枚举所有可能的半径,然后将所有满足这个半径的点按角度(与x轴正半轴的夹角)排序。 然后一遍扫描求出在这个半径下选k个点所需的最小面积 。
思路还是比较简单,实现略有些繁琐。
要先将点的坐标转换为角度。 如果用斜率的方法的话有些繁琐。
Fire-Control System
Time Limit: 12000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2047 Accepted Submission(s): 350
Problem Description
A new mighty weapon has just been developed, which is so powerful that it can attack a sector of indefinite size, as long as the center of the circle containing the sector is the location of the weapon. We are interested in developing a fire-control system that calculates firing-solutions automatically.
The following example gives an example of a firing solution:
Figure 1
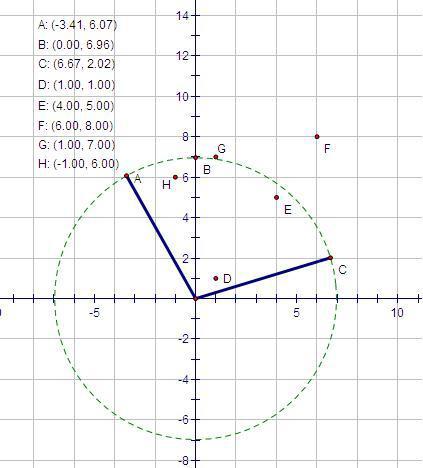
Here the firing region is the sector "ABC" that covers six points: A, B, C, D, E, H. You may further assume that the weapon is always located at point (0, 0), no targets will be on the point (0, 0) and the coordinates of the targets will be distinct.
A firing solution is called effective if and only if it covers a minimum of K points
out of N given points (targets) on the two-dimensional Cartesian plane. Furthermore,since the cost of a particular fire solution is in direct proportion to the size of the area it covers, a firing could be quite costly; thus we are only interested in the optimal firing solution with the minimum cost.
The following example gives an example of a firing solution:
Figure 1

Here the firing region is the sector "ABC" that covers six points: A, B, C, D, E, H. You may further assume that the weapon is always located at point (0, 0), no targets will be on the point (0, 0) and the coordinates of the targets will be distinct.
A firing solution is called effective if and only if it covers a minimum of K points
out of N given points (targets) on the two-dimensional Cartesian plane. Furthermore,since the cost of a particular fire solution is in direct proportion to the size of the area it covers, a firing could be quite costly; thus we are only interested in the optimal firing solution with the minimum cost.
Input
There are multiple test cases in the input file.
Each test case starts with two non-negative integers, N and K
(1 ≤ N ≤ 5000 , K ≤ N ), followed by N lines each containing two integers, X, and Y, describing the distinct location of one target. It is guaranteed that the absolute value of any integer does not exceed 1000.
Two successive test cases are separated by a blank line. A case with N = 0 and K = 0 indicates the end of the input file, and should not be processed by your program.
Each test case starts with two non-negative integers, N and K
(1 ≤ N ≤ 5000 , K ≤ N ), followed by N lines each containing two integers, X, and Y, describing the distinct location of one target. It is guaranteed that the absolute value of any integer does not exceed 1000.
Two successive test cases are separated by a blank line. A case with N = 0 and K = 0 indicates the end of the input file, and should not be processed by your program.
Output
For each test case, please print the required size (to two decimal places), in the
format as indicated in the sample output.
format as indicated in the sample output.
Sample Input
3 1
0 1
1 0
-5 -6
3 2
0 2
2 0
-5 -6
0 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 0.00
Case #2: 3.14
Source
Recommend
lcy
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <string.h> using namespace std; #define N 100100 #define PI (2*asin(1.0)) struct node { int x,y; double r;//表示半径 double du;//用来表示角度 }g[N]; int n,k; double g1[N]; int cmp(node t,node t1) { return t.du<t1.du; } double que[2*N]; double mabs(double x) { if(x<0) return -x; return x; } int main() { //freopen("//home//ismdeep//xianchang1//in","r",stdin); int tt=1; double pi=PI; while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)&&(n+k)) { for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&g[i].x,&g[i].y); g[i].r=sqrt((double)g[i].x*g[i].x+g[i].y*g[i].y); g1[i]=g[i].r; double tmp; if(mabs(g[i].x-0)<1e-8) { if(g[i].y>0) tmp=90.0; else tmp=270.0; } else { tmp=((double)g[i].y/(double)g[i].x); //将这个点的斜率求出来 if(mabs(g[i].y-0)<1e-8) { if(g[i].x>0) tmp=0.0; else tmp=180.0; } else { tmp=atan(tmp);//求出角度 tmp=(180.0/PI)*tmp; if(g[i].y*g[i].x > 0&&g[i].y<0) tmp+=180.0; if(g[i].y*g[i].x<0) { tmp*=-1; if(g[i].x<0) tmp=180.0-tmp; else { tmp=360-tmp; } } } } g[i].du=tmp; } // 角度求好了 if(k==0) { printf("Case #%d: 0.00 ",tt++); continue; } //sort(g1+1,g1+n+1); //半径从小到大来搞一搞啊 sort(g+1,g+1+n,cmp); double mi=1999999999; for(int ii=1;ii<=n;ii++) { double key=g1[ii]; //表示固定的半径 int flag=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)//提前 { if(g[i].r <= key+1e-6) { que[flag++]=g[i].du; } } for(int i=0;i<flag;i++) { que[flag+i] = que[i]+360.0; } if(flag<k) continue; for(int i=0;i<flag;i++) { double tmp=que[i]; int tt=i+k-1; double tmp1=que[tt]; tmp=tmp1-tmp; tmp=(tmp/(360.0))*PI*key*key; mi=min(tmp,mi); } } printf("Case #%d: ",tt++); printf("%.2lf ",mi); } return 0; }