=============================================================================
=============================================================================
涉及到的知识点有:
1:StringBuffer类的概述及其使用(掌握)
(1)StringBuffer类的概述
(2)StringBuffer类的构造方法
(3)StringBuffer类的常见功能
(4)StringBuffer类的练习(做一遍)
(5)StringBuffer类的两个面试题
(6)StringBuffer类作为形式参数的问题
2:数组高级以及Arrays类的概述及其使用(掌握)
(1)数组排序
A:冒泡排序
B:选择排序
(2)数组查找
A:基本查找
B:二分查找(折半查找)
(3)Arrays工具类
(4)Arrays工具类的源码解析
3:Integer类(掌握)
(1)Integer类的概述
(2)Integer类的构造方法
(3)String引用数据类型和int基本数据类型的相互转换(推荐方法)
(4)Integer类的成员方法
(5)Integer类的其他的功能(了解)
(6)JDK5的新特性:自动装箱和自动拆箱
(7)Integer类的面试题
4:Character类(了解)
(1)Character类的概述
(2)Character类的构造方法
(3)Character类要掌握的方法
(4)Character类的案例
=============================================================================
=============================================================================
1:StringBuffer类的概述及其使用(掌握)
(1)StringBuffer类的概述
我们用字符串做拼接,每次拼接,都会构建一个新的String对象,比较耗时并且也耗内存。
而这种拼接操作又是比较常见的,为了解决这个问题,Java就提供了一个字符串缓冲区类StringBuffer供我们使用。
StringBuffer:是线程安全的可变字符串(字符序列)。
线程安全(多线程讲解)
安全 --> 同步 --> 数据是安全的
不安全 --> 不同步 --> 效率高一些
安全和效率问题是永远困扰我们的问题。
要安全:医院的网站,银行网站等等。
要效率:新闻网站,论坛之类等等。
StringBuffer和String的区别?
StringBuffer的长度和内容可变,String的不可变。
如果使用StringBuffer做字符串的拼接,不会浪费太多的资源。
---------------------------------------
(2)StringBuffer类的构造方法
A:public StringBuffer() 无参构造方法
B:public StringBuffer(int capacity) 指定容量的字符串缓冲区对象
C:public StringBuffer(String str) 指定字符串内容的字符串缓冲区对象
D:public StringBuffer(CharSequence seq)
CharSequence是接口,其所有已知实现类:CharBuffer, Segment, String, StringBuffer, StringBuilder
E:StringBuffer的方法:
public int capacity() 返回当前容量。 理论值
public int length() 返回长度(字符数)。 实际值
---------------------------------------
(3)StringBuffer类的常见功能
A:添加功能
public StringBuffer append(String str) 可以把任意类型数据添加到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区对象本身,所以不需要再去创建对象接收了(该点很重要)。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, String str) 在指定位置把任意类型数据插入到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区对象本身。
B:删除功能
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) 删除指定位置的字符,并返回字符串缓冲区对象本身。
public StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) 删除从指定位置开始到指定位置结束的内容,并返回字符串缓冲区对象本身(包头不包尾)。
C:替换功能
public StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) 从start开始到end用str替换,并返回字符串缓冲区对象本身(包头不包尾)。
D:反转功能
public StringBuffer reverse() 反转字符串缓冲区内容,并返回字符串缓冲区对象本身。
E:截取功能(注意返回值类型不再是StringBuffer对象本身了)
public String substring(int start) 从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾(包含start这个索引),返回的是字符串对象。
public String substring(int start, int end) 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串(包括start索引但是不包end索引),返回的是字符串对象。
---------------------------------------
(4)StringBuffer类的练习(做一遍)
为什么我们要讲解类之间的转换?
