一个程序,多个线程同时操作一个变量,给这个变量+1()。功能很简单,可是怎么样去实现呢?这其中涉及到了哪些问题?
最基础想法
见代码:

1 public class Test extends Thread { 2 public static int amount = 0; 3 4 public void run() { 5 amount++; 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 int num_thread = 100; 10 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) { 11 new Test().start(); 12 } 13 try { 14 Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 System.out.println(amount); 19 } 20 }
输出结果:
num_thread = 100时,结果=100;
num_thread = 1000时,结果=1000;
num_thread = 10000时,结果=9995;
num_thread = 1000000时,结果=999936;
程序判定为不安全,当线程数比较少的时候,因为线程是先后启动的,所以看起来没有影响,一旦线程数增大,弊端毕露无疑。其实还有一个更简单看出问题的方法,线程运行时,不是给变量+1,而是+1000*1000,再来看结果:
num_thread = 10时,结果=5034021;——线程数很少,但是结果不是想要的结果。
总之说明,这样的多线程不安全!amount++这个方法并不是原子性的!
升级想法1.0:用volatile修饰的变量,线程在每次使用变量的时候,都会读取变量修改后的最新值。
见代码:
1 public class Test extends Thread { 2 public static volatile int amount = 0;//只是这里的变量声明为volatile修饰 3 4 public void run() { 5 int i = 0; 6 while (i < 1000 * 1000) { 8 amount++; 9 i++; 10 } 11 } 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 int num_thread = 10; 15 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) { 16 new Test().start(); 17 } 18 try { 19 Thread.sleep(1 * 1000); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 System.out.println(amount); 24 } 25 }
输出结果:
num_thread = 10时,结果=2375833;——结果仍然不是想要的。
那问题出在哪里了呢?处在了对volatile修饰符的理解上。(参考博客:java中volatile关键字的含义)
volatile很容易被误用,被误用来进行原子性操作。
在 java 垃圾回收整理一文中,描述了jvm运行时刻内存的分配。其中有一个内存区域是jvm虚拟机栈,每一个线程运行时都有一个线程栈,线程栈保存了线程运行时候变量值信息。当线程访问某一个对象时候值的时候,首先通过对象的引用找到对应在堆内存的变量的值,然后把堆内存变量的具体值load到线程本地内存中,建立一个变量副本,之后线程就不再和对象在堆内存变量值有任何关系,而是直接修改副本变量的值,在修改完之后的某一个时刻(线程退出之前),自动把线程变量副本的值回写到对象在堆中变量。这样在堆中的对象的值就产生变化了。下面一幅图描述这种交互:
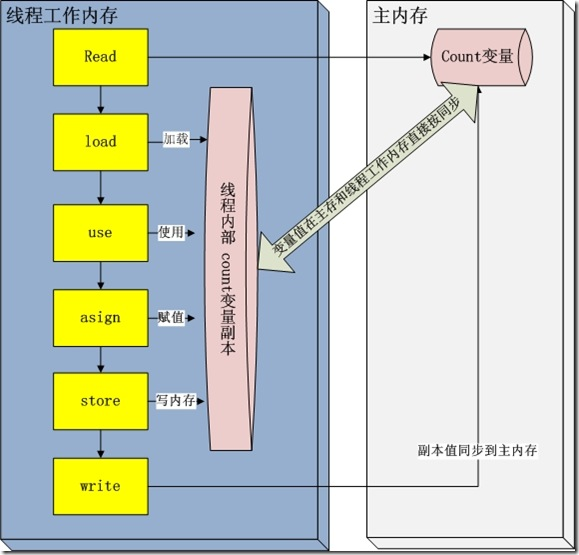
read and load ——从主存复制变量到当前工作内存
use and assign ——执行代码,改变共享变量值
store and write ——用工作内存数据刷新主存相关内容
其中use and assign 可以多次出现,但是这一些操作并不是原子性,也就是 在read load之后,如果主内存count变量发生修改之后,线程工作内存中的值由于已经加载,不会产生对应的变化,所以计算出来的结果会和预期不一样。
对于volatile修饰的变量,jvm虚拟机只是保证从主内存加载到线程工作内存的值是最新的。
这项问题搞清楚之后可以继续想法了。
升级想法3.0:同步代码块——通过 synchronized 关键字,所有加上synchronized 的块语句,在多线程访问的时候,同一时刻只能有一个线程能够用synchronized 修饰的方法或者代码块。
java为了解决线程并发的问题,在语言内部引入了 同步块 和 volatile 关键字机制。
对于synchronized的使用,又有不同的方式:同步代码块和同步方法
首先来看同步代码块的运用。语法见代码:
synchronized(syncObject){ //code }
synchronized 块是这样一个代码块,其中的代码必须获得对象 syncObject 的锁方能执行。由于可以针对任意代码块,且可任意指定上锁的对象,故灵活性较高。
这里面的syncObject,可以是 类实例 或 类。
针对我们的场景,修改代码如下:
1 public class Test extends Thread { 2 public static volatile Integer amount = new Integer(0);//修改为对象 3 4 public void run() { 5 int i = 0; 6 synchronized (amount) { 7 while (i < 1000 * 1000) { 9 amount++; 10 i++; 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 int num_thread = 10; 17 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) { 18 new Test().start(); 19 } 20 try { 21 Thread.sleep(1 * 1000); 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 System.out.println(amount); 26 } 27 }
变动包括,amount的类型由int变为Interger,这样amount才是一个可以被synchronized使用的Integer实例。
然而程序的输出:1902241 —— 仍然不是我们想要的。问题出在了哪里?测试发现在synchronized后面sleep 10ms 以上同步成功,sleep 1ms 的话就不会成功!!!!!!!!!!!什么鬼!!!!!!!!详情见代码注释:
1 public class Test implements Runnable { 2 // public static volatile AtomicInteger amount = new AtomicInteger(0); 3 private Integer amount = new Integer(0); 4 private InClass inClass = new InClass("adfas"); 5 6 public void run() { 7 synchronized (amount) { 8 // synchronized (inClass) {// 注意!!这里换成inClass就成功了,即便没有sleep,简直郁闷啊啊啊啊啊!!! 9 // synchronized (this){ 或者synchronized (Test.class)都可以,即便没有sleep 10 System.out.println( 11 Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---------begin--------------" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(1);//sleep(10)的话可以成功,查看输出,程序输出时间确实是递增的!!! 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 for (int i = 0; i < 200000;) { 19 // addOne(); 20 amount++; 21 i++; 22 } 23 System.out.println( 24 Thread.currentThread().getName() + "------------end-------------" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 25 } 26 } 27 28 public synchronized void addOne() { 29 amount++; 30 } 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) { 33 int num_thread = 50; 34 Test test = new Test(); 35 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) { 36 (new Thread(test)).start(); 37 } 38 try { 39 Thread.sleep(10 * 1000); 40 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 System.out.println(test.amount); 44 } 45 46 class InClass { 47 public InClass(String name) { 48 // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 49 } 50 } 51 }
