数据结构题目专题
数据结构的题目都比较死,套路比较单一,只要各个数据结构都熟悉它们的操作,就可以上手去干题目了。
大概分为三种类型:顺序表类型、树类型、图类型。
细分为:数组、链表、栈、队列、二叉树、无向图、有向图等。
2. Add Two Numbers
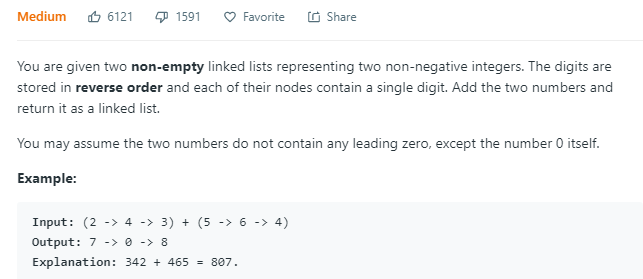
比如这题,使用链表来表示一个整数,将两个数加起来然后返回一个链表,据说今日某条的笔试题有这道题。看着submit好像是三年前的,代码写得太丑了,抽空重写下再贴吧。
思路就是把他俩反转,挨个加了之后返回一个链表。
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
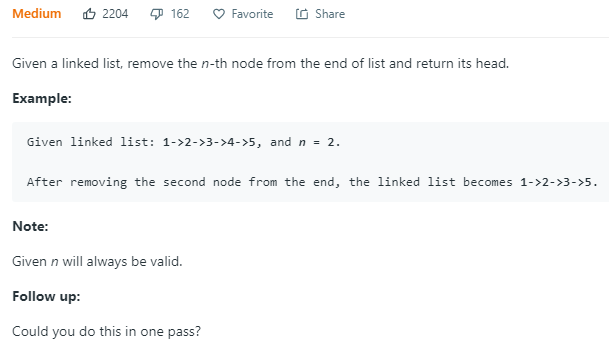
要求去掉从末尾往前数n位的节点,好几种思路。比如可以把链表反转,顺序去掉,或者统计长度,对n取补,去掉算出来的位置就好。这题有坑,去掉第一个节点时候掉坑里了。
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { if(head == null){ return null; } int len = 0 ; ListNode tmp = head; while (tmp != null){ len ++; tmp = tmp.next; } int fromHead = len - n; if(fromHead < 1){ head = head.next; }else { ListNode skip = head; for(int i=1;i<fromHead;i++){ if(skip != null) skip = skip.next; } if(skip != null){ ListNode skipNext = skip.next; if(skipNext != null){ skip.next = skipNext.next; } } } return head; }
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
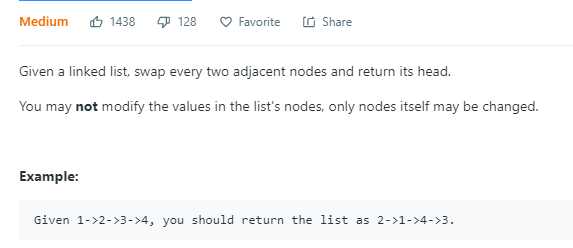
链表每两个节点反转,先做这题就会做k group了,自从用了LC,就喜欢上了绿色。
class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { if(head == null){ return null; } ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1); pre.next = head; ListNode change1 = null; ListNode change2 = null; int control = 0; ListNode runner = head; while(runner != null){ if(control == 0){ change1 = runner; control ++; runner = runner.next; }else if(control == 1){ change2 = runner; runner = runner.next; if(pre.next == head){ head = change2; } pre.next = change2; change1.next = change2.next; change2.next = change1; pre = change1; control --; } } return head; } }
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
这个题的题意就是一个链表可以根据k分成它的等差区间:(0,k-1),(k,2k-1).....