A --> B的转换
我们把A转换为B,其实是为了使用B的功能。
B --> A的转换
我们可能要的结果是A类型,所以还得转换回来。
---------------------------------------
A:String类和StringBuffer类的相互转换
String --> StringBuffer
方式1:通过StringBuffer类的构造方法(推荐)
String s = "hello";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(s);
方式2:通过StringBuffer类的append()方法
String s = "hello";
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer();
sb2.append(s);
---------------------------------------
StringBuffer --> String
方式1:通过String类的构造方法
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("java");
String str = new String(buffer);
方式2:通过StringBuffer类的toString()方法(推荐)
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("java");
String str2 = buffer.toString();
---------------------------------------
注意:不能把字符串的值直接赋值给StringBuffer的。
StringBuffer sb = "hello";
StringBuffer sb = s;
---------------------------------------
B:把数组拼接成一个字符串
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_07; 2 3 /* 4 * 把数组拼接成一个字符串 5 */ 6 public class StringBufferTest2 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // 定义一个数组 9 int[] arr = { 44, 33, 55, 11, 22 }; 10 11 // 定义功能 12 // 方式1:用String做拼接的方式,开辟内存特别多,效率低。 13 String s1 = arrayToString(arr); 14 System.out.println("s1:" + s1); 15 16 // 方式2:用StringBuffer做拼接的方式 17 String s2 = arrayToString2(arr); 18 System.out.println("s2:" + s2); 19 } 20 21 // 用StringBuffer做拼接的方式 22 public static String arrayToString2(int[] arr) { 23 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 24 25 sb.append("["); 26 for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) { 27 if (x == arr.length - 1) { 28 sb.append(arr[x]); 29 } else { 30 sb.append(arr[x]).append(", "); 31 } 32 } 33 sb.append("]"); 34 35 return sb.toString(); // StringBuffer --> String 36 } 37 38 // 用String做拼接的方式 39 public static String arrayToString(int[] arr) { 40 String s = ""; 41 42 s += "["; 43 for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) { 44 if (x == arr.length - 1) { 45 s += arr[x]; 46 } else { 47 s += arr[x]; 48 s += ", "; 49 } 50 } 51 s += "]"; 52 53 return s; 54 } 55 }
C:把字符串反转
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_07; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 /* 6 * 把字符串反转 7 */ 8 public class StringBufferTest3 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 键盘录入数据 11 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 12 System.out.println("请输入数据:"); 13 String s = sc.nextLine(); 14 15 // 方式1:用String做拼接 16 String s1 = myReverse(s); 17 System.out.println("s1:" + s1); 18 // 方式2:用StringBuffer的reverse()的反转功能 19 String s2 = myReverse2(s); 20 System.out.println("s2:" + s2); 21 22 sc.close(); 23 } 24 25 // 方式2:用StringBuffer的reverse()的反转功能 26 public static String myReverse2(String s) { 27 // StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(s); 28 // sb.reverse(); 29 // return sb.toString(); 30 31 // 简易版 32 return new StringBuffer(s).reverse().toString(); 33 } 34 35 // 方式1:用String做拼接 36 public static String myReverse(String s) { 37 String result = ""; 38 39 char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); // 把字符串转换为字符数组 40 for (int x = chs.length - 1; x >= 0; x--) { 41 // char ch = chs[x]; // 得到每一个字符 42 // result += ch; 43 result += chs[x]; 44 } 45 46 return result; 47 } 48 }
D:判断一个字符串是否是对称字符串
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_07; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 /* 6 * 判断一个字符串是否是对称字符串 7 * 例如"abc"不是对称字符串,"aba"、"abba"、"aaa"、"mnanm"是对称字符串 8 * 9 * 分析: 10 * 判断一个字符串是否是对称的字符串,我只需要把 11 * 第一个和最后一个比较 12 * 第二个和倒数第二个比较 13 * ... 14 * 比较的次数是长度除以2。 15 */ 16 public class StringBufferTest4 { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 // 创建键盘录入对象 19 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 20 System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:"); 21 String s = sc.nextLine(); 22 23 // 一个一个的比较 24 boolean b = isSame(s); 25 System.out.println("b:" + b); 26 27 // 用字符串缓冲区的反转功能 28 boolean b2 = isSame2(s); 29 System.out.println("b2:"+b2); 30 31 sc.close(); 32 } 33 34 public static boolean isSame2(String s) { 35 return new StringBuffer(s).reverse().toString().equals(s); 36 } 37 38 39 // public static boolean isSame(String s) { 40 // // 把字符串转成字符数组 41 // char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); 42 // 43 // for (int start = 0, end = chs.length - 1; start <= end; start++, end--) { 44 // if (chs[start] != chs[end]) { 45 // return false; 46 // } 47 // } 48 // 49 // return true; 50 // } 51 52 public static boolean isSame(String s) { 53 boolean flag = true; 54 55 // 把字符串转成字符数组 56 char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); 57 for (int start = 0, end = chs.length - 1; start <= end; start++, end--) { 58 if (chs[start] != chs[end]) { 59 flag = false; 60 break; 61 } 62 } 63 64 return flag; 65 } 66 67 }
---------------------------------------
(5)StringBuffer类的两个面试题
小细节:
StringBuffer 同步的,数据安全,效率低。
StringBuilder 不同步的,数据不安全,效率高。
StringBuilder是一个可变的字符序列。此类提供一个与 StringBuffer 兼容的 API,但不保证同步。
该类被设计用作 StringBuffer 的一个简易替换,用在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候(这种情况很普遍)。
A:String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别?
a:String是内容不可变的,而StringBuffer、StringBuilder都是内容可变的。
b:StringBuffer是同步的,数据安全,效率低;StringBuilder是不同步的,数据不安全,效率高。
B:StringBuffer和数组的区别?
二者都可以看出是一个容器,装其他的数据。
但是呢,StringBuffer可以放置多种数据,但最终是一个字符串数据。
而数组可以放置多种数据,但必须是同一种数据类型的。
(6)StringBuffer类作为形式参数的问题:
String类作为形式参数。
StringBuffer类作为形式参数。
形式参数:
基本数据类型:形式参数的改变不影响实际参数。
引用数据类型:形式参数的改变直接影响实际参数。
String类作为形式参数传递时,效果和基本数据类型作为形式参数传递是一样的。
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_08; 2 3 /* 4 * 面试题: 5 * 1:String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别? 6 * A:String是内容不可变的,而StringBuffer、StringBuilder都是内容可变的。 7 * B:StringBuffer是同步的,数据安全,效率低;StringBuilder是不同步的,数据不安全,效率高。 8 * 9 * 2:StringBuffer和数组的区别? 10 * 二者都可以看出是一个容器,装其他的数据。 11 * 但是呢,StringBuffer可以放置多种数据,但最终是一个字符串数据。 12 * 而数组可以放置多种数据,但必须是同一种数据类型的。 13 * 14 * 3:形式参数问题 15 * String类作为参数传递 16 * StringBuffer类作为参数传递 17 * 18 * 形式参数: 19 * 基本数据类型:形式参数的改变不影响实际参数。 20 * 引用数据类型:形式参数的改变直接影响实际参数。 21 * 22 * 注意: 23 * String类作为形式参数传递时,效果和基本数据类型作为形式参数传递是一样的。 24 */ 25 public class StringBufferDemo { 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 String s1 = "hello"; 28 String s2 = "world"; 29 System.out.println(s1 + "---" + s2); // hello---world 30 change(s1, s2); 31 System.out.println(s1 + "---" + s2); // hello---world 32 33 StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("hello"); 34 StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("world"); 35 System.out.println(sb1 + "---" + sb2); // hello---world 36 change(sb1, sb2); 37 System.out.println(sb1 + "---" + sb2); // hello---worldworld 38 } 39 40 public static void change(StringBuffer sb1, StringBuffer sb2) { 41 sb1 = sb2; // sb1的地址值由于赋值临时发生改变,但在main函数里面的sb1的地址值没有变。 42 sb2.append(sb1); // append函数使sb2的内容发生改变,但在main函数里面的sb2的地址值没有变。即通过change函数里面的append函数sb2指向的内容发生改变。 43 } 44 45 public static void change(String s1, String s2) { 46 s1 = s2; // sb1的地址值由于赋值临时发生改变,但在main函数里面的sb1的地址值没有变。 47 s2 = s1 + s2; // sb2的地址值由于赋值临时发生改变,但在main函数里面的sb2的地址值没有变。 48 } 49 }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
2:数组高级以及Arrays类的概述及其使用(掌握)
(1)数组排序
A:冒泡排序
相邻元素两两比较,大的往后放,第一次比较完毕,最大值出现在了最大索引处。同理,其他的元素就可以排好。01_数组冒泡排序原理图解如下图所示:
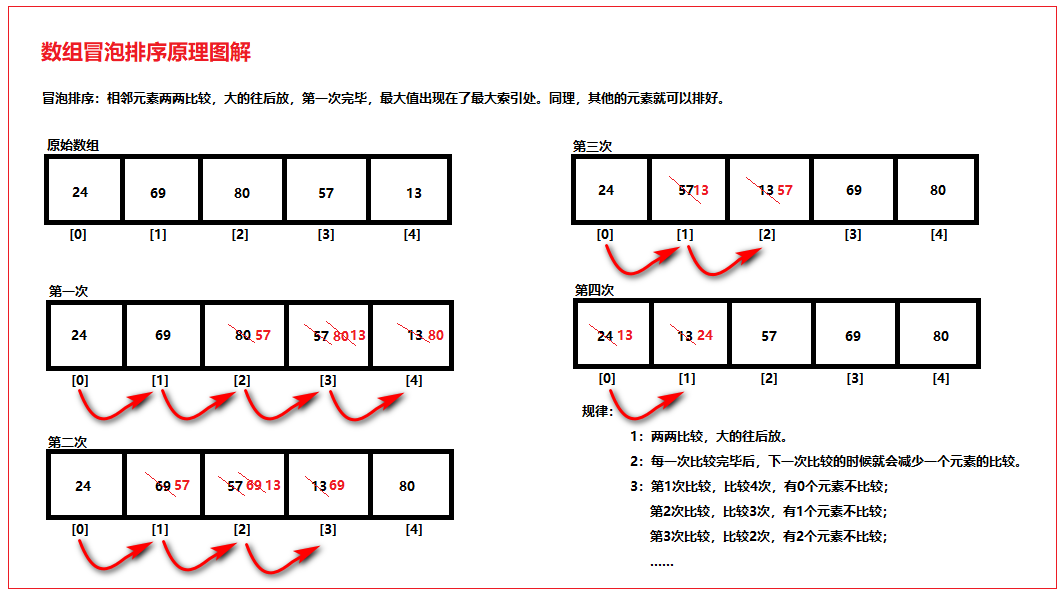
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) { for (int x = 0; x < arr.length - 1 ; x++) { for (int y = 0; y < arr.length - 1 - x; y++) { if (arr[y] > arr[y+1]) { int temp = arr[y]; arr[y] = arr[y+1]; arr[y+1] = temp; } } } }
B:选择排序
把0索引的元素,依次和后面的元素进行比较,小的往前放,第一次比较完毕,最小值出现在了0索引。同理,其他的元素就可以排好。02_数组选择排序原理图解如下图所示:
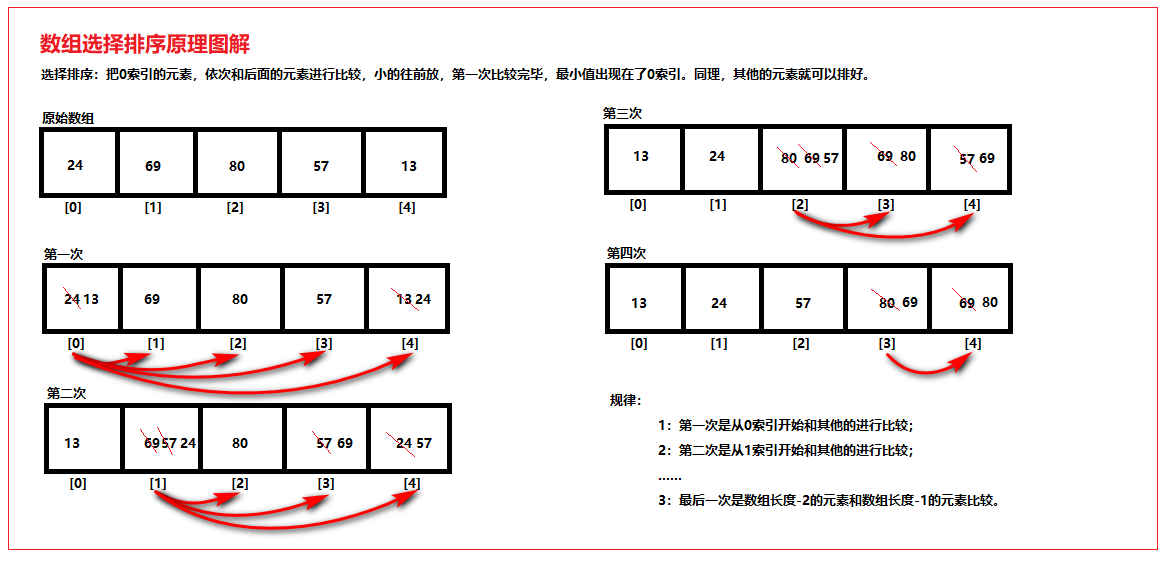
public static void selectSort(int[] arr) { for (int x = 0; x < arr.length - 1; x++) { for (int y = x + 1; y < arr.length; y++) { if (arr[y] < arr[x]) { int temp = arr[x]; arr[x] = arr[y]; arr[y] = temp; } } } }
练习:把字符串中的字符进行排序。
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 /* 4 * 把字符串中的字符进行排序。 5 * 举例:"dacgebf" 6 * 结果:"abcdefg" 7 * 8 * 分析: 9 * A:定义一个字符串 10 * B:把字符串转换为字符数组 11 * C:把字符数组进行排序 12 * D:把排序后的字符数组转成字符串 13 * E:输出最后的字符串 14 */ 15 public class ArrayTest { 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 // 定义一个字符串 18 String s = "dacgebf"; 19 20 // 把字符串转换为字符数组 21 char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); 22 23 // 把字符数组进行排序 24 bubbleSort(chs); 25 26 // 把排序后的字符数组转成字符串 27 String result = String.valueOf(chs); 28 29 // 输出最后的字符串 30 System.out.println("result:"+result); 31 } 32 33 // 冒泡排序 34 public static void bubbleSort(char[] chs) { 35 for (int x = 0; x < chs.length - 1; x++) { 36 for (int y = 0; y < chs.length - 1 - x; y++) { 37 if (chs[y] > chs[y + 1]) { 38 char temp = chs[y]; 39 chs[y] = chs[y + 1]; 40 chs[y + 1] = temp; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 }
---------------------------------------
(2)数组查找
A:基本查找
针对数组无序的情况
public static int getIndex(int[] arr, int value) { int index = -1; for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) { if (arr[x] == value) { index = x; break; } } return index; }
B:二分查找(折半查找)
针对数组有序的情况(千万不要先将无须数组排序,再查找,无序数组就用基本查找法)
A:定义最大索引,最小索引;
B:计算出中间索引;
C:拿中间索引的值和要查找的值进行比较:
相等:就返回当前的中间索引。
不相等:
大 左边找
小 右边找
D:重新计算出中间索引:
大 左边找
max = mid - 1;
小 右边找
min = mid + 1;
E:回到B。
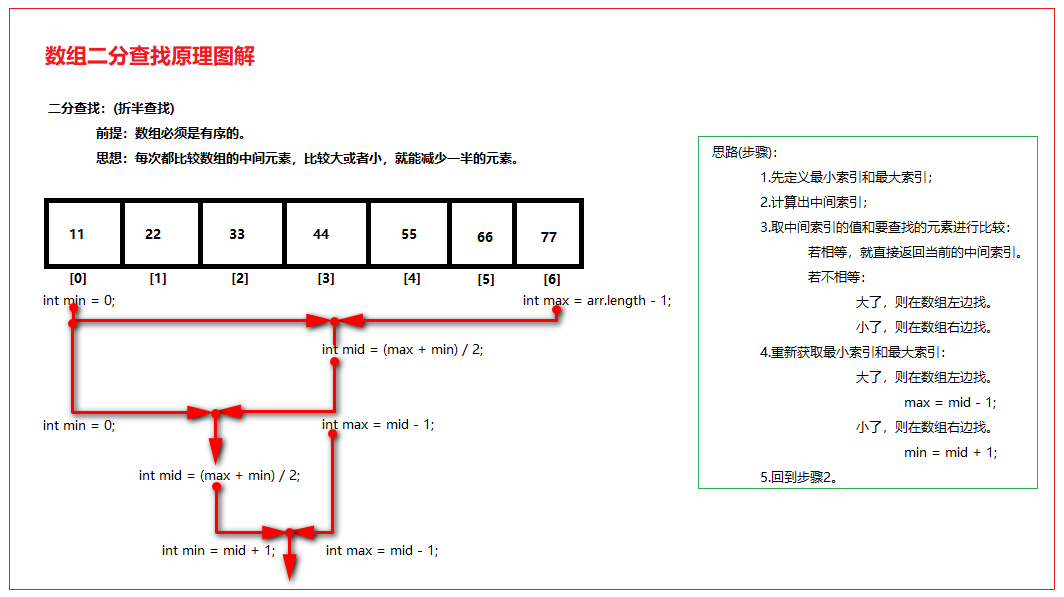
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int value) { int min = 0; int max = arr.length - 1; int mid = (min + max) / 2; while (arr[mid] != value) { if (arr[mid] > value) { max = mid - 1; } else if (arr[mid] < value) { min = mid + 1; } if (min > max) { return -1; } mid = (min+max) / 2; } return mid; }
---------------------------------------
(3)Arrays工具类
A:是针对数组进行操作的工具类。包括排序和查找等功能(注意:该类没有构造方法,都是静态的方法,通过类名调用。)
B:要掌握的方法(自己补齐方法)
1:public static String toString(int[] a) 把数组转成字符串(数组可以是任何类型的数组哦)
2:public static void sort(int[] a) 对数组进行排序
3:public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) 二分查找
(4)Arrays工具类的源码解析
Arrays类的底层排序方法是快速排序。
能用JDK提供的就不用自己写的,因为JDK提供的会做很多优化。
---------------------------------------