对于上面这个例子,是我最大的疑惑。讲道理的话,amount是一个Integer的实例,我本认为synchronized(amount)锁住的是amount这个实例的同步方法或者同步代码块,按道理来说对程序是没有影响的,也就是synchronized并不起作用,但是使用inClass实例告诉我们,上面的想法是错误的(具体原因需要分析)!但是既然synchronized(syncObject)表明了可以用的话,amount抽象来看,和inClass是同一个东西,都是实例!但是amount为什么就不能用呢???感觉非常奇怪,贴一下测试结果:
测试结果1:synchronized(amount)没有sleep(),可以明显看出,代码块没有被锁住。另外,sleep(1)的时候,结果类似。

Thread-0---------begin--------------1483240909596 Thread-7---------begin--------------1483240909596 Thread-9---------begin--------------1483240909597 Thread-10---------begin--------------1483240909597 Thread-11---------begin--------------1483240909598 Thread-12---------begin--------------1483240909603 Thread-8---------begin--------------1483240909617 Thread-18---------begin--------------1483240909617 Thread-9------------end-------------1483240909628 Thread-17---------begin--------------1483240909628 Thread-10------------end-------------1483240909631 Thread-12------------end-------------1483240909631 Thread-16---------begin--------------1483240909632 Thread-20---------begin--------------1483240909632 Thread-11------------end-------------1483240909632 Thread-19---------begin--------------1483240909633 Thread-18------------end-------------1483240909636 Thread-13---------begin--------------1483240909636 Thread-14---------begin--------------1483240909632 Thread-15---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-48---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-49---------begin--------------1483240909654 Thread-20------------end-------------1483240909654 Thread-13------------end-------------1483240909655 Thread-22---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-30---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-14------------end-------------1483240909669 Thread-23---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-15------------end-------------1483240909670 Thread-16------------end-------------1483240909651 Thread-7------------end-------------1483240909642 Thread-31---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-48------------end-------------1483240909673 Thread-38---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-39---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-30------------end-------------1483240909674 Thread-46---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-22------------end-------------1483240909674 Thread-26---------begin--------------1483240909651 Thread-23------------end-------------1483240909686 Thread-34---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-42---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-21---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-25---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-38------------end-------------1483240909693 Thread-31------------end-------------1483240909694 Thread-28---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-26------------end-------------1483240909695 Thread-29---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-37---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-36---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-34------------end-------------1483240909705 Thread-25------------end-------------1483240909709 Thread-44---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-21------------end-------------1483240909711 Thread-33---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-28------------end-------------1483240909713 Thread-41---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-45---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-29------------end-------------1483240909713 Thread-35---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-42------------end-------------1483240909714 Thread-27---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-17------------end-------------1483240909650 Thread-24---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-32---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-44------------end-------------1483240909730 Thread-40---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-41------------end-------------1483240909732 