概念:
顾名思义,单调栈即位满足单调性的栈结构,包括递增栈、递减栈。
指的是栈内元素从底到顶是单增、单减。一般来说从栈底到栈顶依次变大的就叫单调递增栈。
用途:
1.对于每个元素而言,可以看到之前比他大的所有的数和数量,且是依次的
比如:10 3 7 4 12

2.在1的基础上我们就可以知道右边第一个大于栈顶元素的数,如果你记录一下他们的位置,还能得到一个元素与第一个比他大的元素之间有多少个元素(这就是我写这个博客的初衷

模版题:洛谷P 5788
传送门
题意:
给n个数的数列,对于每个数求它之后第一个大于t r[i]的元素的下标,若不存在则是0
思路:
没学单调栈之前,我直接无视数据范围无脑双重for循环,一发TLE让我郁闷不已,赛后一查原来可以用单调栈,只有O(n)的复杂度,这里简单的说一下,因为每个数只进一次出一次栈,不会使用第二次,所以是O(n)的复杂度。
先来一个顺序的单调栈,其特点是边输入边求值。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAX 3000000 + 5
typedef long long ll ;
inline int IntRead()//快读
{
char ch = getchar();
int s = 0, w = 1;
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if(ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
struct ran//对于每个数,都用一个结构体来存其下标和值
{
ll id, val;
};
ll tr[MAX], k;//tr数组用来存最终答案,k是输入的每个数
int main()
{
ll n;
cin>>n;
stack<ran>st;//用一个结构体的栈
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
k = IntRead();//输入的数
while (!st.empty() && k > st.top().val) {//看看输入的值是否比栈顶的值大
tr[st.top().id] = i;//如果找到了一个比栈顶的值的数,那么第一个大于栈顶元素的数就出现了,就是第i个数:k
st.pop();//将原来的栈顶扔出去,进行下一次比较
}
st.push({i,k});//操作完之后别忘了把这个数k塞进去。这个写法在有的编译器下会报错,CE,比如VJ,但是洛谷不会报错,报错的话就在写个单独的结构体塞进去,我后面会写的
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(i == 1)//控制输出的空格,我开始就这样wa了,郁闷好一会呢
cout<<tr[i];
else
cout<<" "<<tr[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
再来个倒序的。
倒叙的特点是,得先输入完全以后才能进行下一步操作
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAX 3000000 + 5
typedef long long ll ;
inline int IntRead()
{
char ch = getchar();
int s = 0, w = 1;
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if(ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
struct ran
{
ll id, val;
};
ll tr[MAX], k, ar[MAX];
int main()
{
ll n;
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
tr[i] = IntRead();
stack<ran>st;
for(ll i = n; i >= 1; i--)
{
while (!st.empty() && tr[i] >= st.top().val) {
st.pop();
}
ar[i] = st.empty()?0:st.top().id;//判断是否栈的元素为空,不然会RE的
st.push({i, tr[i]});
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(i == 1)
cout<<ar[i];
else
cout<<" "<<ar[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
对于10 3 7 4 12 2的样例来说
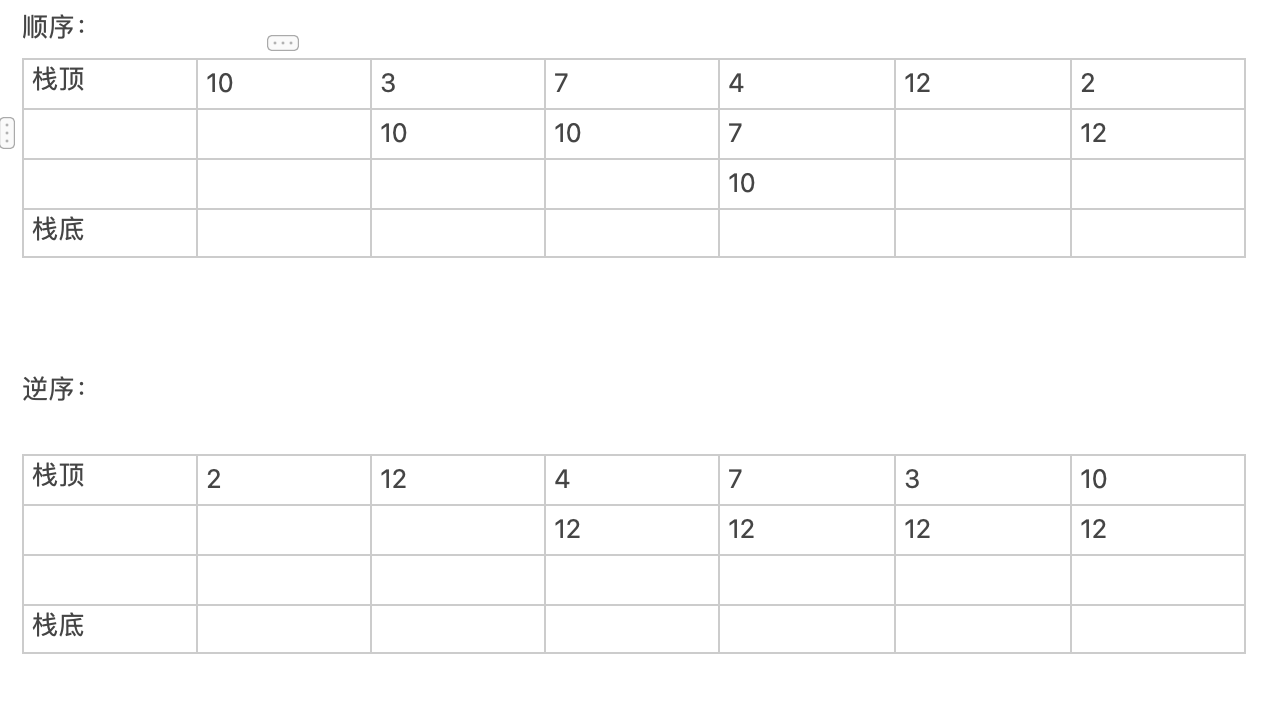
顺序是在每次循环扔出数字时得出扔出数字的答案
而逆序数在每一次循环就能得到对应的答案
需要注意的是顺序的时候写的是>,而逆序写的是>=,这是因为需要的是严格的大于x的数的位置,顺序是从前往后入栈,所以判断的时候是看这个数和下一个数是否满足严格的大于,满足就得到答案,不满足就将其入栈。而逆序是从后往前入栈,所以相当于反过来的,逆着输入,而我们要求的是大于一个数的第一个数的位置,就要求这个数小于下一个数的位置,所以就要将不满足的扔出去,也就是将满足前面的数(本次循环到的数)大于等于栈顶的数的扔出去,所以这里是大于等于,我知道你看到这里可能没听懂,没关系,我理解的也感觉差点意思(-_-),实在不行就直接背
升级版:Bad Hair Day
传送门
题意:
英文题偷个懒不翻译辽