--------------------------------------- public static String toString(int[] a) public static void sort(int[] a) 底层是快速排序,知道就可以了。有空看,有问题再问我。 public static int binarySearch(int[] a,int key) 开发原则: 只要是形参是对象,我们就要首先判断该对象是否为null。 也即只要是形参是引用数据类型,我们就要首先判断该数据类型是否为null。 --------------------------------------- int[] arr = { 24, 69, 80, 57, 13 }; System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr)); public static String toString(int[] a) { //a --> arr --> { 24, 69, 80, 57, 13 } if (a == null) return "null"; // 说明数组对象不存在。 int iMax = a.length - 1; // iMax = 5 - 1 = 4; if (iMax == -1) return "[]"; // 说明数组存在,但是没有元素。 StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder(); b.append('['); // "[" for (int i = 0; ; i++) { // 第二个条件不写,默认为true。 b.append(a[i]); // "[24, 69, 80, 57, 13" if (i == iMax) return b.append(']').toString(); // "[24, 69, 80, 57, 13]" b.append(", "); // "[24, 69, 80, 57, " } } --------------------------------------- int[] arr = { 13, 24, 57, 69, 80 }; System.out.println("binarySearch:" + Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 577)); public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) { // a --> arr --> { 13, 24, 57, 69, 80 } // key --> 577 return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key); } private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int key) { // a --> arr --> { 13, 24, 57, 69, 80 } // fromIndex --> 0 // toIndex --> 5 // key --> 577 int low = fromIndex; // low=0 int high = toIndex - 1; // high=4 while (low <= high) { // 无符号右移一位,相当于除以2。 int mid = (low + high) >>> 1; // mid=2,mid=3,mid=4 int midVal = a[mid]; // midVal=57,midVal=69,midVal=80 if (midVal < key) low = mid + 1; // low=3,low=4,low=5 else if (midVal > key) high = mid - 1; else return mid; // key found } return -(low + 1); // key not found. } ---------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
3:Integer类(掌握)
(1)Integer类的概述
为了对基本数据类型进行更多的操作,更方便的操作,Java就针对每一种基本数据类型提供了对应的类类型。包装类类型。
将基本数据类型封装成对象的好处在于可以在对象中定义更多的功能方法操作该数据。
简言之:只有我们把某个东西看成一个类的时候,我们使用这个东西的功能和属性的时候就特别方便。
常用的操作之一:用于基本数据类型与字符串之间的转换。
基本数据类型 引用数据类型 byte Byte short Short int Integer long Long float Float double Double char Character boolean Boolean
---------------------------------------
(2)Integer类的构造方法
public Integer(int value)
Integer i = new Integer(100);
很少使用这个构造函数。 静态工厂valueOf(int)通常是一个更好的选择,因为它可能产生明显更好的空间和时间性能。
public Integer(String s)
Integer i = new Integer("100");
很少使用这个构造函数。 使用parseInt(String)将字符串转换为int原语,或使用valueOf(String)将字符串转换为Integer对象。
注意:这里的字符串必须是由数字字符组成的。
---------------------------------------