把这些按区间反转,没有想到优化方案。

class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) { if(head == null){ return null; } if(k == 0){ return head; } int control = 1; ListNode pre1 = new ListNode(-1); pre1.next = head; ListNode change1 = null; ListNode change2 = null; ListNode runner = head; while(runner != null){ if(control == 1){ change1 = runner; }else if(control == k){ change2 = runner; runner = runner.next; if(pre1.next == head){ head = change2; } ListNode temp = change1; ListNode revertHead = null; while(temp != runner){ ListNode cur = temp; temp = temp.next; if(revertHead == null) { cur.next = runner; }else { cur.next = revertHead; } revertHead = cur; } pre1.next = revertHead; pre1 = change1; control = 1; continue; } control ++; runner = runner.next; } return head; } }
43. Multiply Strings
大整数乘法,别看这玩意的案例才5万多,坑多得很,使用数组模拟列竖式计算,每个数组位只记十位数的一位。
class Solution { public String multiply(String num1, String num2) { if(num1 == null || num2 ==null || num1.isEmpty() || num2.isEmpty() || "0".equals(num1) || "0".equals(num2)){ return "0"; } int[] resultArray = new int[1000]; Arrays.fill(resultArray,-1); int baseCode = 48; int bit = 0; for(int i=num2.length()-1;i>=0;i--){ int j=num1.length()-1; int currentBitBase = num2.charAt(i) - baseCode; int eachK = bit; while(j>=0){ int curResult = (num1.charAt(j) - baseCode)*currentBitBase ; if(resultArray[eachK] < 0){ resultArray[eachK] = curResult ; }else { resultArray[eachK] += curResult; } eachK ++; j--; } bit ++; } int lastIndex ; int carry = 0; for(lastIndex = 0;lastIndex<resultArray.length;lastIndex++){ if(resultArray[lastIndex] < 0) break; else { resultArray[lastIndex] += carry; carry = 0; if(resultArray[lastIndex] >= 10){ carry = resultArray[lastIndex]/10; resultArray[lastIndex] %= 10; } } } if(carry > 0){ resultArray[lastIndex] = carry; }else { lastIndex--; } StringBuilder intValue = new StringBuilder(); for(;lastIndex>=0;lastIndex--){ intValue.append(resultArray[lastIndex]); } return intValue.toString(); } }
49. Group Anagrams
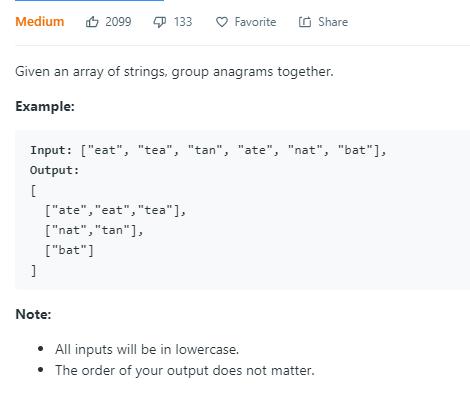
按字母分类,使用哈希表。
每次把拿到的字符按字典序排序一下,作为key。
class Solution { public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) { if (strs.length == 0) return new ArrayList(); Map<String, List<String>> ans = new HashMap<>(); for (String s : strs) { char[] carr = s.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(carr); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for(char c : carr){ sb.append(c); } if(!ans.containsKey(sb.toString())){ ans.put(sb.toString(),new ArrayList<String>()); } ans.get(sb.toString()).add(s); } return new ArrayList(ans.values()); } }
