1.7中HashMap死循环分析
put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);//扩容操作
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i]; //1.7中使用头插法插入
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
综合来说,HashMap一次扩容的过程:
1、取当前table的2倍作为新table的大小
2、根据算出的新table的大小new出一个新的Entry数组来,名为newTable
3、轮询原table的每一个位置,将每个位置上连接的Entry,算出在新table上的位置,并以链表形式连接
4、原table上的所有Entry全部轮询完毕之后,意味着原table上面的所有Entry已经移到了新的table上,HashMap中的table指向newTable
单线程下扩容
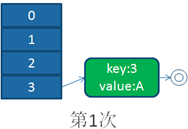
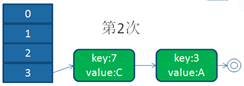
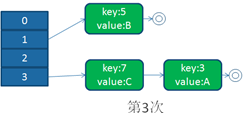
并发下扩容
HashMap之所以在并发下的扩容造成死循环,是因为,多个线程并发进行时,因为一个线程先期完成了扩容,将原Map的链表重新散列到自己的表中,并且链表变成了倒序,后一个线程再扩容时,又进行自己的散列,再次将倒序链表变为正序链表。于是形成了一个环形链表,当get表中不存在的元素时,造成死循环。
1.8中HashMap使用尾插法,避免了扩容时产生链表死循环。
ConcurrentHahsMap实现分析
1.7下的实现

static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {//segment本身也是锁
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
/** * ConcurrentHashMap list entry. Note that this is never exported * out as a user-visible Map.Entry. */ static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; /** * Creates a new, empty map with a default initial capacity (16), * load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16). */ public ConcurrentHashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); } ** * Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial * capacity, load factor and concurrency level. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation * performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @param loadFactor the load factor threshold, used to control resizing. * Resizing may be performed when the average number of elements per * bin exceeds this threshold. * @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently * updating threads. The implementation performs internal sizing * to try to accommodate this many threads. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is * negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are * nonpositive. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public ConcurrentHashMap17(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; // Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments 找到一个离并发度最近的2的平方数作为segment数组大小 int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; } this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this.segmentMask = ssize - 1; if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; // create segments and segments[0] Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0] this.segments = ss; }
ConcurrentHashMap初始化方法是通过initialCapacity、loadFactor和concurrencyLevel(参数concurrencyLevel是用户估计的并发级别,就是说你觉得最多有多少线程共同修改这个map,根据这个来确定Segment数组的大小concurrencyLevel默认是DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;)等几个参数来初始化segment数组、段偏移量segmentShift、段掩码segmentMask和每个segment里的HashEntry数组来实现的。
get()
public V get(Object key) { Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead HashEntry<K,V>[] tab; int h = hash(key);//hash值的高位定位segment ,hash值的全部用于定位table long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null && (tab = s.table) != null) { for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile (tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE); e != null; e = e.next) {//遍历链表定位 K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k))) return e.value; } } return null; }
private int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if ((0 != h) && (k instanceof String)) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// Spread bits to regularize both segment and index locations,
// using variant of single-word Wang/Jenkins hash.
h += (h << 15) ^ 0xffffcd7d;
h ^= (h >>> 10);
h += (h << 3);
h ^= (h >>> 6);
h += (h << 2) + (h << 14);
return h ^ (h >>> 16);
}
HashEntry属性定义使用了 final和volatile get()方法不需要加锁,也能获取到最新的值
put()
public V put(K key, V value) { Segment<K,V> s; if (value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = hash(key); int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment s = ensureSegment(j); return s.put(key, hash, value, false); }
private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment(int k) {//初始化segment的槽
final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this.segments;
long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offset
Segment<K,V> seg;
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {
Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototype
int cap = proto.table.length;
float lf = proto.loadFactor;
int threshold = (int)(cap * lf);
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap];
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) { // recheck
Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab);
while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))//循环CAS操作,保证Segment初始化只有一个线程成功
break;
}
}
}
return seg;
}
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {//segment方法
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);//把当前的头结点变成下一个节点,(头插法)
else
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Sets next field with volatile write semantics. (See above
* about use of putOrderedObject.)
