前面都是value based的方法,现在看一种直接预测动作的方法 Policy Based
Policy Gradient
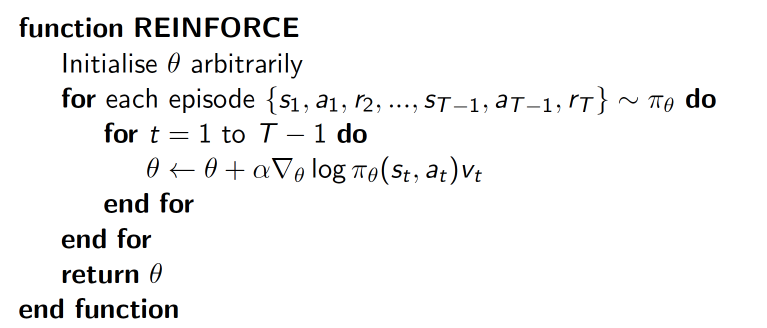
下面的例子实现的REINFORCE算法
1 import sys 2 import gym 3 import pylab 4 import numpy as np 5 from keras.layers import Dense 6 from keras.models import Sequential 7 from keras.optimizers import Adam 8 9 EPISODES = 1000 10 11 #policy gradient的一种,REINFORCE算法 12 # This is Policy Gradient agent for the Cartpole 13 # In this example, we use REINFORCE algorithm which uses monte-carlo update rule 14 class REINFORCEAgent: 15 def __init__(self, state_size, action_size): 16 # if you want to see Cartpole learning, then change to True 17 self.render = True 18 self.load_model = False 19 # get size of state and action 20 self.state_size = state_size#4 21 self.action_size = action_size#2 22 23 # These are hyper parameters for the Policy Gradient 24 self.discount_factor = 0.99 25 self.learning_rate = 0.001 26 self.hidden1, self.hidden2 = 24, 24 27 28 # create model for policy network 29 self.model = self.build_model() 30 31 # lists for the states, actions and rewards 32 self.states, self.actions, self.rewards = [], [], [] 33 34 if self.load_model: 35 self.model.load_weights("./save_model/cartpole_reinforce.h5") 36 37 # approximate policy using Neural Network 38 # state is input and probability of each action is output of network 39 def build_model(self): 40 model = Sequential() 41 model.add(Dense(self.hidden1, input_dim=self.state_size, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform')) 42 model.add(Dense(self.hidden2, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform')) 43 model.add(Dense(self.action_size, activation='softmax', kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform')) 44 model.summary() 45 # Using categorical crossentropy as a loss is a trick to easily 46 # implement the policy gradient. Categorical cross entropy is defined 47 # H(p, q) = sum(p_i * log(q_i)). For the action taken, a, you set 48 # p_a = advantage. q_a is the output of the policy network, which is 49 # the probability of taking the action a, i.e. policy(s, a). 50 # All other p_i are zero, thus we have H(p, q) = A * log(policy(s, a)) 51 model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=Adam(lr=self.learning_rate)) 52 return model 53 54 # using the output of policy network, pick action stochastically 55 def get_action(self, state): 56 policy = self.model.predict(state, batch_size=1).flatten()#2 57 return np.random.choice(self.action_size, 1, p=policy)[0]#choose action accordding to probability 58 59 # In Policy Gradient, Q function is not available. 60 # Instead agent uses sample returns for evaluating policy 61 def discount_rewards(self, rewards): 62 discounted_rewards = np.zeros_like(rewards) 63 running_add = 0 64 for t in reversed(range(0, len(rewards))): 65 running_add = running_add * self.discount_factor + rewards[t] 66 discounted_rewards[t] = running_add 67 return discounted_rewards 68 69 # save <s, a ,r> of each step 70 def append_sample(self, state, action, reward): 71 self.states.append(state) 72 self.rewards.append(reward) 73 self.actions.append(action) 74 75 # update policy network every episode 76 def train_model(self): 77 ''' 78 example: 79 self.states:[array([[-0.00647736, -0.04499117, 0.02213829, -0.00486359]]), array([[-0.00737719, -0.24042351, 0.02204101, 0.2947212 ]]), array([[-0.01218566, -0.04562261, 0.02793544, 0.00907036]]), array([[-0.01309811, -0.24113382, 0.02811684, 0.31043471]]), array([[-0.01792078, -0.04642351, 0.03432554, 0.02674995]]), array([[-0.01884925, -0.24202048, 0.03486054, 0.33006229]]), array([[-0.02368966, -0.04741166, 0.04146178, 0.04857336]]), array([[-0.0246379 , -0.24310286, 