23. Merge k Sorted Lists
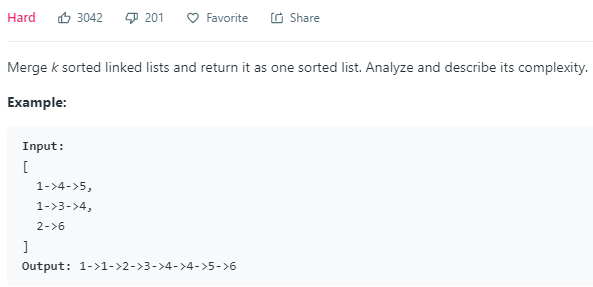
将一个链表数组,合成一个链表。使用优先队列,把所有节点全扔进去,然后再拿出来。
class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue(); for(ListNode h : lists){ ListNode temp = h; while(temp != null){ queue.add(temp.val); temp = temp.next; } } ListNode head = null; ListNode tail = null; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ if(head == null){ head = new ListNode(queue.poll()); tail = head; }else { tail.next = new ListNode(queue.poll()); tail = tail.next; } } return head; } }
57. Insert Interval
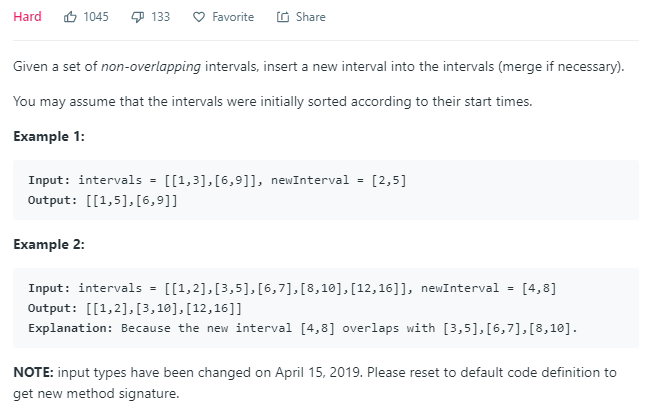
区间插入,虽然是hard但是略水,没beat 100,提高了10倍也还是20%的水平,无爱了。
class Solution { /** * 区间插入 * */ public int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newInterval) { List<int[]> orgin = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(intervals)); boolean append = false; for(int i=0;i<orgin.size();i++){ if(newInterval[0]<=orgin.get(i)[0]){ orgin.add(i,newInterval); append = true; break; } } if(!append) orgin.add(newInterval); int[][] newIntervals = orgin.toArray(new int[orgin.size()][]); List<int[]> mergeList = new ArrayList<>(newIntervals.length); for (int[] newInterval1 : newIntervals) { if (mergeList.size() > 0) { int[] last = mergeList.get(mergeList.size() - 1); if (last[1] >= newInterval1[0]) { last[1] = Math.max(last[1], newInterval1[1]); mergeList.set(mergeList.size() - 1, last); } else { mergeList.add(newInterval1); } } else { mergeList.add(newInterval1); } } return mergeList.toArray(new int[mergeList.size()][]); } }
61. Rotate List
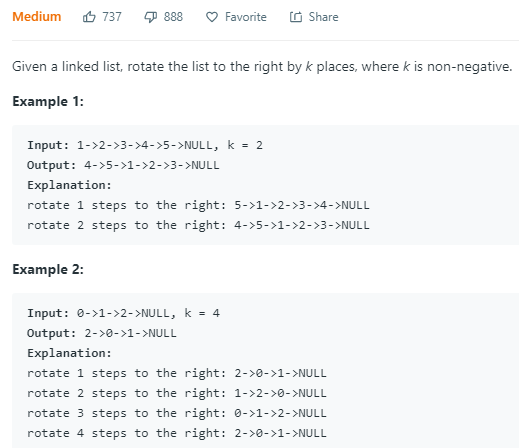
题意是链表像一个环一样,每个位置向右滚动k个位置。思路就是将它弄成环,然后找到新的head,再断开。

class Solution { public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) { if(head == null || k == 0){ return head; } int len = 1; ListNode runner = head; while(runner.next != null){ len ++; runner = runner.next; } runner.next = head; int runTimes = len - (k % len); ListNode pre = head; ListNode newHead = head.next; for(int i=1;i<runTimes;i++){ pre = pre.next; newHead = newHead.next; } pre.next = null; return newHead; } }
86. Partition List
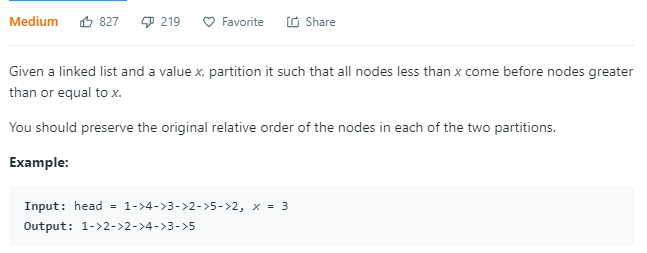