*/
final void setNext(HashEntry<K,V> n) {
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, n);
}
private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {//segment方法,尝试一定次数循序拿锁
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
HashEntry<K,V> node = null;
int retries = -1; // negative while locating node
while (!tryLock()) {
HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below
if (retries < 0) {
if (e == null) {
if (node == null) // speculatively create node
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
retries = 0;
}
else if (key.equals(e.key))
retries = 0;
else
e = e.next;
}
else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
lock();//循序拿锁失败则 阻塞式拿锁
break;
}
else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed
retries = -1;
}
}
return node;
}
rehash()扩容
/** * Doubles size of table and repacks entries, also adding the * given node to new table */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) {//扩容操作 /* * Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we * are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from * each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a * power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node * creation by catching cases where old nodes can be * reused because their next fields won't change. * Statistically, at the default threshold, only about * one-sixth of them need cloning when a table * doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage * collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by * any reader thread that may be in the midst of * concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain * array indexing because they are followed by volatile * table write. */ HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;//变为原来的2倍大小 threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable = (HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity]; int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1; for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) { HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i]; if (e != null) { HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next; int idx = e.hash & sizeMask; if (next == null) // Single node on list newTable[idx] = e; else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e; int lastIdx = idx; for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next; last != null; last = last.next) { int k = last.hash & sizeMask; if (k != lastIdx) { lastIdx = k; lastRun = last; } } newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun; // Clone remaining nodes for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { V v = p.value; int h = p.hash; int k = h & sizeMask; HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k]; newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n); } } } } int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]); newTable[nodeIndex] = node; table = newTable; }
remove()
public V remove(Object key) {
int hash = hash(key);
Segment<K,V> s = segmentForHash(hash);
return s == null ? null : s.remove(key, hash, null);
}
/**
* Remove; match on key only if value null, else match both.
*/
final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
if (!tryLock())
scanAndLock(key, hash);
V oldValue = null;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> e = entryAt(tab, index);
HashEntry<K,V> pred = null;
while (e != null) {
K k;
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) {
if (pred == null)
setEntryAt(tab, index, next);
else
pred.setNext(next);
++modCount;
--count;
oldValue = v;
}
break;
}
pred = e;
e = next;
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
size() 统计ConcurrentHashMap元素个数(一般不提倡使用,还有相同的containsValue(Object value)方法,同样存在对整个segment加锁的情况,不提倡使用)
/** * Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. If the * map contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns * <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>. * * @return the number of key-value mappings in this map */ public int size() { // Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to // continuous async changes in table, resort to locking. final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; int size; boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits long sum; // sum of modCounts long last = 0L; // previous sum int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry try { for (;;) { if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation//segment全部加锁 } sum = 0L; size = 0; overflow = false; for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j); if (seg != null) { sum += seg.modCount; int c = seg.count; if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0) overflow = true; } } if (sum == last) break; last = sum; } } finally { if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) segmentAt(segments, j).unlock(); } } return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size; }
JDK1.8中的ConcurrentHashMap()
取消了Segment,采用 数组+链表(n)+红黑树(logN)结构
数据结构
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V val; volatile Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.val = val; this.next = next; }
TreeNode 红黑树下的节点
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;//链表节点数达到8个时变为红黑树
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;//红黑树节点变为6个时重新成为链表
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red;
TreeBin 红黑树的根节点
static final class TreeBin<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> root; volatile TreeNode<K,V> first; volatile Thread waiter; volatile int lockState; // values for lockState//读写锁状态 static final int WRITER = 1; // set while holding write lock static final int WAITER = 2; // set when waiting for write lock static final int READER = 4; // increment value for setting read lock
HashMap与ConcurrentHashMap中Node区别:
HashMap中TreeNode继承自LinkedHashMap
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red;
ForwardingNode (扩容时,作为一个占位符放在table中,表示当前节点为null或者已经被移除)
/** * A node inserted at head of bins during transfer operations. */ static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { final Node<K,V>[] nextTable; ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) { super(MOVED, null, null, null); this.nextTable = tab; }
private transient volatile int sizeCtl 控制1.8里table 初始化或扩容操作
/** * Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the * table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization, * else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise, * when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon * creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the * next element count value upon which to resize the table. */-1 表示当前线程正在进行初始化,其他表示当前有多少个线程正在进行扩容操作,默认0尚未初始化 private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
核心方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
/*利用硬件级别的原子操作,获得在i位置上的Node节点
* Unsafe.getObjectVolatile可以直接获取指定内存的数据,
* 保证了每次拿到数据都是最新的*/
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
/*利用CAS操作设置i位置上的Node节点*/
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
/*利用硬件级别的原子操作,设置在i位置上的Node节点
* Unsafe.putObjectVolatile可以直接设定指定内存的数据,
* 保证了其他线程访问这个节点时一定可以看到最新的数据*/
static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) {
U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v);
}
get()方法
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; int h = spread(key.hashCode());/*计算hash值*/ /*根据hash值确定节点位置*/ if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) { /*Node数组中的节点就是要找的节点*/ if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val; } /*eh<0 说明这个节点在树上 调用树的find方法寻找*/ else if (eh < 0) return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null; /*到这一步说明是个链表,遍历链表找到对应的值并返回*/ while ((e = e.next) != null) { if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val; } } return null; }
put()
