一、异常拦截器是什么?
异常拦截器的作用是提供一个机会,可以设置在action执行过程中发生异常的时候映射到一个结果字符串而不是直接中断。
将异常整合到业务逻辑中,比如在分层系统的调用中可以从底层抛出一个异常,高层捕捉到这个异常就知道发生了什么事情啦。
二、如何使用?
1.两种异常映射类型:
1.1.global
global的异常映射对整个package下的action都有效:
<struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <!-- 全局异常配置 --> <global-exception-mappings> <exception-mapping result="login" exception="struts_practice_004.UsernameIsNullException" /> </global-exception-mappings> <action name="loginAction" class="struts_practice_004.LoginAction"> <result name="login">/login.jsp</result> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
1.2.action
action级别的异常映射只对单个的action有效:
<struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="loginAction" class="struts_practice_004.LoginAction"> <!-- action级别的异常映射 --> <exception-mapping exception="struts_practice_004.UsernameIsNullException" result="login" /> <result name="login">/login.jsp</result> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
2.配置异常映射的可选参数
logEnabled 日志是否开启,默认关闭
logCategory 日志种类
logLevel 日志级别
3.使用异常映射的例子:
User实体:
/** * 用户实体 * @author CC11001100 * */ public class User { private String username; private String passwd; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPasswd() { return passwd; } public void setPasswd(String passwd) { this.passwd = passwd; } }
LoginAction:
/** * 登录Action * * @author CC11001100 * */ public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport { private User user; private LoginService loginService; public LoginAction() { loginService=new LoginService(); } @Override public String execute() throws Exception { //尝试登录 User u1=loginService.login(user); //如果为空,说明登录失败. if(u1==null){ return LOGIN; } return SUCCESS; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } }
LoginService:
public class LoginService { /** * 登录是否成功 * @param user * @return */ public User login(User user){ if(true) throw new UsernameIsNullException(); return user; } }
struts.xml
<struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="loginAction" class="struts_practice_004.LoginAction"> <exception-mapping exception="struts_practice_004.UsernameIsNullException" result="login" /> <result name="login">/login.jsp</result> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
前端页面:
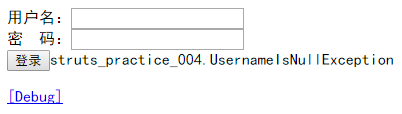
<form action="loginAction" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user.username" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="user.passwd" /><br/> <input type="submit" value="登录" /><s:property value="exception"/> </form> <s:debug />
结果:
提示不太友好,感觉例子设计得很牵强....凑活着吧,我们都知道Action会被压入值栈的栈顶,但是这里有一个<s:property value="exception"/> 这个是怎么访问得到的呢?请看下面的源代码分析。
三、工作原理?
异常拦截器处在默认拦截器栈的第一层,它的实现类是ExceptionMappingInterceptor,源代码如下:
1 /** 2 * 3 * 异常映射拦截器: 4 * 5 * 1.捕捉异常 6 * 2.将异常映射到结果字符串 7 * 8 */ 9 public class ExceptionMappingInterceptor extends AbstractInterceptor { 10 11 protected static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionMappingInterceptor.class); 12 13 protected Logger categoryLogger; 14 //是否将异常信息打印到日志 15 protected boolean logEnabled = false; 16 //logger的种类 17 protected String logCategory; 18 //日志的级别,默认是debug,从哪儿知道的?耐心往下看... 19 protected String logLevel; 20 21 /*------------------------- 在这下面是getter和setter ------------------------------*/ 22 public boolean isLogEnabled() { 23 return logEnabled; 24 } 25 26 public void setLogEnabled(boolean logEnabled) { 27 this.logEnabled = logEnabled; 28 } 29 30 public String getLogCategory() { 31 return logCategory; 32 } 33 34 public void setLogCategory(String logCatgory) { 35 this.logCategory = logCatgory; 36 } 37 38 public String getLogLevel() { 39 return logLevel; 40 } 41 42 public void setLogLevel(String logLevel) { 43 this.logLevel = logLevel; 44 } 45 /*----------------------------- getter和setter结束 ----------------------------------*/ 46 47 /** 48 * 拦截器方法 49 */ 50 @Override 51 public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { 52 53 String result; 54 55 try { 56 //正常执行,继续往下递归调用,如果执行过程中没有抛出异常就相当于没有异常拦截器 57 //意思就是异常拦截器只有在抛出异常的时候才发挥作用,如果没发生异常就感觉不到它的存在 58 result = invocation.invoke(); 59 } catch (Exception e) { 60 //如果在执行的过程catch到了异常,异常拦截器才会发挥作用 61 62 //如果开启日志记录的话,默认是false,上面已经写死了 63 if (isLogEnabled()) { 64 //记录一下 65 handleLogging(e); 66 } 67 68 //获得异常映射信息,这个信息是在struts.xml中的<exception-mapping>中配置的 69 List<ExceptionMappingConfig> exceptionMappings = invocation.getProxy().getConfig().getExceptionMappings(); 70 71 //找一下当前抛出的异常有没有配置对应的结果字符串 72 String mappedResult = this.findResultFromExceptions(exceptionMappings, e); 73 74 if (mappedResult != null) { 75 //如果找到了异常对应的结果字符串,那么保存结果 76 result = mappedResult; 77 //同时将这个异常包裹起来放到ValueStack的栈顶 78 publishException(invocation, new ExceptionHolder(e)); 79 } else { 80 //没有没有配置结果字符串,我也不知道该怎么处理了,直接往上抛吧 81 throw e; 82 } 83 } 84 85 //执行正常或者发生异常但配置了异常映射结果字符串才会执行到这里 86 return result; 87 } 88 89 /** 90 * Handles the logging of the exception. 91 * 打印日志 92 * @param e the exception to log. 93 */ 94 protected void handleLogging(Exception e) { 95 //决定日志的打印方式 96 if (logCategory != null) { 97 //使用categoryLogger 98 if (categoryLogger == null) { 99 // init category logger 100 categoryLogger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(logCategory); 101 } 102 doLog(categoryLogger, e); 103 } else { 104 //或是使用默认的这个 105 doLog(LOG, e); 106 } 107 } 108 109 /** 110 * Performs the actual logging. 111 * 112 * 打印日志的具体实现 113 * 114 * @param logger the provided logger to use. 115 * @param e the exception to log. 116 */ 117 protected void doLog(Logger logger, Exception e) { 118 //如果没有指定logLevel的话,默认就是debug级别了 119 if (logLevel == null) { 120 logger.debug(e.getMessage(), e); 121 return; 122 } 123 124 //根据指定的日志级别打印 125 if ("trace".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { 126 logger.trace(e.getMessage(), e); 127 } else if ("debug".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { 128 logger.debug(e.getMessage(), e); 129 } else if ("info".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { 130 logger.info(e.getMessage(), e); 131 } else if ("warn".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { 132 logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e); 133 } else if ("error".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { 134 logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); 135 } else if ("fatal".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { 136 logger.fatal(e.getMessage(), e); 137 } else { 138 //都不匹配啊,说明指定的日志级别不合法(这种情况八成是拼写错误,血泪经验....),抛出异常警告一下搞开发的这傻小子~ 139 throw new IllegalArgumentException("LogLevel [" + logLevel + "] is not supported"); 140 } 141 } 142 143 /** 144 * 看看映射列表中有没有对应的映射 145 */ 146 protected String findResultFromExceptions(List<ExceptionMappingConfig> exceptionMappings, Throwable t) { 147 String result = null; 148 149 // Check for specific exception mappings 150 //看看是否配置了异常映射,即<exception-mapping exception="" result="" /> 151 if (exceptionMappings != null) { 152 //因为后面要比惨..啊是比小,所以就预先给一个最大值,比较简单的技巧 153 int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 154 //遍历映射列表项 155 for (Object exceptionMapping : exceptionMappings) { 156 //看不大懂,为什么放着泛型不用呢,直接取出来不就是ExceptionMappingConfig类型的么? - - 157 ExceptionMappingConfig exceptionMappingConfig = (ExceptionMappingConfig) exceptionMapping; 158 //看看当前的异常类跟配置的<exception-mapping exception="就是这一个" />能不能匹配的上,是不是它本身或者其子类 159 int depth = getDepth(exceptionMappingConfig.getExceptionClassName(), t); 160 if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) { 161 //说明找到了,当前抛出的异常类是配置的类本身或者是其子类 162 //按照一般想法找到了就直接return就可以了呗,我刚开始也是这样子想的, 163 //但是呢仔细看一看,结合上面的depth < deepest和下面的deepest = depth; 164 //所以呢,这里只是保存了一下仍然继续的意思就是要从这些映射列表中找到一个跟当前类最接近的 165 //这里的接近是从t(此时的t是超类引用子类对象,它的运行时类型并不是Throwable)一直到Throwable 166 //的这段距离,从[t,Throwable]这个区间上找一个最靠左的,感觉这样就能解释清楚了, 167 //这样做是为了最细程度的映射 168 deepest = depth; 169 result = exceptionMappingConfig.getResult(); 170 } 171 } 172 } 173 174 return result; 175 } 176 177 /** 178 * Return the depth to the superclass matching. 