Thread-35------------end-------------1483240909733 Thread-19------------end-------------1483240909650 Thread-43---------begin--------------1483240909650 Thread-0------------end-------------1483240909650 Thread-6---------begin--------------1483240909734 Thread-8------------end-------------1483240909644 Thread-45------------end-------------1483240909735 Thread-33------------end-------------1483240909733 Thread-37------------end-------------1483240909722 Thread-36------------end-------------1483240909722 Thread-39------------end-------------1483240909691 Thread-46------------end-------------1483240909691 Thread-49------------end-------------1483240909674 Thread-47---------begin--------------1483240909657 Thread-27------------end-------------1483240909740 Thread-24------------end-------------1483240909740 Thread-32------------end-------------1483240909741 Thread-40------------end-------------1483240909748 Thread-6------------end-------------1483240909751 Thread-5---------begin--------------1483240909751 Thread-43------------end-------------1483240909751 Thread-47------------end-------------1483240909751 Thread-5------------end-------------1483240909752 Thread-4---------begin--------------1483240909752 Thread-4------------end-------------1483240909754 Thread-3---------begin--------------1483240909754 Thread-3------------end-------------1483240909756 Thread-2---------begin--------------1483240909756 Thread-2------------end-------------1483240909757 Thread-1---------begin--------------1483240909757 Thread-1------------end-------------1483240909758 2589439
测试结果2:synchronized(amount)并且sleep(10),可以看出,代码是被同步了的。为了看的更清楚,sleep(1000),结果类似。

Thread-0---------begin--------------1483241058337 Thread-0------------end-------------1483241058353 Thread-49---------begin--------------1483241058353 Thread-49------------end-------------1483241058365 Thread-48---------begin--------------1483241058365 Thread-48------------end-------------1483241058378 Thread-47---------begin--------------1483241058379 Thread-47------------end-------------1483241058390 Thread-46---------begin--------------1483241058390 Thread-46------------end-------------1483241058401 Thread-45---------begin--------------1483241058401 Thread-45------------end-------------1483241058412 Thread-44---------begin--------------1483241058412 Thread-44------------end-------------1483241058423 Thread-43---------begin--------------1483241058423 Thread-43------------end-------------1483241058434 Thread-42---------begin--------------1483241058434 Thread-42------------end-------------1483241058446 Thread-41---------begin--------------1483241058446 Thread-41------------end-------------1483241058461 Thread-40---------begin--------------1483241058461 Thread-40------------end-------------1483241058472 Thread-39---------begin--------------1483241058472 Thread-39------------end-------------1483241058483 Thread-38---------begin--------------1483241058483 Thread-38------------end-------------1483241058494 Thread-37---------begin--------------1483241058494 Thread-37------------end-------------1483241058504 Thread-36---------begin--------------1483241058504 Thread-36------------end-------------1483241058515 Thread-35---------begin--------------1483241058516 Thread-35------------end-------------1483241058526 Thread-34---------begin--------------1483241058526 Thread-34------------end-------------1483241058540 Thread-33---------begin--------------1483241058541 Thread-33------------end-------------1483241058552 Thread-32---------begin--------------1483241058552 Thread-32------------end-------------1483241058563 Thread-31---------begin--------------1483241058564 Thread-31------------end-------------1483241058577 Thread-29---------begin--------------1483241058577 Thread-29------------end-------------1483241058588 Thread-30---------begin--------------1483241058588 Thread-30------------end-------------1483241058598 Thread-28---------begin--------------1483241058599 Thread-28------------end-------------1483241058610 Thread-27---------begin--------------1483241058610 Thread-27------------end-------------1483241058621 Thread-26---------begin--------------1483241058621 Thread-26------------end-------------1483241058632 