte offset, size of transfer, compute delay in milliseconds. This option is useful if one has
taken a system call trace of the application that is of interest. This allows Iozone to replicate the I/O operations that this specific application generates and provide benchmark results for this file behavior. (if column 1 contains # then the line is a comment)
-z
Used in conjunction with -a to test all possible record sizes. Normally Iozone omits testing
of small record sizes for very large files when used in full automatic mode. This option forces
Iozone to include the small record sizes in the automatic tests also.
-Z
启动混合 mmap I/O 和文件 I/O.
-+m filename
Use this file to obtain the configuration information of the clients for cluster testing. The file contains one line for each client. Each line has three fields. The fields are space delimited. A # sign in column zero is a comment line. The first field is the name of the client. The second field is the path, on the client, for the working directory where Iozone will execute. The third field is the path, on the client, for the executable Iozone.
To use this option one must be able to execute commands on the clients without being challenged for a password. Iozone will start remote execution by using “rsh”.
-+u
Enable CPU utilization mode.
-+d
启动诊断模式。在这一模式下每个字节都将被验证。这在怀疑I/O子系统出错时有用。
-+p percent_read
Set the percentage of the thread/processes that will perform random read testing. Only valid in throughput mode and with more than 1 process/thread.
-+r
Enable O_RSYNC and O_SYNC for all I/O testing.
-+t
启动网络性能测试。需要 -+m
-+A
Enable madvise. 0 = normal, 1=random, 2=sequential, 3=dontneed, 4=willneed.
For use with options that activate mmap() file I/O. See: -B