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false); } /** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */ final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = spread(key.hashCode());/*计算hash值*/ int binCount = 0; /*死循环 何时插入成功 何时跳出*/ for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable();/*如果table为空的话,初始化table*/ else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { /*Node数组中的元素,这个位置没有值 ,使用CAS操作放进去*/ if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) /*正在进行扩容,当前线程帮忙扩容*/ tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { V oldVal = null; /*锁Node数组中的元素,这个位置是Hash冲突组成链表的头结点 * 或者是红黑树的根节点*/ synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { /*fh>0 说明这个节点是一个链表的节点 不是树的节点*/ if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; /*put操作和putIfAbsent操作业务实现*/ if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; /*如果遍历到了最后一个结点,使用尾插法,把它插入在链表尾部*/尾插法 if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } /*按照树的方式插入值*/ else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0) { /*达到临界值8 就需要把链表转换为树结构*/ if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } /*Map的元素数量+1,并检查是否需要扩容*/ addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
/*小于0表示有其他线程正在进行初始化操作,把当前线程CPU时间让出来。
因为对于table的初始化工作,只能有一个线程在进行。*/
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
/*利用CAS操作把sizectl的值置为-1 表示本线程正在进行初始化*/
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
/*n右移2位本质上就是n变为n原值的1/4,所以
* sc=0.75*n */
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
/*将设置成扩容的阈值*/
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
remove()
public V remove(Object key) { return replaceNode(key, null, null); } /** * Implementation for the four public remove/replace methods: * Replaces node value with v, conditional upon match of cv if * non-null. If resulting value is null, delete. */ final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) { int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 || (f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) break; else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { V oldVal = null; boolean validated = false; synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { validated = true; for (Node<K,V> e = f, pred = null;;) { K ek; if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { V ev = e.val; if (cv == null || cv == ev || (ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) { oldVal = ev; if (value != null) e.val = value; else if (pred != null) pred.next = e.next; else setTabAt(tab, i, e.next); } break; } pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) break; } } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { validated = true; TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f; TreeNode<K,V> r, p; if ((r = t.root) != null && (p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) { V pv = p.val; if (cv == null || cv == pv || (pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) { oldVal = pv; if (value != null) p.val = value; else if (t.removeTreeNode(p)) setTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first)); } } } } } if (validated) { if (oldVal != null) { if (value == null) addCount(-1L, -1); return oldVal; } break; } } } return null; }
transfer()扩容
/** * Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See * above for explanation. */ private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) { int n = tab.length, stride; if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE) stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range 每个线程负责一定的长度的Node进行扩容(并发扩容) if (nextTab == null) { // initiating try { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1]; nextTab = nt; } catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } nextTable = nextTab; transferIndex = n; } int nextn = nextTab.length; ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab); boolean advance = true; boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) { Node<K,V> f; int fh; while (advance) { int nextIndex, nextBound; if (--i >= bound || finishing) advance = false; else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) { i = -1; advance = false; } else if (U.compareAndSwapInt (this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex, nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ? nextIndex - stride : 0))) { bound = nextBound; i = nextIndex - 1; advance = false; } } if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) { int sc; if (finishing) { nextTable = null; table = nextTab; sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1); return; } if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) { if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) return; finishing = advance = true; i = n; // recheck before commit } } else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null) advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd); else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) advance = true; // already processed else { synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { Node<K,V> ln, hn; if (fh >= 0) { int runBit = fh & n; Node<K,V> lastRun = f; for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) { int b = p.hash & n; if (b != runBit) { runBit = b; lastRun = p; } } if (runBit == 0) { ln = lastRun; hn = null; } else { hn = lastRun; ln = null; } for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val; if ((ph & n) == 0) ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln); else hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn); } setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln); setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn); setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); advance = true; } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f; TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null; TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null; int lc = 0, hc = 0; for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) { int h = e.hash; TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V> (h, e.key, e.val, null, null); if ((h & n) == 0) { if ((p.prev = loTail) == null) lo = p; else loTail.next = p; loTail = p; ++lc; } else { if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null) hi = p; else hiTail.next = p; hiTail = p; ++hc; } } ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) : (hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t; hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) : (lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t; setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln); setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn); setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); advance = true; } } } } } }
treeifyBin()
/* ---------------- Conversion from/to TreeBins -------------- */ /** * Replaces all linked nodes in bin at given index unless table is * too small, in which case resizes instead. */ private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) { Node<K,V> b; int n, sc; if (tab != null) { if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) tryPresize(n << 1); else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) { synchronized (b) { if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) { TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val, null, null); if ((p.prev = tl) == null) hd = p; else tl.next = p; tl = p; } setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd)); } } } } }
size()
public int size() { long n = sumCount(); return ((n < 0L) ? 0 : (n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : (int)n); }
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;//两部分组成
}
}
return sum;
}
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {//cas操作,尝试将次数加入到BASECOUNT中,
CounterCell a; long v; int m;//失败的话则由CountCell进行记录,所以size()方法中统计count包括这两部分
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {//伪共享
volatile long value;
CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
}
ConcurrentSkipListMap和ConcurrentSkipListSet存储有序的Map和set
TreeMap和TreeSet(TreeSet是对TreeMap的重新包装)并发编程不安全。
SkipList(跳表)(概率数据结构)
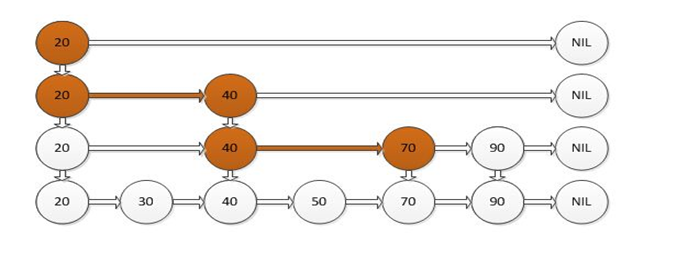
跳跃表其实也是一种通过“空间来换取时间”的一个算法,令链表的每个结点不仅记录next结点位置,还可以按照level层级分别记录后继第level个结点。此法使用的就是“先大步查找确定范围,再逐渐缩小迫近”的思想进行的查找。跳跃表在算法效率上很接近红黑树。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue (LinkedList的并发版本)
无界非阻塞队列,它是一个基于链表的无界线程安全队列。该队列的元素遵循先进先出的原则。头是最先加入的,尾是最近加入的。插入元素是追加到尾上。提取一个元素是从头提取。
oncurrentLinkedQueue.add("c");
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer("d"); // 将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部。
concurrentLinkedQueue.peek(); // 检索并不移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
concurrentLinkedQueue.poll(); // 检索并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
CopyOnWriteArrayList和CopyOnWriteArraySet(写时复制容器)
使用场景:大多数读,偶尔写时(白名单,黑名单)
CopyOnWrite容器即写时复制的容器。通俗的理解是当我们往一个容器添加元素的时候,不直接往当前容器添加,而是先将当前容器进行Copy,复制出一个新的容器,然后新的容器里添加元素,添加完元素之后,再将原容器的引用指向新的容器。
这样做的好处是我们可以对CopyOnWrite容器进行并发的读,而不需要加锁,因为当前容器不会添加任何元素。所以CopyOnWrite容器也是一种读写分离的思想,读和写不同的容器。如果读的时候有多个线程正在向CopyOnWriteArrayList添加数据,读还是会读到旧的数据,因为写的时候不会锁住旧的CopyOnWriteArrayList。
使用CopyOnWriteMap需要注意两件事情:
1. 减少扩容开销。根据实际需要,初始化CopyOnWriteMap的大小,避免写时CopyOnWriteMap扩容的开销。
2. 使用批量添加。因为每次添加,容器每次都会进行复制,所以减少添加次数,可以减少容器的复制次数。
写时复制容器的问题
性能问题
每次修改都创建一个新数组,然后复制所有内容,如果数组比较大,修改操作又比较频繁,可以想象,性能是很低的,而且内存开销会很大。
数据一致性问题。
CopyOnWrite容器只能保证数据的最终一致性,不能保证数据的实时一致性。所以如果你希望写入的的数据,马上能读到,不要使用CopyOnWrite容器。
阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。
在队列中插入一个队列元素称为入队,从队列中删除一个队列元素称为出队。因为队列只允许在一端插入,在另一端删除,所以只有最早进入队列的元素才能最先从队列中删除,故队列又称为先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)线性表。
阻塞队列:
1)支持阻塞的插入方法:意思是当队列满时,队列会阻塞插入元素的线程,直到队列不满。
2)支持阻塞的移除方法:意思是在队列为空时,获取元素的线程会等待队列变为非空
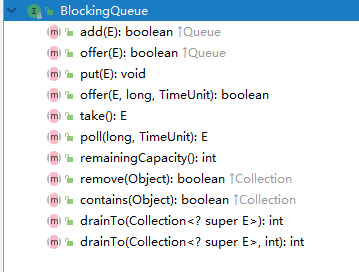

抛出异常:当队列满时,如果再往队列里插入元素,会抛出IllegalStateException("Queuefull")异常。当队列空时,从队列里获取元素会抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
返回特殊值:当往队列插入元素时,会返回元素是否插入成功,成功返回true。如果是移除方法,则是从队列里取出一个元素,如果没有则返回null。
一直阻塞:当阻塞队列满时,如果生产者线程往队列里put元素,队列会一直阻塞生产者线程,直到队列可用或者响应中断退出。当队列空时,如果消费者线程从队列里take元素,队列会阻塞住消费者线程,直到队列不为空。
超时退出:当阻塞队列满时,如果生产者线程往队列里插入元素,队列会阻塞生产者线程一段时间,如果超过了指定的时间,生产者线程就会退出
一般在生产者,消费者模式中使用较多;
常用阻塞队列:
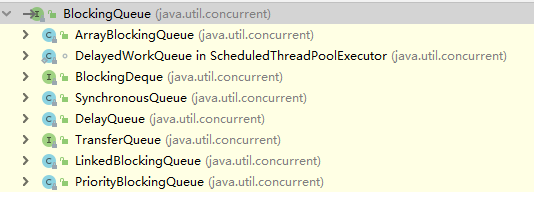
·ArrayBlockingQueue:一个由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。(有界表示队列有长度,满了以后就后产生阻塞,反正表示无界,但实际过程中,由于系统资源限制,无界也会受空间限制)
·LinkedBlockingQueue:一个由链表结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
·PriorityBlockingQueue:一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
·DelayQueue:一个使用优先级队列实现的无界阻塞队列。
·SynchronousQueue:一个不存储元素的阻塞队列。
·LinkedTransferQueue:一个由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
·LinkedBlockingDeque:一个由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue
是一个用数组实现的有界阻塞队列。此队列按照先进先出(FIFO)的原则对元素进行排序。默认情况下不保证线程公平的访问队列,所谓公平访问队列是指阻塞的线程,可以按照阻塞的先后顺序访问队列,即先阻塞线程先访问队列。非公平性是对先等待的线程是非公平的,当队列可用时,阻塞的线程都可以争夺访问队列的资格,有可能先阻塞的线程最后才访问队列。初始化时有参数可以设置
LinkedBlockingQueue
是一个用链表实现的有界阻塞队列。此队列的默认和最大长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE。此队列按照先进先出的原则对元素进行排序。
Array实现和Linked实现的区别
1. 队列中锁的实现不同
ArrayBlockingQueue实现的队列中的锁是没有分离的,即生产和消费用的是同一个锁;
LinkedBlockingQueue实现的队列中的锁是分离的,即生产用的是putLock,消费是takeLock
2. 在生产或消费时操作不同
ArrayBlockingQueue实现的队列中在生产和消费的时候,是直接将枚举对象插入或移除的;
LinkedBlockingQueue实现的队列中在生产和消费的时候,需要把枚举对象转换为Node<E>进行插入或移除,会影响性能
3. 队列大小初始化方式不同
ArrayBlockingQueue实现的队列中必须指定队列的大小;
LinkedBlockingQueue实现的队列中可以不指定队列的大小,但是默认是Integer.MAX_VALUE
PriorityBlockingQueue
PriorityBlockingQueue是一个支持优先级的无界阻塞队列。默认情况下元素采取自然顺序升序排列。也可以自定义类实现compareTo()方法来指定元素排序规则,或者初始化PriorityBlockingQueue时,指定构造参数Comparator来对元素进行排序。需要注意的是不能保证同优先级元素的顺序。
DelayQueue
是一个支持延时获取元素的无界阻塞队列。队列使用PriorityQueue来实现。队列中的元素必须实现Delayed接口,在创建元素时可以指定多久才能从队列中获取当前元素。只有在延迟期满时才能从队列中提取元素。
DelayQueue非常有用,可以将DelayQueue运用在以下应用场景。
缓存系统的设计:可以用DelayQueue保存缓存元素的有效期,使用一个线程循环查询DelayQueue,一旦能从DelayQueue中获取元素时,表示缓存有效期到了。还有订单到期,限时支付等等
SynchronousQueue
是一个不存储元素的阻塞队列。每一个put操作必须等待一个take操作,否则不能继续添加元素。SynchronousQueue可以看成是一个传球手,负责把生产者线程处理的数据直接传递给消费者线程。队列本身并不存储任何元素,非常适合传递性场景。SynchronousQueue的吞吐量高于LinkedBlockingQueue和ArrayBlockingQueue。
LinkedTransferQueue
多了tryTransfer和transfer方法,
(1)transfer方法
如果当前有消费者正在等待接收元素(消费者使用take()方法或带时间限制的poll()方法时),transfer方法可以把生产者传入的元素立刻transfer(传输)给消费者。如果没有消费者在等待接收元素,transfer方法会将元素存放在队列的tail节点,并等到该元素被消费者消费了才返回。
(2)tryTransfer方法
tryTransfer方法是用来试探生产者传入的元素是否能直接传给消费者。如果没有消费者等待接收元素,则返回false。和transfer方法的区别是tryTransfer方法无论消费者是否接收,方法立即返回,而transfer方法是必须等到消费者消费了才返回。
LinkedBlockingDeque
LinkedBlockingDeque是一个由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列。所谓双向队列指的是可以从队列的两端插入和移出元素。双向队列因为多了一个操作队列的入口,在多线程同时入队时,也就减少了一半的竞争。
多了addFirst、addLast、offerFirst、offerLast、peekFirst和peekLast等方法,以First单词结尾的方法,表示插入、获取(peek)或移除双端队列的第一个元素。以Last单词结尾的方法,表示插入、获取或移除双端队列的最后一个元素。另外,插入方法add等同于addLast,移除方法remove等效于removeFirst。但是take方法却等同于takeFirst,使用时还是用带有First和Last后缀的方法更清楚。在初始化LinkedBlockingDeque时可以设置容量防止其过度膨胀。另外,双向阻塞队列可以运用在“工作窃取”模式中。
阻塞队列实现原理:
使用了等待通知模式实现。所谓通知模式,就是当生产者往满的队列里添加元素时会阻塞住生产者,当消费者消费了一个队列中的元素后,会通知生产者当前队列可用。通过查看JDK源码发现ArrayBlockingQueue使用了Condition来实现。其余队列的实现,大家可以自行查看,队列的实现的代码总体来说,并不复杂。
参考:http://enjoy.ke.qq.com/