(3)String引用数据类型和int基本数据类型的相互转换(推荐方法)
A:String --> int
Integer.parseInt("100");
B:int --> String
String.valueOf(100);
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 /* 4 * String引用数据类型和int基本数据类型的相互转换 5 * 6 * int --> String 7 * String.valueOf(number) 8 * 9 * String --> int 10 * Integer.parseInt(s) 11 */ 12 public class IntegerDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 // int --> String 15 int number = 100; 16 // 方式1:字符串的拼接 17 String s1 = "" + number; 18 System.out.println("s1:" + s1); 19 // 方式2:String类的valueof方法 20 String s2 = String.valueOf(number); 21 System.out.println("s2:" + s2); 22 // 方式3:通过Integer作为桥梁 23 // int --> Integer --> String 24 Integer i = new Integer(number); 25 String s3 = i.toString(); 26 System.out.println("s3:" + s3); 27 // 方式4:Integer类的toString方法 28 // public static String toString(int i) 29 String s4 = Integer.toString(number); 30 System.out.println("s4:" + s4); 31 System.out.println("-----------------"); 32 33 // String --> int 34 String s = "100"; 35 // 方式1:通过Integer作为桥梁 36 // String --> Integer --> int 37 Integer ii = new Integer(s); 38 // public int intValue() 39 int x = ii.intValue(); 40 System.out.println("x:" + x); 41 // 方式2:Integer类的parseInt方法 42 // public static int parseInt(String s) 43 int y = Integer.parseInt(s); 44 System.out.println("y:"+y); 45 } 46 }
---------------------------------------
(4)Integer类的成员方法
public int intValue()
public static int parseInt(String s)
public static String toString(int i)
public static Integer valueOf(int i)
public static Integer valueOf(String s)
---------------------------------------
(5)Integer类的其他的功能(了解)
常用的基本进制转换:十进制到二进制、八进制、十六进制
public static String toBinaryString(int i)
public static String toOctalString(int i)
public static String toHexString(int i)
十进制到其他进制
public static String toString(int i, int radix)
进制的范围:2-36
为什么呢?0,...9,a...z
其他进制到十进制
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 /* 4 * 常用的基本进制转换 5 * public static String toBinaryString(int i) 6 * public static String toOctalString(int i) 7 * public static String toHexString(int i) 8 * 9 * 十进制到其他进制 10 * public static String toString(int i, int radix) 11 * 由这个我们也看到了进制的范围:2-36 12 * 为什么呢?0,...9,a...z 13 * 14 * 其他进制到十进制 15 * public static int parseInt(String s, int radix) 16 */ 17 public class IntegerDemo { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 // 十进制到二进制、八进制、十六进制 20 System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(100)); //1100100 