Thread-25---------begin--------------1483241058632 Thread-25------------end-------------1483241058643 Thread-24---------begin--------------1483241058643 Thread-24------------end-------------1483241058654 Thread-23---------begin--------------1483241058654 Thread-23------------end-------------1483241058665 Thread-22---------begin--------------1483241058665 Thread-22------------end-------------1483241058680 Thread-21---------begin--------------1483241058680 Thread-21------------end-------------1483241058693 Thread-20---------begin--------------1483241058693 Thread-20------------end-------------1483241058706 Thread-19---------begin--------------1483241058706 Thread-19------------end-------------1483241058718 Thread-18---------begin--------------1483241058718 Thread-18------------end-------------1483241058731 Thread-17---------begin--------------1483241058731 Thread-17------------end-------------1483241058743 Thread-16---------begin--------------1483241058743 Thread-16------------end-------------1483241058757 Thread-15---------begin--------------1483241058757 Thread-15------------end-------------1483241058770 Thread-14---------begin--------------1483241058772 Thread-14------------end-------------1483241058783 Thread-13---------begin--------------1483241058783 Thread-13------------end-------------1483241058794 Thread-12---------begin--------------1483241058794 Thread-12------------end-------------1483241058805 Thread-11---------begin--------------1483241058805 Thread-11------------end-------------1483241058816 Thread-10---------begin--------------1483241058817 Thread-10------------end-------------1483241058828 Thread-9---------begin--------------1483241058828 Thread-9------------end-------------1483241058839 Thread-8---------begin--------------1483241058839 Thread-8------------end-------------1483241058850 Thread-7---------begin--------------1483241058850 Thread-7------------end-------------1483241058861 Thread-6---------begin--------------1483241058861 Thread-6------------end-------------1483241058872 Thread-3---------begin--------------1483241058872 Thread-3------------end-------------1483241058883 Thread-5---------begin--------------1483241058883 Thread-5------------end-------------1483241058895 Thread-4---------begin--------------1483241058896 Thread-4------------end-------------1483241058907 Thread-2---------begin--------------1483241058907 Thread-2------------end-------------1483241058919 Thread-1---------begin--------------1483241058919 Thread-1------------end-------------1483241058930
升级想法3.1:基于上面出现的各种问题,可以把amount++这一步直接用一个synchronized修饰的方法代替,简单明了,粗暴高效!
详见上面的代码里面的addOne()方法!但是这里其实是有问题的:毕竟真是程序中一般可能出现各种同步情况,很多时候同步代码块儿的灵活性非常好,而同步方法使用起来可能不方便;所以上面的问题还是需要解决,在网上很多的例子中我们看到的都是synchronized(this)和synchronized(Test.class),关于这两种用法的对比,见之后的补充。当我们不想锁住类的对象,只是想同步代码块的时候,可以考虑创建一个对象实例,如下图所示:

升级想法4.0:java里面有些对数变量的操作是原子性的,
Java中的原子操作包括:
1)除long和double之外的基本类型的赋值操作
2)所有引用reference的赋值操作
3)java.concurrent.Atomic.* 包中所有类的一切操作
count++不是原子操作,是3个原子操作组合
1.读取主存中的count值,赋值给一个局部成员变量tmp
2.tmp+1
3.将tmp赋值给count
方法:使用java.util.concurrent.AtomicInteger,详见代码!

1 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 2 3 public class Test implements Runnable { 4 public static volatile AtomicInteger amount = new AtomicInteger(0); 5 6 public void run() { 7 System.out.println( 8 Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---------begin--------------" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 9 for (int i = 0; i < 200000;) { 10 amount.incrementAndGet(); 11 i++; 12 } 13 System.out.println( 14 Thread.currentThread().getName() + "------------end-------------" + System.currentTimeMillis()); 15 } 16 } 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 int num_thread = 50; 20 Test test = new Test(); 21 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) { 22 (new Thread(test)).start(); 23 } 24 try { 25 Thread.sleep(10 * 1000); 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 System.out.println(test.amount); 30 } 31 32 }
另外补充!synchronized(this) VS synchronize(MyClass.class)
引用国外一个问答网站的精辟回答:
"
MyClass.class and this are different things, are different references to different objects.
this - is the reference to particular this instance of class, and
MyClass.class - is the reference to MyClass description object.