被快排的partition荼毒了,它的要求是将大于等于x的划分成一个链表,小于x的分成另一个链表,然后再进行拼接。注意,这里的链表顺序是不能变的。
比如小于3的,就是1,2,2;大于等于3的是4,3,5;然后他们合起来是1,2,2,4,3,5。
class Solution { public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { if(head == null) return head; ListNode smallHead = null; ListNode small = null; ListNode big = null; ListNode bigHead = null; while (head != null){ ListNode current = head; head = head.next; if(current.val < x){ if(small == null){ small = current; smallHead = small; }else { small.next = current; small = small.next; } small.next = bigHead; }else { if(big == null){ big = current; bigHead = big; }else { big.next = current; big = big.next; } big.next = null; } } if(small != null){ small.next = bigHead; } return smallHead == null ? bigHead : smallHead; } }
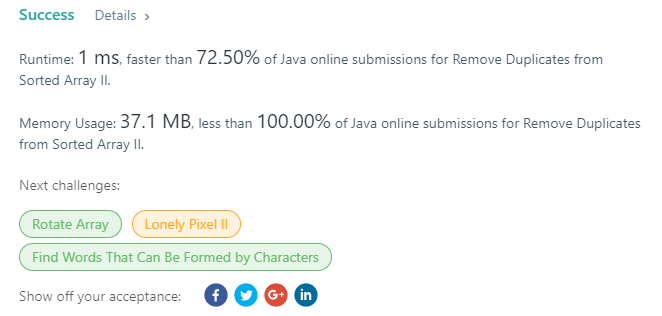
80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
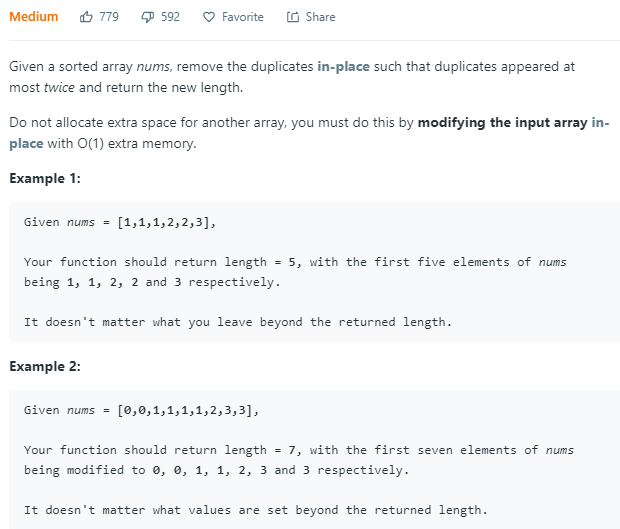
这题是给定一个数组,去掉它的duplicate值,然后返回长度,它的长度是原数组从头开始算的长度,所有的操作都在原数组上执行。
竟然还有人比我快,O(n)的系数比我小么。
class Solution { public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) { if(nums.length < 3){ return nums.length; } int len = 0; int duplicates = 0; int currentVal = nums[0]; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i] == currentVal && duplicates < 2){ duplicates ++; nums[len++] = nums[i]; }else if(nums[i] == currentVal){ continue; }else if(nums[i] != currentVal){ currentVal = nums[i]; duplicates = 1; nums[len++] = nums[i]; } } return len; } }
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
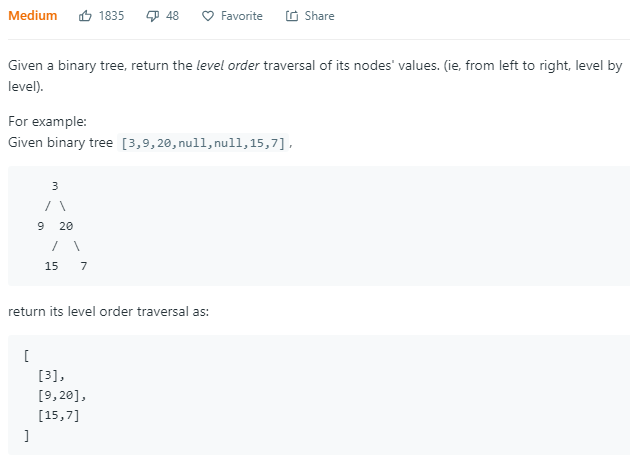
二叉树层序遍历。
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return result; } Queue<TreeNode> currentLevel = new ArrayDeque<>(); currentLevel.add(root); Queue<TreeNode> nextLevel = new ArrayDeque<>(); List<Integer> levelResult = new ArrayList<>(); while (!currentLevel.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = currentLevel.poll(); levelResult.add(node.val); if(node.left != null){ nextLevel.add(node.left); } if(node.right != null){ nextLevel.add(node.right); } if(currentLevel.isEmpty()){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(levelResult)); levelResult.clear(); currentLevel = nextLevel; nextLevel = new ArrayDeque<>(); } } return result; } }
103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
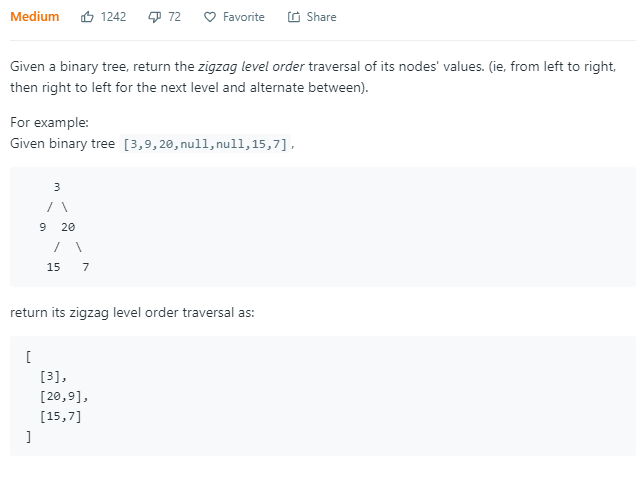
二叉树z字型遍历,花式。
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return result; } Stack<TreeNode> currentStack = new Stack<>(); Stack<TreeNode> nextStack = new Stack<>(); currentStack.push(root); List<Integer> levelResult = new ArrayList<>(); while (!currentStack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = currentStack.pop(); levelResult.add(node.val); if(result.size() % 2 == 0){ if(node.left != null){ nextStack.push(node.left); } if(node.right != null){ nextStack.push(node.right); } }else { if(node.right != null){ nextStack.push(node.right); } if(node.left != null){ nextStack.push(node.left); } } if(currentStack.isEmpty()){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(levelResult)); levelResult.clear(); currentStack = nextStack; nextStack = new Stack<>(); } } return result; } }
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal

二叉树前序遍历,也就是根->左->右。学到了俩单词,Preorder,Traversal。
最后还问你,能整成循环么?当然不能,天天加料加需求。
class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return result; } preorder(root,result); return result; } void preorder(TreeNode node,List<Integer> result){ if(node == null){ return; } result.add(node.val); preorder(node.left,result); preorder(node.right,result); } }
void preorderIteratively(TreeNode node,List<Integer> result){ Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(node); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); if (cur.right != null) { stack.push(cur.right); } if (cur.left != null) { stack.push(cur.left); } result.add(cur.val); } }
145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
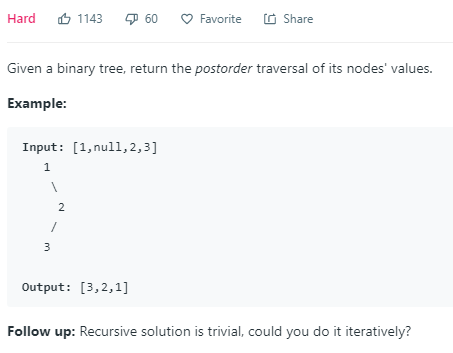
水题,白给hard。后序遍历,不过循环做还是难的。
class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null) return result; postorderIteratively(root,result); return result; } /** * post order means left->right->root * */ void postorderIteratively(TreeNode node,List<Integer> result){ Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode curr = node; while(!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null){ if(curr != null){ stack.push(curr); result.add(0, curr.val); curr = curr.right; }else{ TreeNode top = stack.pop(); curr = top.left; } } } }
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
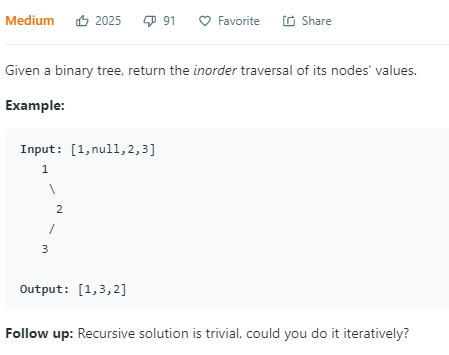
中序遍历。
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode cur = root; while(!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null){ if(cur != null){ stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; }else { TreeNode n = stack.pop(); result.add(n.val); cur = n.right; } } return result; } }
133. Clone Graph
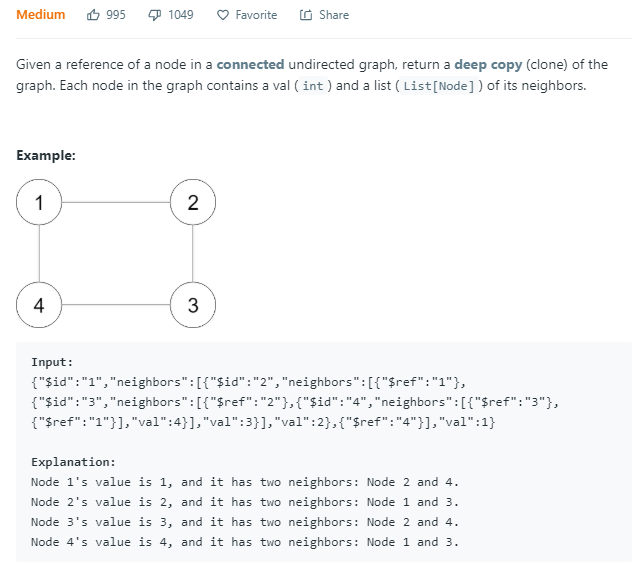
克隆一个无向图,实际上就是遍历,图的定义就是这么简洁。遍历图一定要有visitd标识。
深度优先,就是使用栈。每次将未访问的邻居节点加入stack。
广度优先,使用队列。
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() {} public Node(int _val,List<Node> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } };
class Solution { /** * 克隆一个图 */ public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { return dfs(node); } /** * 深度优先拷贝 */ Node dfs(Node node){ if(node == null){ return null; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); Set<Node> visited = new HashSet<>(); Map<Integer,Node> newGraph = new HashMap<>(); newGraph.put(node.val,cloneGraphNode(node)); visited.add(node); stack.push(node); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ Node cur = stack.pop(); Node newNode = newGraph.get(cur.val); if(newNode == null){ newNode = cloneGraphNode(cur); newGraph.put(newNode.val,newNode); } for(Node n : cur.neighbors){ if(!visited.contains(n)){ stack.push(n); visited.add(n); } Node nn = newGraph.get(n.val); if(nn == null){ nn = cloneGraphNode(n); newGraph.put(nn.val,nn); } newNode.neighbors.add(nn); } } return newGraph.get(node.val); } Node cloneGraphNode(Node n){ if(n == null){ return null; } return new Node(n.val,new ArrayList<>()); } }
class Solution { /** * 克隆一个图 */ public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { return bfs(node); } /** * 广度优先拷贝 */ Node bfs(Node node){ if(node == null){ return null; } Queue<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); Set<Node> visited = new HashSet<>(); Map<Integer,Node> newGraph = new HashMap<>(); queue.add(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ Node cur = queue.poll(); if(visited.contains(cur)) continue; Node newNode = null; if((newNode = newGraph.get(cur.val)) == null){ newGraph.put(cur.val,newNode=cloneGraphNode(cur)); } for(Node n :cur.neighbors){ Node nn = newGraph.get(n.val); if(nn == null){ newGraph.put(n.val,nn = cloneGraphNode(n)); } newNode.neighbors.add(nn); if(!visited.contains(n)){ queue.add(n); } } visited.add(cur); } return newGraph.get(node.val); } Node cloneGraphNode(Node n){ if(n == null){ return null; } return new Node(n.val,new ArrayList<>()); } }
树状数组(Binary Indexed Tree)
这是一种非常巧妙的数据结构,是为了解决前缀和n次询问的产生的。
有一个数组n,它是一个离散的列,要求他的前i项和怎么办。
第一种解法,就是for循环,从0加到i,这样的复杂度是O(n)。
第二种解法,使用一个额外的数组,去保存前n项和。这样,询问的复杂度是O(1),但是更新的复杂度是O(n)。
有一种解法,是树状数组。它的询问和更新都能到达O(logn)
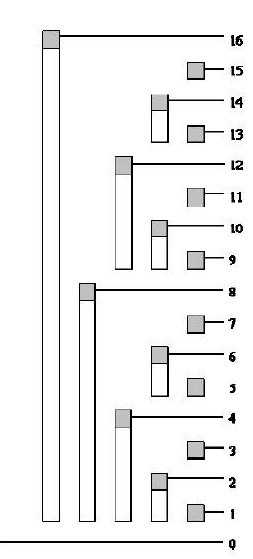
它的原理和证明,我不是很能理解,但是它这种数据结构是用来计算前n项和的n次询问的,这样的复杂度能到达O(logn),并且在支持动态更新的时候非常良好。
实现这种数据结构很简单,只需要三个方法。lowbit方法,是计算下一个值所在位置;update是更新数组,getSum 或者 平时叫的 query 是查询前n项和。
int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x); } void update(int[] array,int x,int k){ int i = x + 1; while(i<array.length){ array[i] += k; i += lowbit(i); } } int getSum(int[] array,int x){ int res = 0; int i = x + 1; while (i>0){ res += array[i]; i -= lowbit(i); } return res; }
这道题,使用前n项和去解。
public class ReversePairs { public void test(){ int[] nums1 = {1,3,2,3,1}; // 2 System.out.println(reversePairs(nums1)); int[] nums2 = {2,4,3,5,1}; // 3 System.out.println(reversePairs(nums2)); int[] nums3 = {5,4,3,2,1,2,1}; // 8 System.out.println(reversePairs(nums3)); // 0 int[] nums4 = {2147483647,2147483647,2147483647,2147483647,2147483647,2147483647}; System.out.println(reversePairs(nums4)); } /** * binary indexed tree * build a BIT count nums[i]/2 * rule : i<j ,nums[i] > 2*nums[j] */ public int reversePairs(int[] nums) { int res = 0; int n = nums.length; // for binary search long[] copy = new long[n]; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ copy[i] = nums[i]; } Arrays.sort(copy); int[] BIT = new int[n+1]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { // for current i // we count 2*nums[i]+1 for each nums[i] res += getSum(BIT,copy.length - 1) - getSum(BIT,binarySearch(copy, 2 * (long)nums[i] + 1) - 1); update(BIT,binarySearch(copy, (long)nums[i]),1); } return res; } int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x); } void update(int[] array,int x,int k){ int i = x + 1; while(i<array.length){ array[i] += k; i += lowbit(i); } } int getSum(int[] array,int x){ int res = 0; int i = x + 1; while (i>0){ res += array[i]; i -= lowbit(i); } return res; } int binarySearch(long[] sortArray,long value){ int n = sortArray.length; int l = 0; int r = n - 1; while (l + 1 < r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; if (sortArray[m] >= value) { r = m; } else { l = m; } } if (sortArray[l] >= value) { return l; } else if (sortArray[r] >= value) { return r; } else { return r + 1; } } }