21 System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(100)); //144 22 System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(100)); //64 23 System.out.println("-------------------------"); 24 25 // 十进制到其他进制 26 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 10)); // 100 27 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 2)); // 1100100 28 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 8)); // 144 29 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 16)); // 64 30 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 5)); // 400 31 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 7)); // 202 32 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, -7)); // 100 33 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 70)); // 100 34 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 1)); // 100 35 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 17)); // 5f 36 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 32)); // 34 37 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 37)); // 100 38 System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 36)); // 2s 39 System.out.println("-----------------------"); 40 41 // 其他进制到十进制 42 System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 10)); // 100 43 System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 2)); // 4 44 System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 8)); // 64 45 System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 16)); // 256 46 System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 23)); // 529 47 // NumberFormatException 48 // System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123", 2)); 49 } 50 }
---------------------------------------
(6)JDK5的新特性:自动装箱和自动拆箱
自动装箱:把基本数据类型转换为包装类数据类型。
自动拆箱:把包装类数据类型转换为基本数据类型。
把下面的这个代码理解即可:
Integer i = 100;
i += 200;
System.out.println("ii:" + ii);
// 上面三句,通过反编译后的代码如下:
// Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(100); // 自动装箱
// ii = Integer.valueOf(ii.intValue() + 200); // 自动拆箱,再自动装箱
// System.out.println((new StringBuilder("ii:")).append(ii).toString());
示例代码如下:
package cn.itcast_05; /* * JDK5的新特性: * 自动装箱:把基本数据类型转换为包装类数据类型。 * 自动拆箱:把包装类数据类型转换为基本数据类型。 * * 注意一个小问题: * 在使用时,Integer x = null; 代码就会出现NullPointerException。 * 在使用Integer类的对象的时候,建议先判断该对象是否为null,然后再使用。 */ public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义了一个int类型的包装类类型变量i // Integer i = new Integer(100); // 等价于下面这句 Integer ii = 100; ii += 200; System.out.println("ii:" + ii); // 通过反编译后的代码 // Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(100); // 自动装箱 // ii = Integer.valueOf(ii.intValue() + 200); // 自动拆箱,再自动装箱 // System.out.println((new StringBuilder("ii:")).append(ii).toString()); /* Integer iii = null; // NullPointerException 因为通过反编译可以知道,iii是对象要调用方法,但iii是空指针。 if (iii != null) { iii += 1000; System.out.println(iii); } */ } }
---------------------------------------
(7)Integer类的面试题
byte常量池,即-128到127之间的数据缓冲池问题。
这句 Integer i = 100; 等价于 Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(100); // 自动装箱
通过查看valueOf方法的源码,我们就知道了,当Integer类型的数据直接赋值时,如果在-128到127之间,会直接从缓冲池里获取数据,每次并不创建新的空间。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
4:Character类(了解)
(1)Character类的概述
Character 类在对象中包装一个基本类型 char 的值
此外,该类提供了几种方法,以确定字符的类别(小写字母,数字,等等),并将字符从大写转换成小写,反之亦然。
(2)Character类的构造方法
Character ch = new Character('a');
很少使用这个构造函数。 静态工厂valueOf(char)通常是一个更好的选择,因为它可能产生明显更好的空间和时间性能。
(3)Character类要掌握的方法:(自己补齐)
public static boolean isUpperCase(char ch) 判断给定的字符是否是大写字符
public static boolean isLowerCase(char ch) 判断给定的字符是否是小写字符
public static boolean isDigit(char ch) 判断给定的字符是否是数字字符
public static char toUpperCase(char ch) 把给定的字符转换为大写字符
public static char toLowerCase(char ch) 把给定的字符转换为小写字符
(4)Character类的案例:
统计字符串中大写、小写及数字字符出现的次数。
示例代码如下:
1 package cn.itcast_06; 2 3 /* 4 * 看程序写结果 5 * 6 * 注意:当Integer类型的数据直接赋值时,如果在-128到127之间,会直接从缓冲池里获取数据,每次并不创建新的空间。 7 */ 8 public class IntegerDemo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Integer i1 = new Integer(127); 11 Integer i2 = new Integer(127); 12 System.out.println(i1 == i2); // false 13 System.out.println(i1.equals(i2)); // true 14 System.out.println("-----------"); 15 16 Integer i3 = new Integer(128); 17 Integer i4 = new Integer(128); 18 System.out.println(i3 == i4); // false 19 System.out.println(i3.equals(i4)); // true 20 System.out.println("-----------"); 21 22 // JDK5的新特性 23 Integer i5 = 128; 24 Integer i6 = 128; 25 System.out.println(i5 == i6); // false 重新new出来的。 26 System.out.println(i5.equals(i6)); // true 27 System.out.println("-----------"); 28 29 Integer i7 = 127; 30 Integer i8 = 127; 31 System.out.println(i7 == i8); // true 缓冲池中来的(byte常量池)。 32 System.out.println(i7.equals(i8)); // true 33 34 // 通过查看源码,我们就知道了,针对-128到127之间的数据,做了一个数据缓冲池,如果数据是该范围内的,则每次并不创建新的空间。 35 // Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(127); 36 } 37 }
=============================================================================