This synchronization blocks differs in that the first will synchronize all threads that deal concretely with this instance of MyClass, and the second one will synchronize all threads independently of which object on which this method was called.
"
翻译过来就是:this同步的是一个具体的对象,所有由这个对象产生的线程在运行同一个方法时都会被阻塞(补充:所有的synchronized标示的方法用也会被阻塞,原因是等同1);MyClass.class同步的是当前类,获取锁的方法将阻塞所有这个类的实例对象,这些对象都无权调用该方法。理解这里的this和MyClass.class非常重要!比如对于上面的例子来说,如果我们的Test extends Thread,如果每次启动线程都是new Test().start(),使用synchronized(this)是无效的(程序中amount要声明为static,属于类),因为每个线程都是一个独立的对象产生的。(注意下面两个等同)。
等同1:
public void test() { synchronized(this) { // todo your code } }
public synchronized void test() { // todo your code }
等同2:
如果某方法为类方法,即其修饰符为static,那么synchronized 意味着某个调用此方法的线程当前会拥有该类的锁,只要该线程持续在当前方法内运行,其他线程依然无法获得方法的使用权!
测试代码:

1 public class TestSynchronized { 2 private InClass inClass = new InClass("name"); 3 4 public void test1() { 5 synchronized (inClass) { 6 int i = 5; 7 while (i-- > 0) { 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i); 9 try { 10 Thread.sleep(500); 11 } catch (InterruptedException ie) { 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 17 public synchronized void test2() { 18 19 int i = 5; 20 while (i-- > 0) { 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i); 22 try { 23 Thread.sleep(500); 24 } catch (InterruptedException ie) { 25 } 26 } 27 28 } 29 30 public void test3() { 31 synchronized (TestSynchronized.class) { 32 int i = 5; 33 while (i-- > 0) { 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i); 35 try { 36 Thread.sleep(500); 37 } catch (InterruptedException ie) { 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 public void test4() { 44 synchronized (this) { 45 int i = 5; 46 while (i-- > 0) { 47 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i); 48 try { 49 Thread.sleep(500); 50 } catch (InterruptedException ie) { 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 public synchronized void test5() { 57 58 int i = 5; 59 while (i-- > 0) { 60 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i); 61 try { 62 Thread.sleep(500); 63 } catch (InterruptedException ie) { 64 } 65 } 66 67 } 68 69 public static void main(String[] args) { 70 final TestSynchronized myt1 = new TestSynchronized(); 71 final TestSynchronized myt2 = new TestSynchronized(); 72 Thread test1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 73 public void run() { 74 myt1.test2(); 75 } 76 }, "test1"); 77 try { 78 Thread.sleep(10); 79 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 80 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 81 e.printStackTrace(); 82 } 83 Thread test2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { 84 public void run() { 85 myt1.test5(); 86 } 87 }, "test2"); 88 test1.start(); 89 test2.start(); 90 } 91 92 class InClass { 93 public InClass(String name) { 94 // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 95 } 96 } 97 }
测试会发现,synchronized(this)会锁住代码块本身的方法、synchronized标示的方法和其它synchroized(this)的代码块;而synchronized(MyClass.class)只能锁住不同对象对应的这一个方法块儿!其他方法(即便是同步的)不会被锁住!
纸上得来终觉浅,还盼诸君勤实践啊!!!啊啊啊啊啊啊!!!!!
参考:synchronize类锁和对象锁详解;深入理解java中的synchronized关键字;java中volatile关键字的含义(这个的评论要看一下)
-------------------------------------- 我 是 华 丽 的 分 割 线 ------------------------------------------
--->>>原因找到了!
关键在于amount is an instance of Integer,synchronized锁的是amount这个对象,但是for循环中amount++这个操作会使得amount这个对象发生变化,这个通过hashcode可以看出来,对于instance of Integer,amount.intValue()==amount.hashcode().所以当这个对象变了之后,之前对象的锁自然就没用了,其它线程开始竞争新对象的锁,由此造成了这样的结果。
--->>>关于synchronized一点补充
synchronized的实现机制需要参照jvm,了解的知识比较多。synchronized(syncObject)类似于给某个对象加锁,{\code}代码块里面的东西在执行之前都需要获取这把锁,运行完之后马上释放锁。