0.04243325, 0.35404415]]), array([[-0.02949995, -0.43880168, 0.04951413, 0.65979978]]), array([[-0.03827599, -0.2444025 , 0.06271013, 0.38310959]]), array([[-0.04316404, -0.44035616, 0.07037232, 0.69488702]]), array([[-0.05197116, -0.63637999, 0.08427006, 1.00886738]]), array([[-0.06469876, -0.83251953, 0.10444741, 1.32677873]]), array([[-0.08134915, -0.63885961, 0.13098298, 1.06852366]]), array([[-0.09412634, -0.44569036, 0.15235346, 0.8196508 ]]), array([[-0.10304015, -0.25294509, 0.16874647, 0.57850069]]), array([[-0.10809905, -0.44997994, 0.18031649, 0.91923131]]), array([[-0.11709865, -0.25769299, 0.19870111, 0.68820344]])] 80 self.rewards:[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -100] 81 self.actions:[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1] 82 ''' 83 episode_length = len(self.states)#18 84 85 discounted_rewards = self.discount_rewards(self.rewards) 86 ''' 87 example: 88 disconnted_rewards:array([ -68.58863868, -70.29155422, -72.01167093, -73.74916255,-75.5042046 , -77.27697434, -79.06765085, -80.876415 , -82.7034495 , -84.54893889, -86.41306958, -88.29602988,-90.19800998, -92.119202 , -94.0598,-96.02,-98., -100. ]) 89 ''' 90 discounted_rewards -= np.mean(discounted_rewards) 91 discounted_rewards /= np.std(discounted_rewards)#将作为神经网络预测对象 92 ''' 93 array([ 1.59468271, 1.41701722, 1.23755712, 1.05628429, 0.87318042, 94 0.68822702, 0.50140541, 0.3126967 , 0.12208185, -0.0704584 , 95 -0.26494351, -0.46139311, -0.65982705, -0.86026537, -1.06272832, 96 -1.26723636, -1.47381013, -1.6824705 ]) 97 ''' 98 update_inputs = np.zeros((episode_length, self.state_size))#shape(18,4) 99 advantages = np.zeros((episode_length, self.action_size))#shape(18,2) 100 101 for i in range(episode_length): 102 update_inputs[i] = self.states[i] 103 advantages[i][self.actions[i]] = discounted_rewards[i] 104 105 self.model.fit(update_inputs, advantages, epochs=1, verbose=0) 106 self.states, self.actions, self.rewards = [], [], [] 107 108 if __name__ == "__main__": 109 # In case of CartPole-v1, you can play until 500 time step 110 env = gym.make('CartPole-v1') 111 # get size of state and action from environment 112 state_size = env.observation_space.shape[0] 113 action_size = env.action_space.n 114 115 # make REINFORCE agent 116 agent = REINFORCEAgent(state_size, action_size) 117 118 scores, episodes = [], [] 119 120 for e in range(EPISODES): 121 import pdb; pdb.set_trace() 122 done = False 123 score = 0 124 state = env.reset() 125 state = np.reshape(state, [1, state_size]) 126 127 while not done: 128 if agent.render: 129 env.render() 130 131 # get action for the current state and go one step in environment 132 action = agent.get_action(state) 133 next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action) 134 next_state = np.reshape(next_state, [1, state_size]) 135 reward = reward if not done or score == 499 else -100 136 137 # save the sample <s, a, r> to the memory 138 agent.append_sample(state, action, reward) 139 140 score += reward 141 state = next_state 142 143 if done: 144 # every episode, agent learns from sample returns 145 agent.train_model() 146 147 # every episode, plot the play time 148 score = score if score == 500 else score + 100 149 scores.append(score) 150 episodes.append(e) 151 pylab.plot(episodes, scores, 'b') 152 pylab.savefig("./save_graph/cartpole_reinforce.png") 153 print("episode:", e, " score:", score) 154 155 # if the mean of scores of last 10 episode is bigger than 490 156 # stop training 157 if np.mean(scores[-min(10, len(scores)):]) > 490: 158 sys.exit() 159 160 # save the model 161 if e % 50 == 0: 162 agent.model.save_weights("./save_model/cartpole_reinforce.h5")