转换一下,就是数列tr,对每个数求其与大于大的第一个数之间的牛的个数,求总和
思路:
方向1:可以用单调栈对每个数tr[i]求得大于tr[i]的数的下标差减去1,然后求和。这种思路就和上面的模版差不多,两种方法,一个顺序一个逆序。
方向2:利用单调栈中剩余元素的个数求和。举个例子来讲:12 10 9 11
开始时是12,然后10 小于12,可以入栈,在入栈之前,我们求一下栈内元素的数量,也就是1,将其加到sum里,现在栈变成了10 12,然后来个9,发现9小于10,可以入栈,入栈前我们再求一下栈内元素的数目,也就是2,加到sum里,再来个11,我们发现11大于9,也大于10,所以将9和10依次扔出去,再将11塞进去之前,再求一下栈的大小,加到sum里面,最终得到sum的和为1 + 2 + 1.每次都要求栈大小的原因是,对于能塞进来的数,是小于栈内所有元素的,所以这栈内元素的每一个都多了一个小于他的数,最终加起来就可以得到答案
可能我讲的乱七八糟的不太友好,但是理是这样,想一会就明白了
现在是代码实现部分:
方向1 --- 顺序:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f//一个1e9多的数
#define MAX 3000000 + 5
typedef long long ll ;
inline int IntRead()
{
char ch = getchar();
int s = 0, w = 1;
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if(ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int main()
{
ll n;
n = IntRead();
stack<ll>st;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tr[i] = IntRead();
tr[n] = inf;//这个题有些变化,如果一个数后面没有比他大的数,那就不会算他后面的数,所以我们得让栈内元素全扔出去,就在最后面加了一个最大值
ll sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
while (!st.empty() && tr[i] >= tr[st.top()]) {//这个题和上面的题不太一样,这个题如果被同等身高的人遮住了,就不能看见后面的,所以这里是大于等于,遇到等于了就会停
sum += (i - st.top() - 1);
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
方向1---逆序:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAX 3000000 + 5
typedef long long ll ;
inline int IntRead()
{
char ch = getchar();
int s = 0, w = 1;
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if(ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
ll tr[MAX];
int main()
{
ll n, sum = 0;
n = IntRead();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tr[i] = IntRead();
stack<ll>st;
for(ll i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while (!st.empty() && tr[i] > tr[st.top()]) {
st.pop();
}
if(st.empty() == 0)//这里我不明白为什么栈空了还能取栈顶???苣蒻猪之疑惑
{
sum += st.top() - i - 1;
}
else
sum += n - i - 1;
st.push(i);
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
方向2:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAX 3000000 + 5
typedef long long ll ;
inline int IntRead()
{
char ch = getchar();
int s = 0, w = 1;
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if(ch == '-') w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
ll tr[MAX], k;
int main()
{
ll n, sum = 0;
n = IntRead();
stack<ll>st;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
k = IntRead();
while (!st.empty() && k >= st.top()) {
st.pop();
}
sum += st.size();
st.push(k);
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
总感觉没有彻底领会其要领,等再遇到再说吧o(︶︿︶)o