0 means ex matches exactly. Returns -1 if there's no match. 179 * Otherwise, returns depth. Lowest depth wins. 180 * 181 * 找一下这个映射类到抛出的异常类之间有几个超类,可能有三种情况: 182 * 1. 没找到:-1表示exceptionMapping不是t的超类(这样貌似也没办法映射到了,映射的话包括本类和子类) 183 * 2. 本身:如果0的话表示exceptionMapping和t就是同一个类 184 * 3. 子类:其它字符串表示中间的超类个数,表示t是exceptionMapping的一个子类,但我们要的是中间的继承次数 185 * 186 * @param exceptionMapping the mapping classname 187 * @param t the cause 188 * @return the depth, if not found -1 is returned. 189 */ 190 public int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Throwable t) { 191 return getDepth(exceptionMapping, t.getClass(), 0); 192 } 193 194 /** 195 * 找exceptionMapping到exceptionClass的“距离” 196 */ 197 private int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Class exceptionClass, int depth) { 198 //看看这个映射类是不是当前异常类的超类 199 if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(exceptionMapping)) { 200 // Found it! 201 //找到了 202 return depth; 203 } 204 // If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it... 205 //已经找到了顶层(Throwable),但仍然未找到,说明不可能找到了,返回不匹配 206 if (exceptionClass.equals(Throwable.class)) { 207 return -1; 208 } 209 210 //递归顺着继承链往上找 211 return getDepth(exceptionMapping, exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1); 212 } 213 214 /** 215 * Default implementation to handle ExceptionHolder publishing. Pushes given ExceptionHolder on the stack. 216 * Subclasses may override this to customize publishing. 217 * 218 * 将这个ExceptionHolder压入ValueStack的栈顶 219 * 220 * @param invocation The invocation to publish Exception for. 221 * @param exceptionHolder The exceptionHolder wrapping the Exception to publish. 222 */ 223 protected void publishException(ActionInvocation invocation, ExceptionHolder exceptionHolder) { 224 //压入值栈的栈顶,以便OGNL表达式访问 225 invocation.getStack().push(exceptionHolder); 226 } 227 }
放入ValueStack栈顶的wrapper类的源代码分析:
1 /** 2 * 3 * A simple wrapper around an exception, providing an easy way to print out the stack trace of the exception as well as 4 * a way to get a handle on the exception itself. 5 * 6 * 将异常wrapper一下,然后提供两个方法以供简便的获得这个异常和异常追踪栈。 7 * 8 * getException() 9 * getExceptionStack() 10 * 11 * 这两个getter方法是用来给OGNL访问exception信息使用的, 12 * 当发生异常的时候会将异常对象用这个类包裹起来放到ValueStack的栈顶, 13 * 所以直接通过exception就可以访问得到异常对象本身, 14 * 通过exceptionStack就可以访问得到这个异常栈信息。 15 * 16 */ 17 public class ExceptionHolder implements Serializable { 18 19 //要包裹的异常本身 20 private Exception exception; 21 22 /** 23 * Holds the given exception 24 * 实例化这个类必须传进来一个异常,它持有一个异常。 25 * @param exception the exception to hold. 26 */ 27 public ExceptionHolder(Exception exception) { 28 this.exception = exception; 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * Gets the holded exception 33 * 返回持有的异常对象 34 * @return the holded exception 35 */ 36 public Exception getException() { 37 return this.exception; 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * Gets the holded exception stacktrace using {@link Exception#printStackTrace()}. 42 * 以String的形式返回异常栈追踪信息 43 * @return stacktrace 44 */ 45 public String getExceptionStack() { 46 String exceptionStack = null; 47 48 if (getException() != null) { 49 StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); 50 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw); 51 52 try { 53 getException().printStackTrace(pw); 54 exceptionStack = sw.toString(); 55 } 56 finally { 57 try { 58 sw.close(); 59 pw.close(); 60 } catch (IOException e) { 61 // ignore 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 66 return exceptionStack; 67 } 68 69 }
用来表示异常映射的类的源代码:
这个类使用了Builder模式:设计模式之构建者模式(Builder)
1 /** 2 * Configuration for exception mapping. 3 * 异常映射的配置信息 4 */ 5 public class ExceptionMappingConfig extends Located implements Serializable { 6 7 //结果字符串 8 private String name; 9 //异常类的类名 10 private String exceptionClassName; 11 //映射到的结果字符串 12 private String result; 13 //传递的参数 14 private Map<String,String> params; 15 16 protected ExceptionMappingConfig(String name, String exceptionClassName, String result) { 17 this.name = name; 18 this.exceptionClassName = exceptionClassName; 19 this.result = result; 20 this.params = new LinkedHashMap<String,String>(); 21 } 22 23 protected ExceptionMappingConfig(ExceptionMappingConfig target) { 24 this.name = target.name; 25 this.exceptionClassName = target.exceptionClassName; 26 this.result = target.result; 27 this.params = new LinkedHashMap<String,String>(target.params); 28 } 29 30 public String getName() { 31 return name; 32 } 33 34 public String getExceptionClassName() { 35 return exceptionClassName; 36 } 37 38 public String getResult() { 39 return result; 40 } 41 42 public Map<String,String> getParams() { 43 return params; 44 } 45 46 47 @Override 48 public boolean equals(Object o) { 49 if (this == o) { 50 return true; 51 } 52 53 if (!(o instanceof ExceptionMappingConfig)) { 54 return false; 55 } 56 57 final ExceptionMappingConfig exceptionMappingConfig = (ExceptionMappingConfig) o; 58 59 if ((name != null) ? (!name.equals(exceptionMappingConfig.name)) : (exceptionMappingConfig.name != null)) { 60 return false; 61 } 62 63 if ((exceptionClassName != null) ? (!exceptionClassName.equals(exceptionMappingConfig.exceptionClassName)) : (exceptionMappingConfig.exceptionClassName != null)) 64 { 65 return false; 66 } 67 68 if ((result != null) ? (!result.equals(exceptionMappingConfig.result)) : (exceptionMappingConfig.result != null)) 69 { 70 return false; 71 } 72 73 if ((params != null) ? (!params.equals(exceptionMappingConfig.params)) : (exceptionMappingConfig.params != null)) 74 { 75 return false; 76 } 77 78 return true; 79 } 80 81 @Override 82 public int hashCode() { 83 int hashCode; 84 hashCode = ((name != null) ? name.hashCode() : 0); 85 hashCode = (29 * hashCode) + ((exceptionClassName != null) ? exceptionClassName.hashCode() : 0); 86 hashCode = (29 * hashCode) + ((result != null) ? result.hashCode() : 0); 87 hashCode = (29 * hashCode) + ((params != null) ? params.hashCode() : 0); 88 89 return hashCode; 90 } 91 92 /** 93 * The builder for this object. An instance of this object is the only way to construct a new instance. The 94 * purpose is to enforce the immutability of the object. The methods are structured in a way to support chaining. 95 * After setting any values you need, call the {@link #build()} method to create the object. 96 */ 97 public static class Builder{ 98 99 private ExceptionMappingConfig target; 100 101 public Builder(ExceptionMappingConfig toClone) { 102 target = new ExceptionMappingConfig(toClone); 103 } 104 105 public Builder(String name, String exceptionClassName, String result) { 106 target = new ExceptionMappingConfig(name, exceptionClassName, result); 107 } 108 109 public Builder name(String name) { 110 target.name = name; 111 return this; 112 } 113 114 public Builder exceptionClassName(String name) { 115 target.exceptionClassName = name; 116 return this; 117 } 118 119 public Builder result(String result) { 120 target.result = result; 121 return this; 122 } 123 124 public Builder addParam(String name, String value) { 125 target.params.put(name, value); 126 return this; 127 } 128 129 public Builder addParams(Map<String,String> params) { 130 target.params.putAll(params); 131 return this; 132 } 133 134 public Builder location(Location loc) { 135 target.location = loc; 136 return this; 137 } 138 139 public ExceptionMappingConfig build() { 140 target.params = Collections.unmodifiableMap(target.params); 141 ExceptionMappingConfig result = target; 142 target = new ExceptionMappingConfig(target); 143 return result; 144 } 145 } 146 147 }
这是它的内存里的表示: