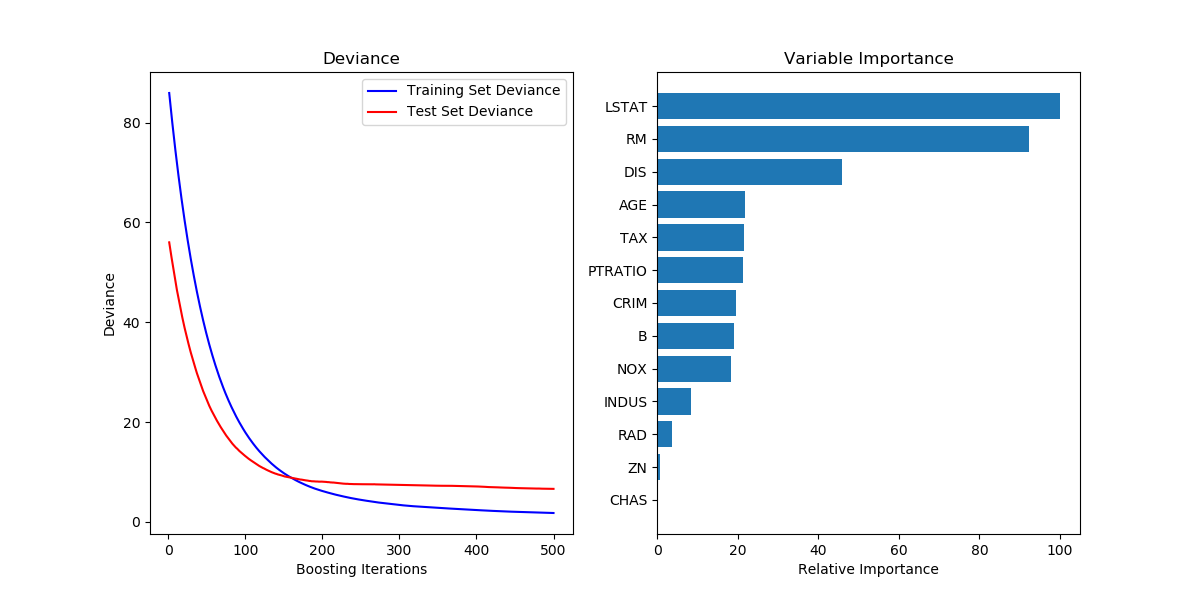
show the code:
# Plot training deviance def plot_training_deviance(clf, n_estimators, X_test, y_test): # compute test set deviance test_score = np.zeros((n_estimators,), dtype=np.float64) for i, y_pred in enumerate(clf.staged_predict(X_test)): test_score[i] = clf.loss_(y_test, y_pred) plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.title('Deviance') train_score = clf.train_score_ logging.info("len(train_score): %s" % len(train_score)) logging.info(train_score) logging.info("len(test_score): %s" % len(test_score)) logging.info(test_score) plt.plot(np.arange(n_estimators) + 1, train_score, 'b-', label='Training Set Deviance') plt.plot(np.arange(n_estimators) + 1, test_score, 'r*', label='Test Set Deviance') plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.xlabel('Boosting Iterations') plt.ylabel('Deviance') plt.show() # Plot feature importance def plot_feature_importance(clf, feature_names): feature_importance = clf.feature_importances_ # make importances relative to max importance feature_importance = 100.0 * (feature_importance / feature_importance.max()) sorted_idx = np.argsort(feature_importance) pos = np.arange(sorted_idx.shape[0]) + .5 plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.barh(pos, feature_importance[sorted_idx], align='center') # plt.yticks(pos, feature_names[sorted_idx]) plt.yticks(pos, [feature_names[idx] for idx in sorted_idx]) plt.xlabel('Relative Importance') plt.title('Variable Importance') plt.show() class Train(object): def __init__(self, data_file): self.data_file = data_file self.x_fields = ["xxx", "xxx", "xxx"] self.x_features, self.y_labels = self.load_data() def load_data(self): x_features, y_labels = [], [] # ...... return x_features, y_labels def train_model(self): model = GradientBoostingRegressor(random_state=42) model.fit(self.x_features, self.y_labels) y_pred = model.predict(self.x_features) logging.info("mean_squared_error: %.6f" % mean_squared_error(self.y_labels, y_pred)) logging.info("mean_squared_log_error: %.6f" % mean_squared_log_error(self.y_labels, y_pred)) plot_training_deviance(clf=model, n_estimators=model.get_params()["n_estimators"], X_test=self.x_features, y_test=self.y_labels) # 输出feature重要性 logging.info("feature_importances_: %s" % model.feature_importances_) plot_feature_importance(clf=model, feature_names=self.x_fields)
参考的是sklearn中的样例: Gradient Boosting regression — scikit-learn 0.19.2 documentation
画出的图如下所示: